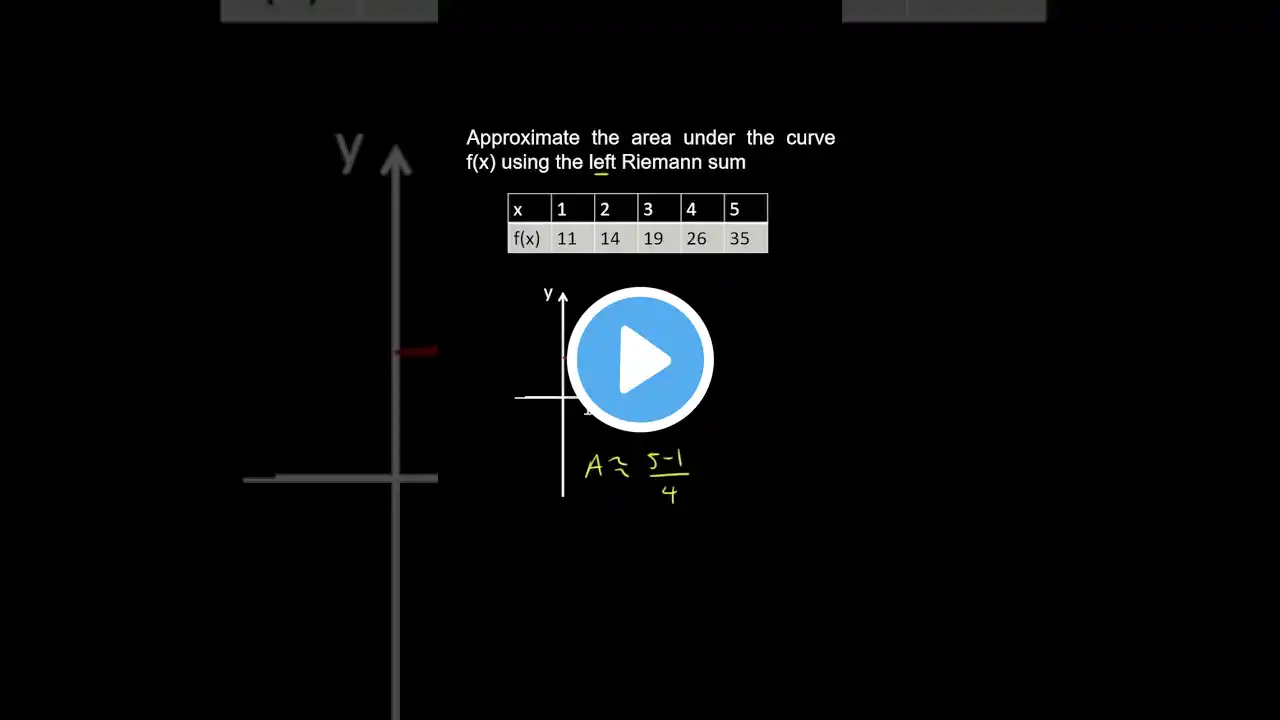
Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) Explained | Left, Right & Midpoint Riemann Sums
Learn how to estimate area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM)! In this in-depth XO Math lesson, we walk through the Left, Right, and Midpoint Riemann Sum techniques, explore when each method overestimates or underestimates, and explain how these approximations relate to exact area via limits. By the end of this video, you'll be able to: Use left, right, and midpoint rectangles to approximate area under a curve Apply RAM using formulas and graphs Calculate Riemann sums from functions, tables, or graphs Understand summation notation and delta x Determine whether an approximation is an overestimate or underestimate Connect Riemann sums to the limit definition of the definite integral Includes step-by-step examples with: Curved and linear graphs Piecewise and tabular data Conceptual animations and full calculations Real AP-style questions 📌 Perfect for Calculus 1, AP Calculus AB, or anyone learning integration techniques! 🔗 For more video lessons and additional resources, visit www.xomath.com