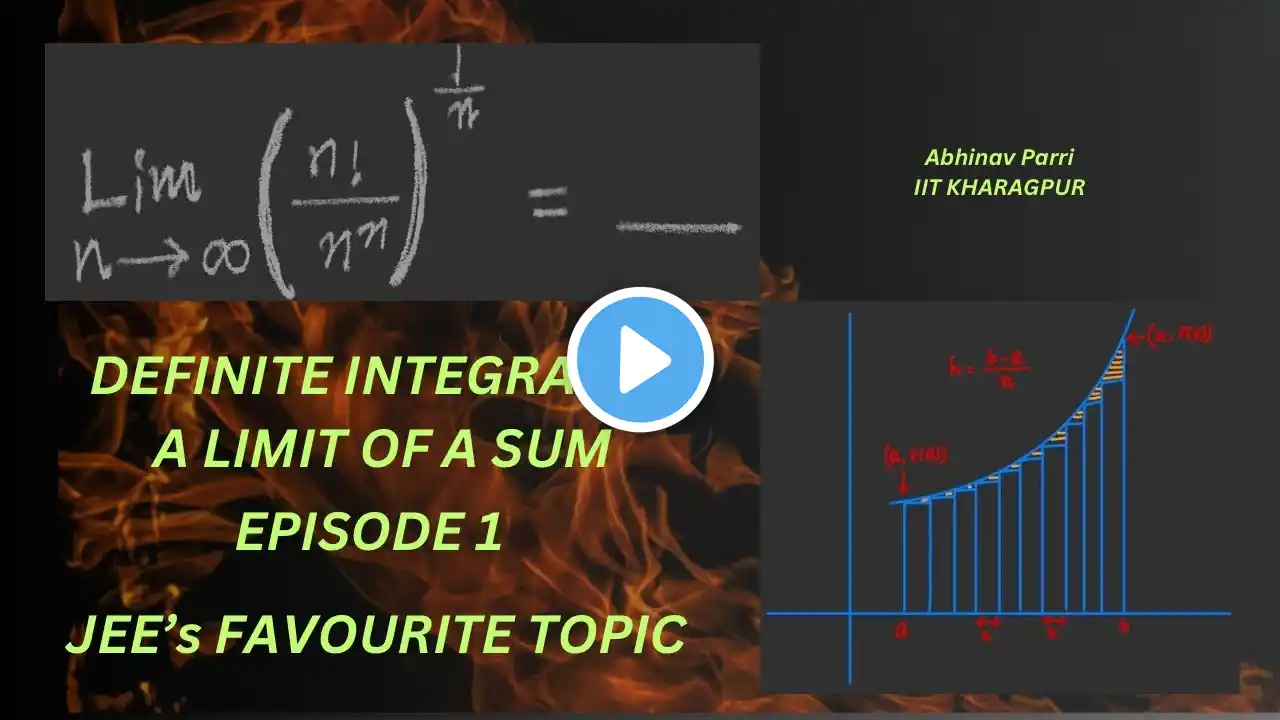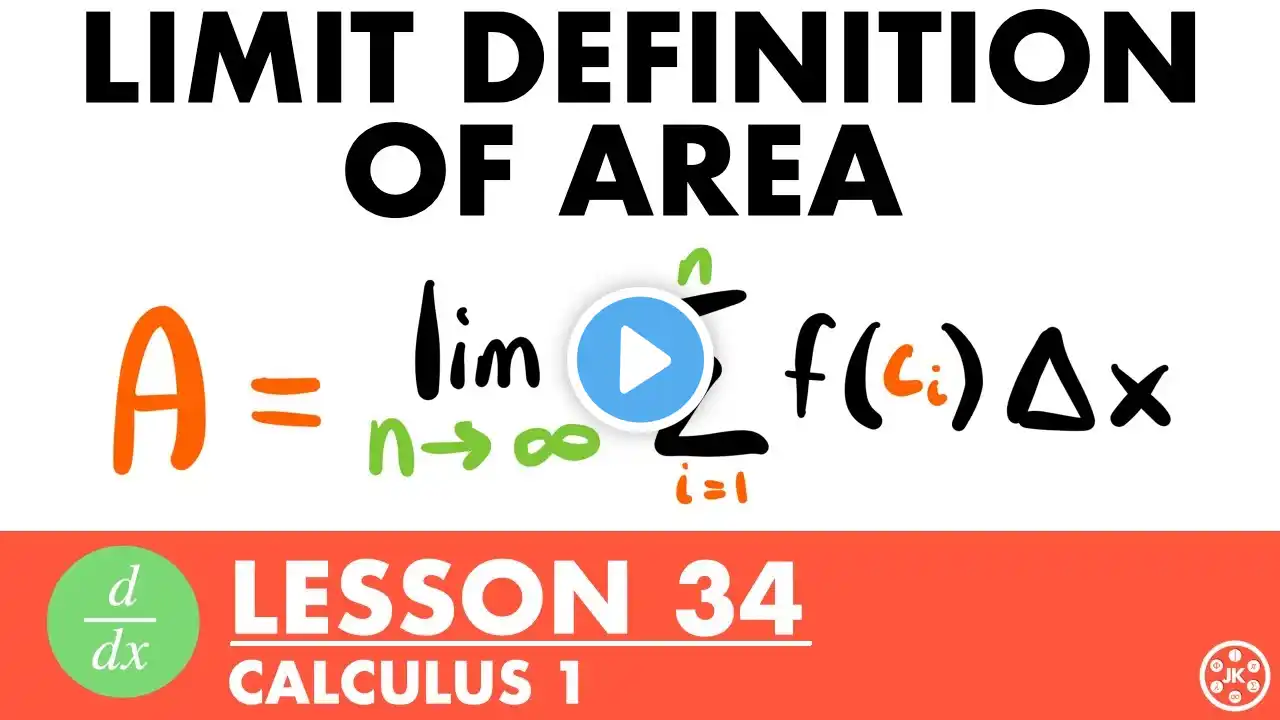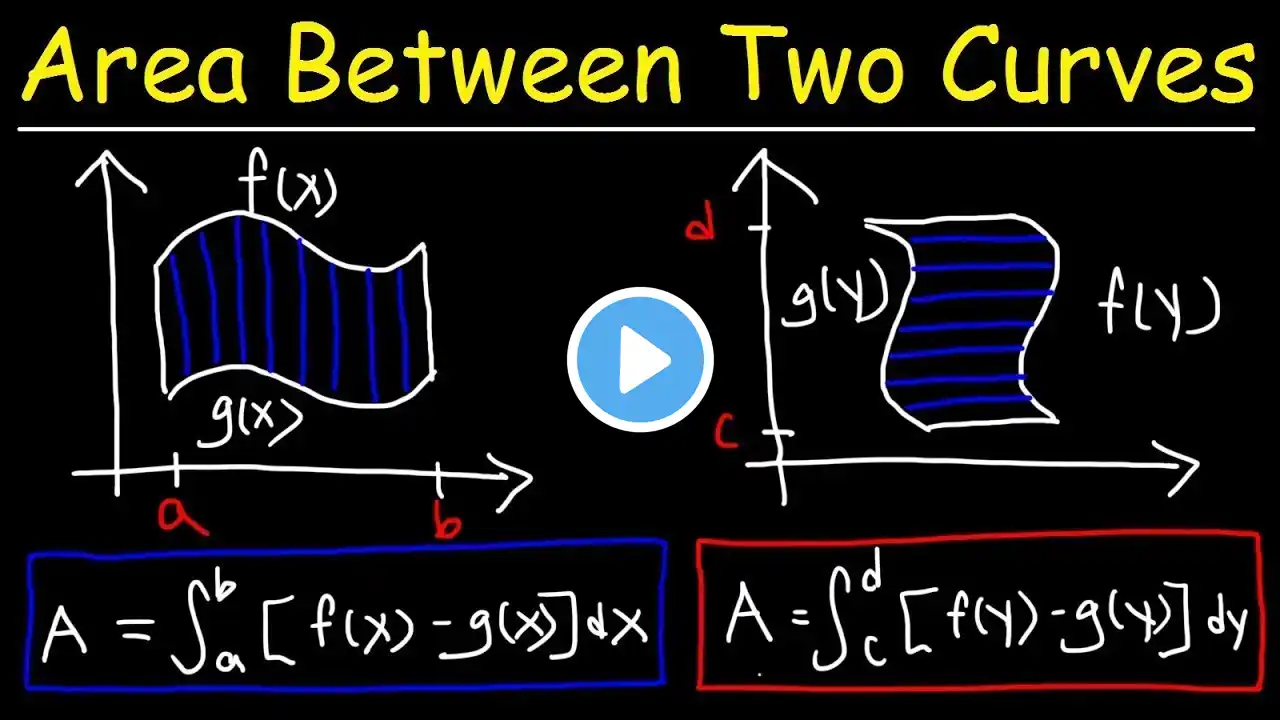
Finding Exact Area Under a Curve Using the Limit Approximation Method | Riemann Sums Explained
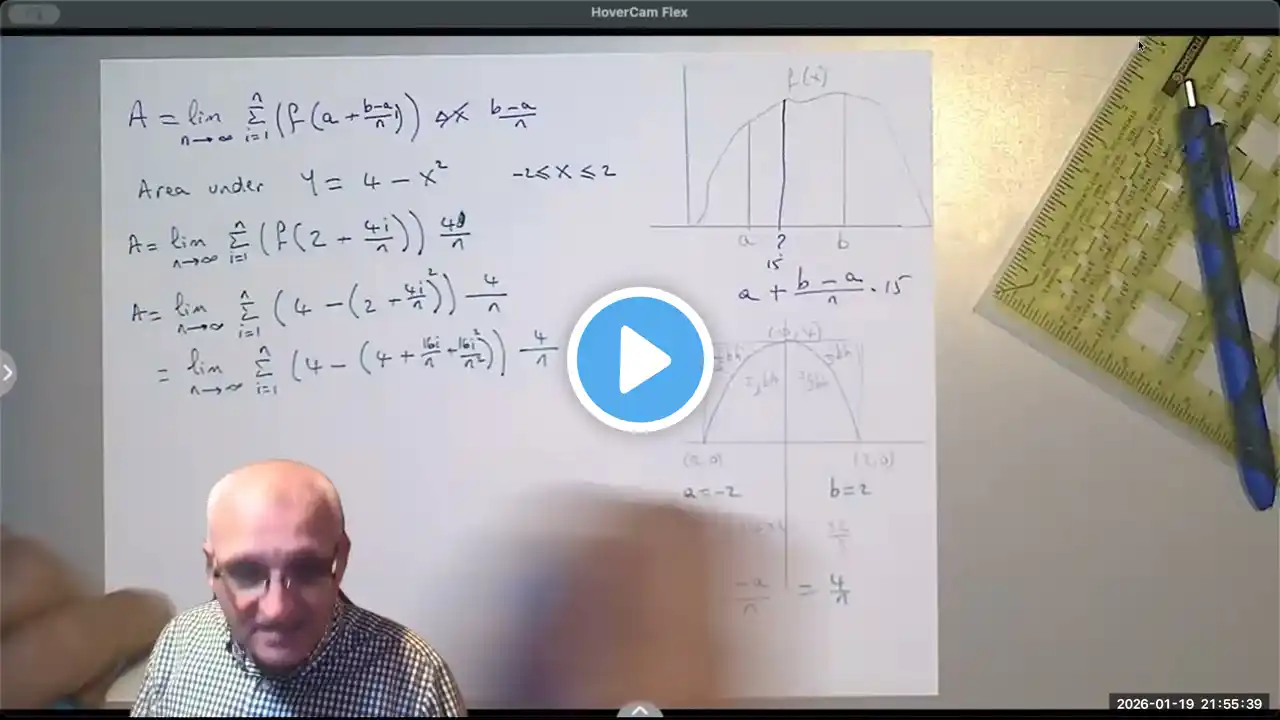
In this lecture, we explore how to find the exact area under a curve using the limit approximation method, the fundamental idea behind definite integrals. Starting from Riemann sums and common numerical approximations (left sums, right sums, trapezoidal rule, Simpson’s rule), we take the limit as the number of rectangles approaches infinity to obtain the exact value of the area. Using a detailed example with a quadratic function, we: Construct the limit definition of area Express the sum using Δx and sample points Evaluate the resulting summation formulas Take the limit as 𝑛→∞ Verify the result using definite integration This lesson bridges algebra, limits, and calculus, helping you understand why integration works—not just how to apply formulas. 📌 Topics covered: Riemann sums Limit approximation method Exact vs approximate area Definite integrals Area under a curve 💬 If you have questions or would like to see more examples, leave a comment below! #Calculus #RiemannSums #DefiniteIntegrals #AreaUnderTheCurve #LimitDefinition #Integration #MathMadeEasy #STEMEducation #APCalculus #EngineeringMath #LearnCalculus #MathTutorial