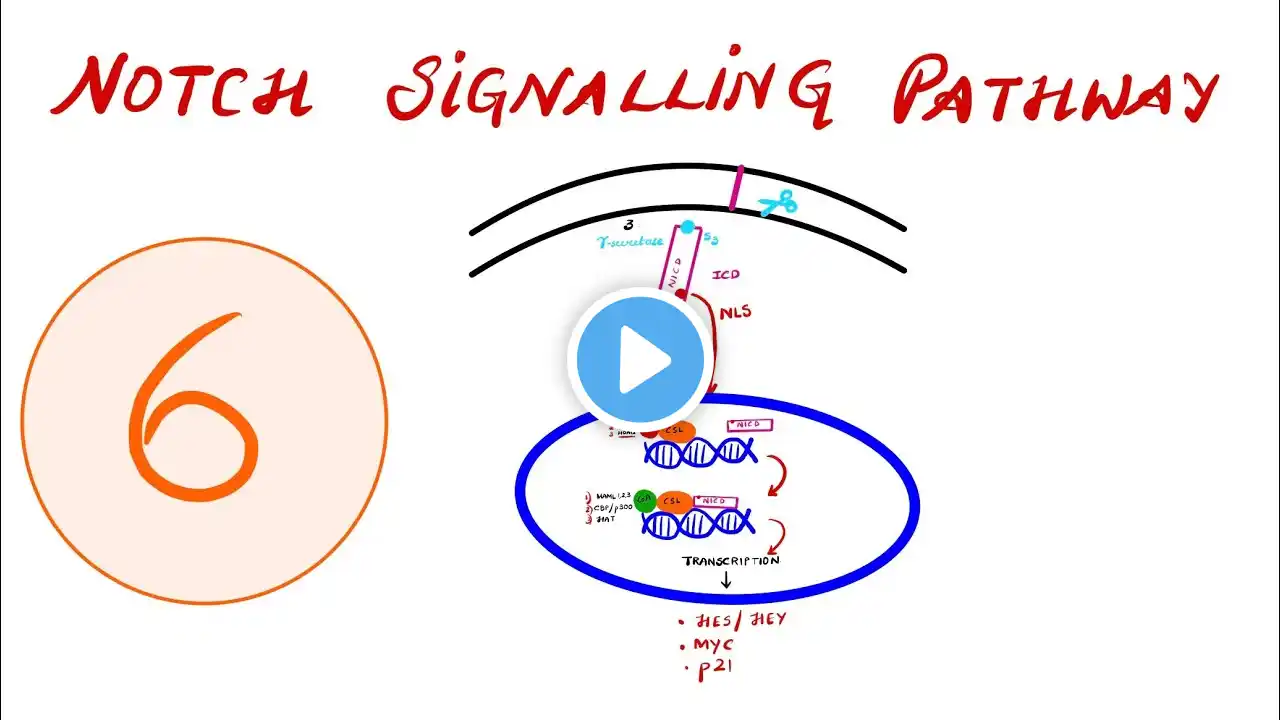
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - NOTCH Signaling Pathway
📚 Watch the Full Series: 👉 Part 1 – Introduction to Signal Transduction Pathways : • SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - INTRODUCTION 👉 Part 2 – Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs): • SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - RECEPTOR TY... 👉 Part 3 – Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (NRTKs): • SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - NON RECEPTO... 👉 Part 4a – GPCRs (G-Protein Coupled Receptors) – Introduction: • G - PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS - INTRO 👉 Part 4b – GPCR Gαs Pathway: • G - PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS - G-Alpha s... 👉 Part 4c – GPCR Gαi Pathway: • G - PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS - G-Alpha I... 👉 Part 4d – G-Alpha-Q (Gq) Pathway: • G - PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS – G-Alpha-Q ... 👉 Part 4e – G-Alpha 12/13 Pathway: • G - PROTEIN COUPLED RECEPTORS – G-Alpha- 1... 👉 Part 5 – Nuclear Hormone Receptors (NHRs): • SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - NUCLEAR HOR... 👉 Part 6 – NOTCH Signaling Pathway: You’re watching this video 🎯 👉 Part 7 – Wnt–Frizzled Signaling Pathway | Canonical Wnt / β-Catenin Pathway: • SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - Wnt–Frizzle... ⸻ Welcome to this detailed masterclass on the NOTCH Signaling Pathway — one of the most unique contact-dependent signaling systems that controls cell fate decisions, differentiation, and tissue patterning. This video explains: ✔️ How Notch is activated by Delta/Jagged ligands ✔️ Proteolytic cleavages (ADAM10 + γ-secretase) ✔️ Release of NICD ✔️ Translocation to the nucleus ✔️ Activation of Notch target genes ✔️ Built-in termination (NICD degradation) ✔️ Clinical significance: cancers, congenital defects, and therapeutic targets Perfect for MBBS, MD Pathology, Biochemistry, Oncology, NEET-SS, USMLE, and all students mastering molecular pathways. ⸻ ⏱️ TIME STAMPS 00:00 – Introduction and definition 06:04 – What makes Notch signaling unique? 08:12 – Components of Notch pathway 10:19 – Mechanism Step 1: Ligand–Notch binding • Mechanism Step 2: S2 cleavage (ADAM protease) • Mechanism Step 3: S3 cleavage by γ-secretase • NICD release and nuclear entry • CSL complex: Co-repressors → Co-activators 19:32 – Built-in termination of Notch signal (NICD degradation) 21:07 – Notch Target Genes (Hes, Hey, Myc, p21 – explained) 31:18 – Clinical significance: • T-ALL • Solid tumors and etc. ⸻ ⭐ WHAT YOU WILL LEARN • Why Notch uses juxtacrine signaling (cell-to-cell contact) • Stepwise S2 → S3 cleavage and NICD production • How NICD converts CSL from repressor → activator • Reasons behind target gene activation • How Notch controls: • Neurogenesis • Angiogenesis • Hematopoiesis • Intestinal crypt maintenance • Why excessive Notch signaling causes tumors • Why loss of Notch signaling causes congenital disorders ⸻ #NotchSignaling #SignalTransduction #MolecularPathways #PathologySeries #CellBiology #Biochemistry #DevelopmentalBiology #NEETSS #USMLE #MedicalEducation #NotchNICD #GammaSecretase #AshmitaPathSeries