AVN Of The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
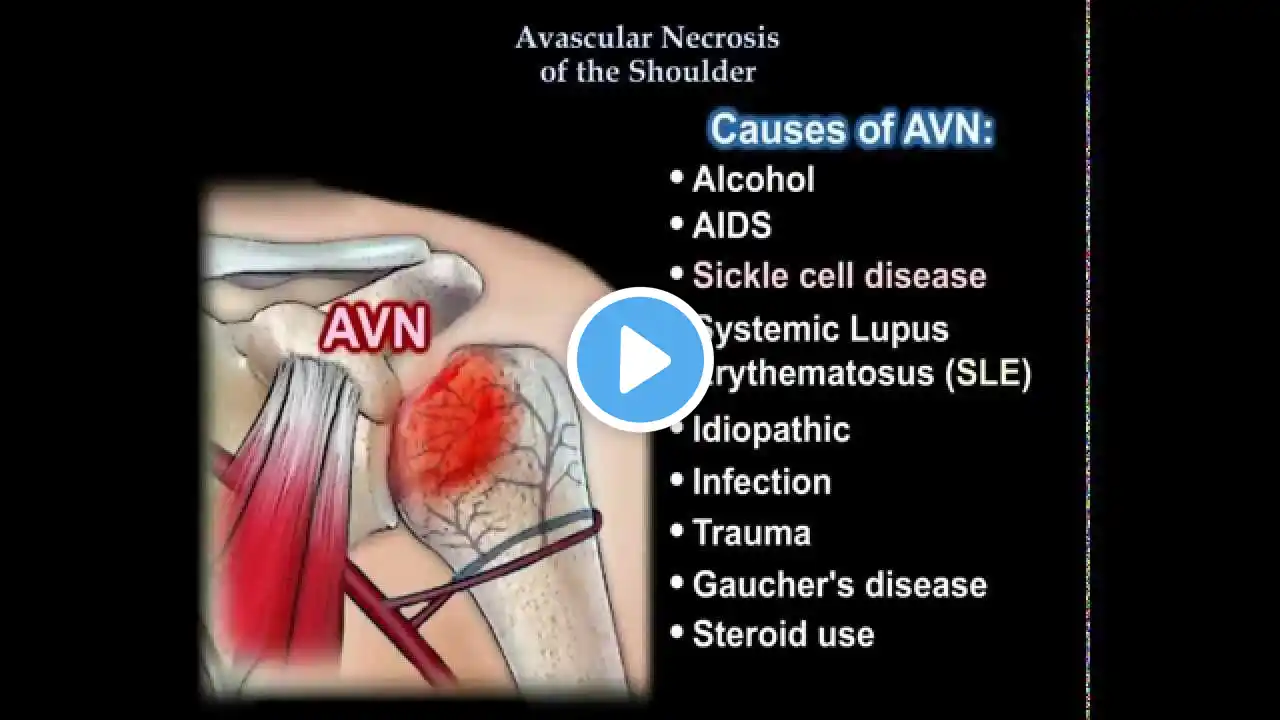
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes avascular necrosis of the shoulder and proximal humerus. Avascular necrosis is the death of a segment of bone. AVN may affect the proximal humerus due to interruption of the blood supply. The ascending branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery runs in the lateral bicipital groove and then becomes the arcuate artery. The other artery that is important to the blood supply is the posterior humeral circumflex artery. Causes of AVN: •Alcohol •AIDS •Sickle cell disease •Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) •Idiopathic •Infection •Trauma •Gaucher’s disease •Steroid use: incidence of AVN is between 5-25% after systemic steroid use. Steroids increase serum lipids in the blood. It may precipitate fat embolism into the humeral head blood vessels. Post trauma: Anterior or posterior dislocation of the humeral head is not associated with AVN. The incidence of AVN: •100% four part fracture dislocation. •50% displaced four part fracture. •15% three part fracture. •10% valgus impact fracture. Classification of proximal humeral AVN •Stage I:normal X-ray •Stage II: sclerosis •Stage III: crescent sign •Stage IV: flattening and collapse •Stage V: degenerative arthritis. Progressive collapse of the humeral head occurs due to bone death, resorption, remodeling, microfractures and final collapse with joint changes and arthritis. Symptoms: •Shoulder pain •Weakness •Crepitus •Decreased range of motion Symptoms are gradual and insidious with delay in the diagnosis and treatment. The patient usually has a history of risk factors. x-rays: shown best in neutral rotation AP view. AVN located on the superior middle part of the humeral head just deep to the articular cartilage. Crescent sign =collapse. MRI is the best study. Patient with AVN of the humerus should have a hip radiograph. If X-ray is negative and the patient has hip pain, obtain an MRI of the hip. It is recommended that a patient with osteonecrosis at the site of the shoulder should undergo an MRI of the hip to rule out asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the hip. You may also need to do an X-ray of the knee. AVN may involve three or more anatomic sites (multifocal osteonecrosis). Treatment •Physical therapy •NSAIDS •Core decompression for stage I & stage II •Resurfacing for stage III •Hemiarthroplasty for stage III & stage IV •Total shoulder surgery for stage V: advanced disease, the results of the total shoulder are inferior to a patient with osteoarthritis. Become a friend on facebook: / drebraheim Follow me on twitter: https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund: https://www.utfoundation.org/foundati... Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library. Song Title: Every Step