1-Way vs 2-Way Slab Reinforcement Explained | Real Site RCC Detailing | Buildiyo
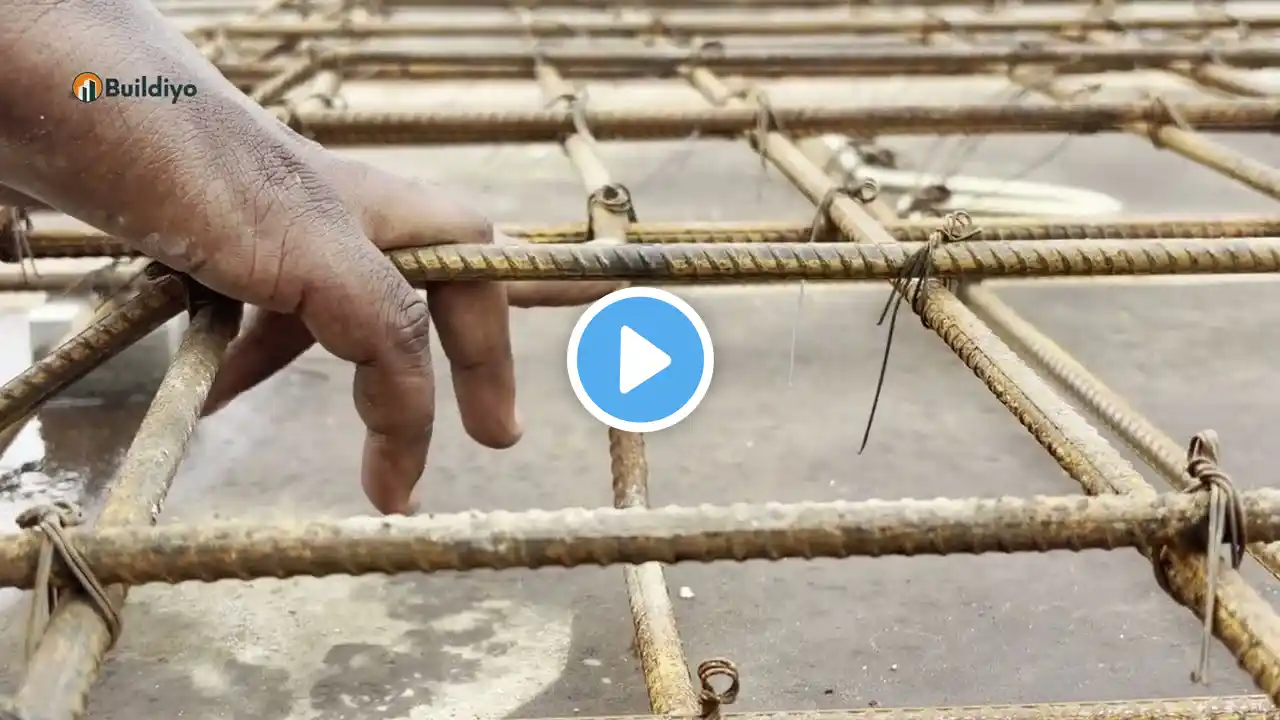
In this comprehensive video, we cover the complete explanation of 1-way and 2-way slab reinforcement, including practical on-site demonstration at a Buildiyo project. Civil engineers, students, and construction enthusiasts will gain an in-depth understanding of how slabs are designed, reinforced, and executed to ensure structural strength, durability, and safety. We show the full detailing process — from formwork setup, bar placement, and lap lengths to beam-slab junction reinforcement and quality checks, all following IS code standards. Whether you’re designing small residential projects or large commercial structures, understanding the differences between 1-way and 2-way slabs is crucial for efficient load distribution and structural integrity. ⸻ 🧱 What You’ll Learn in This Video: 1️⃣ 1-Way Slab • Load Transfer: Predominantly in one direction, supported by two parallel beams. • Reinforcement: Main bars placed along the span; distribution bars perpendicular for stability. • Typical Usage: Rectangular panels where the longer side is at least twice the shorter side. • On-Site Considerations: • Proper spacing of main bars and distribution bars. • Adequate cover and lap length as per IS 456:2000. • Beam-slab junction reinforcement to prevent shear failure. • Advantages: Simple design, cost-effective, easier supervision. • Limitations: Not suitable for nearly square panels or heavy loads in both directions. 2️⃣ 2-Way Slab • Load Transfer: Distributed in both directions; spans supported on four sides by beams. • Reinforcement: Main and distribution bars placed along both axes. • Typical Usage: Square or near-square panels, medium to large spans. • On-Site Considerations: • Accurate bar placement is critical to avoid deflection and cracking. • Proper anchorage at supports, especially corners and column junctions. • Stirrups and shear reinforcement at critical zones if required. • Advantages: • Stronger structural performance with reduced bending and deflection. • Suitable for heavy live and dead loads. • Provides uniform load transfer across spans. • Limitations: Complex detailing, requires precise supervision, difficult to modify after concreting. Both Slabs: • Follow IS 456:2000 and other relevant codes for spacing, cover, and lap length. • Proper beam-slab junction reinforcement is essential for shear resistance. • Use of cover blocks, proper alignment, and secure tying ensures durability and quality. ⸻ 💡 Why Understanding Slabs Matters: Choosing the right slab type and executing it correctly ensures structural integrity, longevity, and safety. At Buildiyo, every slab is designed with precision and executed with on-site best practices, giving clients confidence in their construction projects. ⸻ 📍 Project Location: Buildiyo Site – Chennai, Tamil Nadu 🌐 Website: www.buildiyo.com 📞 Contact: +91 70921 66177