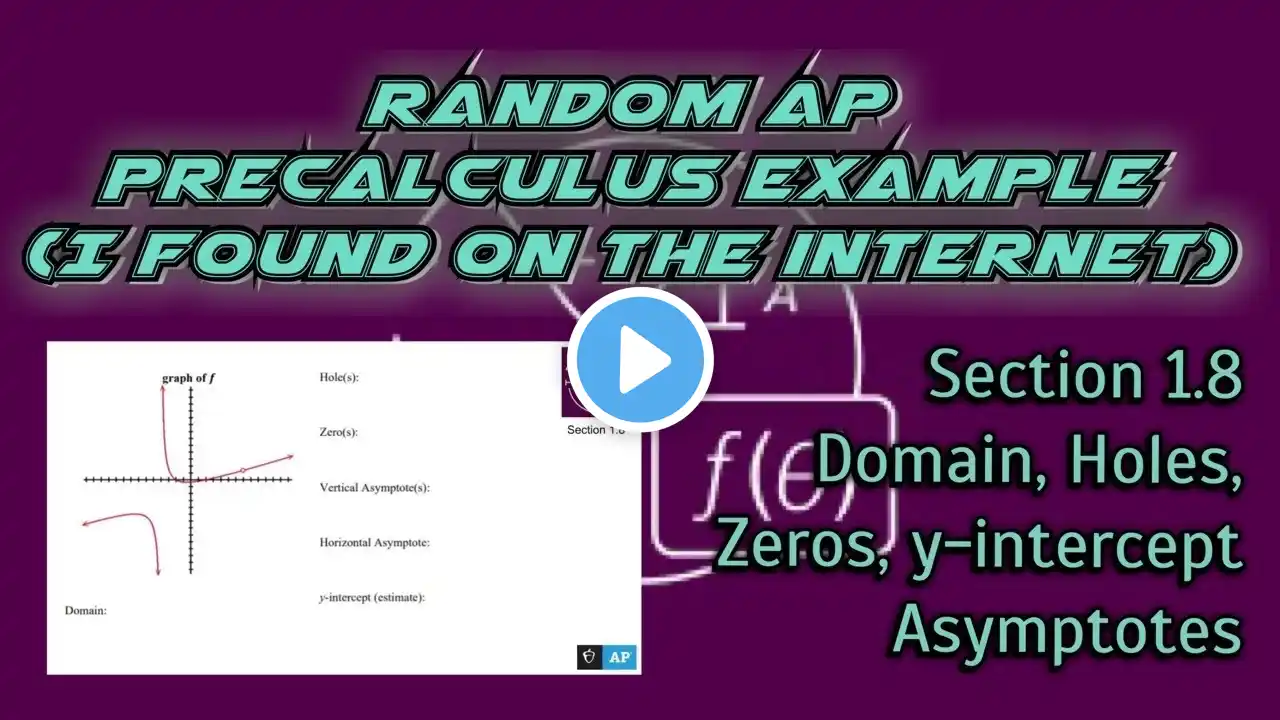
AP Precalculus Section 1.8 Example: Domain, Holes, Zeros, Asymptotes, y-intercept from a Graph
Please subscribe! / nickperich Random AP Precalculus Problems (I found on the Internet). These are not official AP Collegeboard examples, but they will definitely get the job done! Here's a brief overview of how to find various properties of a rational function in precalculus: Domain: *Domain* refers to all valid \( x \) values for the function. To find the domain of a rational function: Exclude any \( x \) values that would make the denominator zero, as division by zero is undefined. Any \( x \) that satisfies the denominator \( q(x) \neq 0 \) is within the domain. Holes: *Holes* occur when factors in the numerator and denominator cancel each other out, resulting in a removable discontinuity. To find holes: Factor both the numerator and the denominator completely. Cancel out any common factors and determine if there's a value of \( x \) that makes the function undefined and yet can be simplified. Zeros: *Zeros* or roots are values of \( x \) where the function equals zero (\( f(x) = 0 \)). To find zeros: Set the numerator equal to zero and solve for \( x \). These values of \( x \) are where the function crosses the x-axis. Asymptotes: *Asymptotes* are lines that the function approaches but never touches. Vertical Asymptotes: Occur where the denominator is zero but the numerator isn't. Set the denominator equal to zero and solve for \( x \) to find vertical asymptotes. Horizontal or Oblique Asymptotes: Compare the degrees of the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator, there's a horizontal asymptote at \( y = 0 \). If the degree of the numerator is equal to the degree of the denominator, divide the leading coefficients to find the horizontal asymptote. If the degree of the numerator is greater, there's no horizontal asymptote, but there might be an oblique (slant) asymptote. Y-intercept: *Y-intercept* is the point where the function crosses the y-axis (\( x = 0 \)). To find the y-intercept: Substitute \( x = 0 \) into the function and solve for the corresponding \( y \) value. By systematically analyzing the rational function, factoring, setting constraints for the domain, finding holes, zeros, and asymptotes, and determining the y-intercept, you can understand its behavior and graphical representation more comprehensively in precalculus. The Topics covered in AP Precalculus are... 1.1 Change in Tandem 1.2 Rates of Change 1.3 Rates of Change in Linear and Quadratic Functions 1.4 Polynomial Functions and Rates of Change 1.5 Polynomial Functions and Complex Zeros 1.6 Polynomial Functions and End Behavior 1.7 Rational Functions and End Behavior 1.8 Rational Functions and Zeros 1.9 Rational Functions and Vertical Asymptotes 1.10 Rational Functions and Holes 1.11 Equivalent Representations of Polynomial and Rational Expressions 1.12 Transformations of Functions 1.13 Function Model Selection and Assumption Articulation 1.14 Function Model Construction and Application 2.1 Change in Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 2.2 Change in Linear and Exponential Functions 2.3 Exponential Functions 2.4 Exponential Function Manipulation 2.5 Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling 2.6 Competing Function Model Validation 2.7 Composition of Functions 2.8 Inverse Functions 2.9 Logarithmic Expressions 2.10 Inverses of Exponential Functions 2.11 Logarithmic Functions 2.12 Logarithmic Function Manipulation 2.13 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 2.14 Logarithmic Function Context and Data Modeling 2.15 Semi-log Plots 3.1 Periodic Phenomena 3.2 Sine, Cosine, and Tangent 3.3 Sine and Cosine Function Values 3.4 Sine and Cosine Function Graphs 3.5 Sinusoidal Functions 3.6 Sinusoidal Function Transformations 3.7 Sinusoidal Function Context and Data Modeling 3.8 The Tangent Function 3.9 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 3.10 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities 3.11 The Secant, Cosecant, and Cotangent Functions 3.12 Equivalent Representations of Trigonometric Functions 3.13 Trigonometry and Polar Coordinates 3.14 Polar Function Graphs 3.15 Rates of Change in Polar Functions I have many informative videos for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Algebra 2, Geometry, Pre-Calculus, and Calculus. Please check it out: / nickperich Nick Perich Norristown Area High School Norristown Area School District Norristown, Pa #APPrecalculus #PreCalcProblems #MathMinds #AdvancedPreCalc #TrigTales #PrecalcPuzzles #FunctionFiesta #GraphGoals #CalcReady #PreCalcLife #AlgebraicAdventures #DerivativeDreams #IntegrationInsights #MathematicsMagic #PreCalcReview #PrecalcConcepts #LogarithmLove #TrigonometryTips #MathMastermind #APCalcPrep #Mathematics #MathMinds #Math #Maths #math #shorts #funny #help #onlineclasses #onlinelearning #online #study


