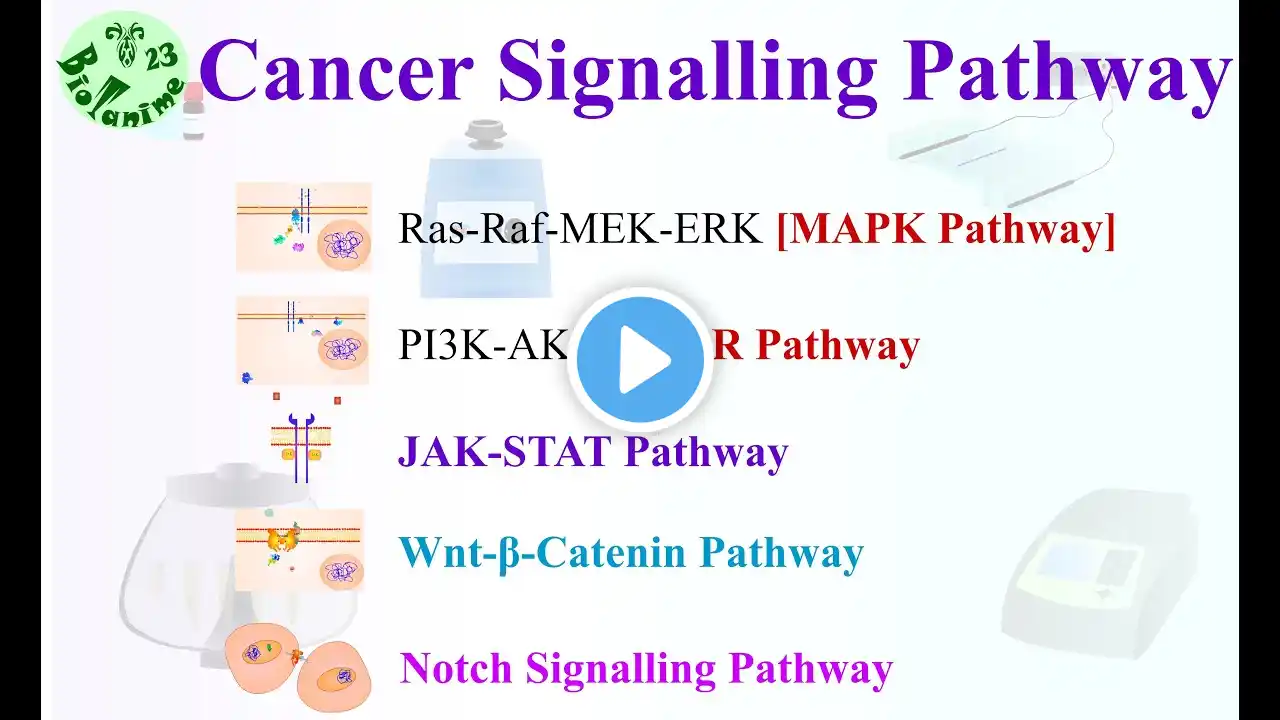
Cancer Signalling Pathway - Part 1
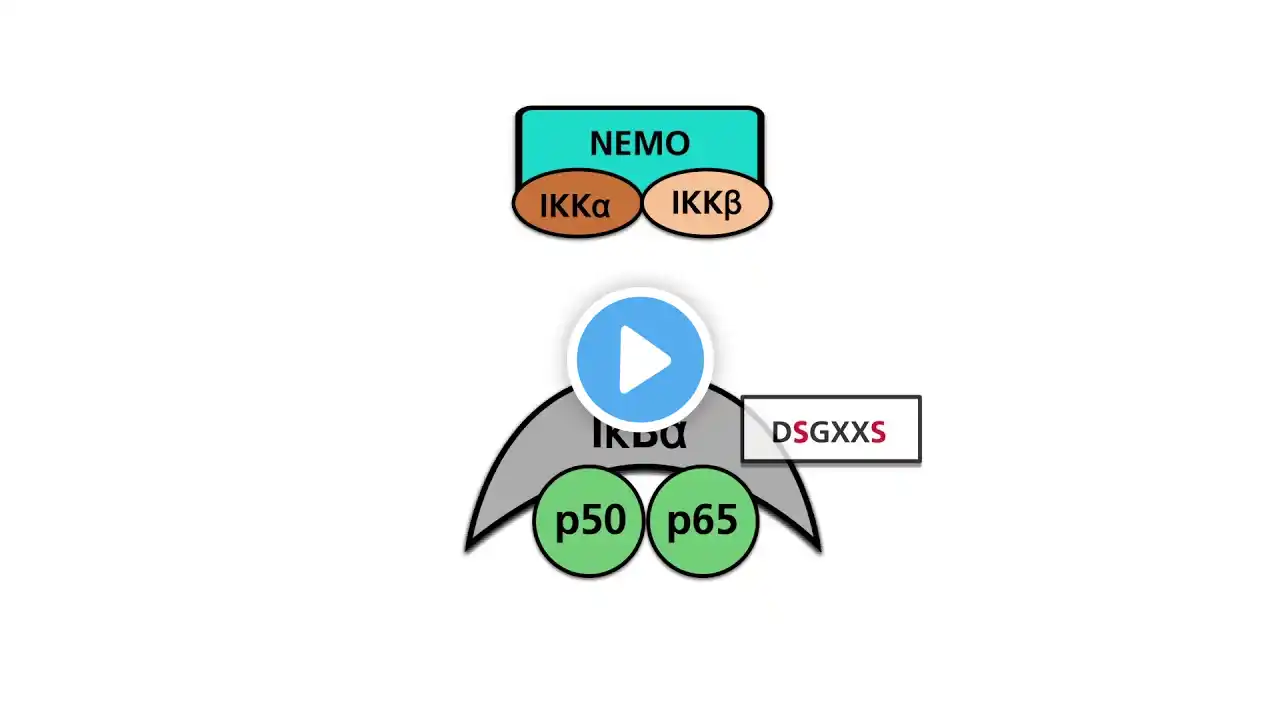
Cancer progression is driven by dysregulated cell signalling, wherein growth-promoting pathways become constitutively active even in the absence of ligands, while tumour suppressor mechanisms are disabled. This aberrant signalling confers hallmark cancer traits, including self-sufficiency in growth signals, resistance to apoptosis, and uncontrolled proliferation. Among the major oncogenic signalling cascades, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)–mediated pathways such as the Ras–Raf–MEK–ERK (MAPK) and PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathways play central roles in transmitting extracellular growth signals to the nucleus, promoting cell survival, metabolism, and proliferation. Cytokine-driven pathways, including JAK–STAT and NF-κB signalling, contribute to sustained inflammatory signalling and tumour cell survival. Developmental pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and Hedgehog, which are tightly regulated in normal tissues, become aberrantly reactivated in cancer, supporting stemness, invasion, and therapy resistance. In parallel, loss of tumour suppressor pathways, notably p53 and TGF-β–SMAD signalling, removes critical checkpoints controlling genomic integrity, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis. Additionally, dysregulation of the Hippo–YAP pathway promotes unchecked transcriptional programs driving growth and organ size control. These pathways are frequently altered across diverse malignancies, including melanoma, colorectal, breast, lung, pancreatic, and haematological cancers, and have become key targets for precision oncology. Targeted therapies such as BRAF, MEK, PI3K, mTOR, JAK, and γ-secretase inhibitors highlight the clinical relevance of understanding cancer signalling networks. Comprehensive insight into these pathways is essential for developing effective targeted and combination therapies to overcome tumour progression and therapeutic resistance. For detailed notes, please visit https://sites.google.com/view/biotani... Other related videos • Signal Transduction Pathway - Signal Transduction Pathway • DNA Damage and Repair - part 1 - DNA Damage and Repair • DNA Damage Repair Mechanism - Part 2 - DNA Damage and Repair 2