Central Dogma of Molecular Biology x Radiohead
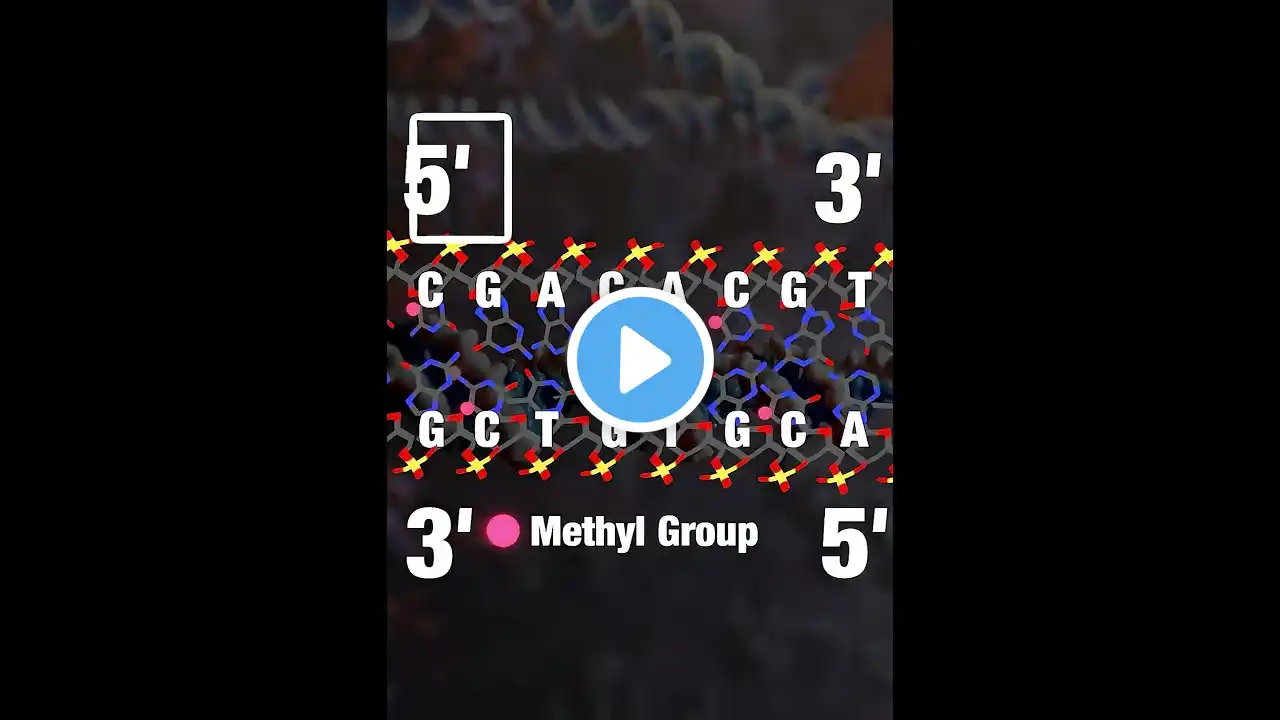
life. central dogma and beyond (epigenetics, CRISPR tools, RNA interference). source footage: NanoRooms Life uses entropy to crack impossible odds. Here’s how. | EoB Ch 2, NanoRooms This physics rule built biology’s language. Here’s how. | EoB Ch1, Ribosome Studio ATP-synthase the tiny power plant in cells, Ribosome Studio Epigenetics in Action: How UHRF1 and DNMT1 Maintain DNA Methylation, McGovern Institute SHERLOCK: A CRISPR Tool to Detect Disease, Katharina Petsche Gene Silencing by Micro RNA - Studio Katharina Petsche. review by Ille AM, Lamont H, Mathews MB. The Central Dogma revisited: Insights from protein synthesis, CRISPR, and beyond. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Sep;13(5):e1718. "The Sequence Hypothesis defines biological information transfer as the residue-by-residue transfer of sequence information between nucleic acids and to proteins. This is commonly summarized as DNA ➔ RNA ➔ protein and is colloquially referred to as the Central Dogma. More specifically, however, the Central Dogma expounded by Crick included a critical restriction, stipulating that “once sequential information has passed into protein it cannot get out again.” Under this definition, the Central Dogma has stood the test of time despite challenges. In principle, a violation of the Central Dogma could transpire through synthetic biology or by natural occurrence. To address these possibilities, we draw insights from existing modes of information transfer in protein synthesis and from synthetic Clustered Regularly-Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) gene-editing. We introduce a three-part evaluation scheme, which we apply to the CRISPR/Cas9 system and the more recent CRISPR prime editing system. Potential mechanisms by which engineered sequence editing systems might violate the Central Dogma are considered." #molecularbiology #dna #rna #protein #apbio