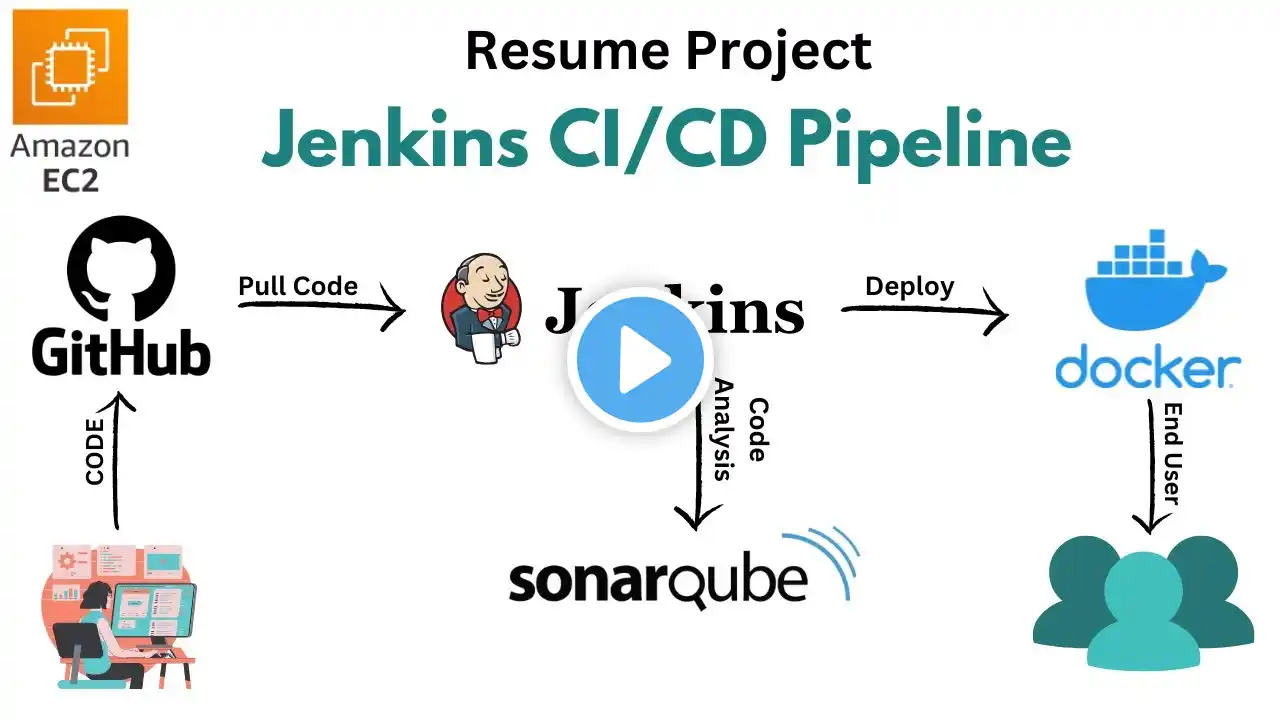
Spring Boot CI/CD to AWS EC2 using Docker & GitHub Actions (Complete Guide)
In today’s video, we are going to see complete CI/CD automation for a Spring Boot application using GitHub Actions, Docker Hub, and AWS EC2. In our last two classes, we deployed Spring Boot manually and also using Docker. Those needed multiple manual steps. But with CI/CD, once you commit code to GitHub, your application will be automatically built, dockerized, pushed to Docker Hub, and deployed to EC2 — without any manual action. I have uploaded all commands used in this video in a text file in the description. This is a slow and detailed video so even beginners can easily understand. Please comment your doubts, I will respond. 🚀 Steps Covered in This Video Step 1: Create Spring Boot Application Create your Spring Boot REST API Add Dockerfile (to convert JAR → Docker Image) Create CI/CD file: .github/workflows/deploy.yml The Dockerfile and deploy.yml are included in the description. What deploy.yml automates: Build Docker image Push to Docker Hub SSH to EC2 Pull Docker image Run application inside EC2 Step 2: Push Project to GitHub Use these commands inside your project folder: echo "# AwsEc2DockerCICDDemoRepo" )) README.md git init git add . git commit -m "first commit" git branch -M main git remote add origin https://github.com/prabhakaranskg-bot... git push -u origin main Provide GitHub username + Personal Access Token. Step 3: Add Secrets in GitHub Go to GitHub → Settings → Environments → Dev → Secrets Add these: Secret Name Value DOCKER_USERNAME your Docker Hub username DOCKER_PASSWORD your Docker Hub password/token EC2_HOST EC2 Public IP EC2_SSH_KEY contents of your .pem file Docker Hub registration: https://hub.docker.com/ Step 4: Create AWS EC2 Instance OS: Ubuntu Instance: t3.micro Create Key Pair (download .pem file) Security Groups: SSH → port 22 HTTP → port 80 Custom TCP → 8080 or 8081 (your app port) Launch instance and note public IP (Example: 18.61.173.206) Step 5: Connect to EC2 & Install Docker Fix .pem permissions (Windows PowerShell): icacls "D:\Youtube\AWS\springboot-ec2-cicd-demo.pem" /reset icacls "D:\Youtube\AWS\springboot-ec2-cicd-demo.pem" /inheritance:r icacls "D:\Youtube\AWS\springboot-ec2-cicd-demo.pem" /grant:r "$($env:USERNAME):R" icacls "D:\Youtube\AWS\springboot-ec2-cicd-demo.pem" /remove "Authenticated Users" "Users" "Administrators" "SYSTEM" Connect: ssh -i "springboot-ec2-cicd-demo.pem" ubuntu@EC2-PUBLICIP Install Docker: sudo apt update sudo apt install docker.io -y sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker sudo usermod -aG docker ubuntu exit Reconnect. Step 6: Create deploy folder & deploy.sh mkdir -p ~/deploy cd ~/deploy nano deploy.sh OR vi ~/deploy/deploy.sh ESC+:WQ --TO SAVE Paste this: #!/bin/bash docker stop springboot-webapp || true docker rm springboot-webapp || true docker pull prabhakaranskg/springboot-ec2-cicd-demo:latest docker run -d -p 8081:8080 --name springboot-webapp prabhakaranskg/springboot-ec2-cicd-demo:latest Save and give permission: chmod +x deploy.sh Step 7: CI/CD Trigger Now commit anything to GitHub: git commit -am "test deployment" git push Go to: GitHub → Actions → build-deploy You will see: ✔ Build Docker image ✔ Push to Docker Hub ✔ SSH to EC2 ✔ Run deploy.sh ✔ Update container Step 8: Test in Postman If app runs on 8081: http://EC2-IP:8081/hello If security group allowed only 8080 earlier, update it to 8081. Example Output: Spring Boot Application Deployed in EC2 Successfully Using CI/CD Second commit will again trigger CI/CD automatically. 🎉 YOU HAVE COMPLETED FULL CI/CD AUTOMATION! GitHub → Auto Build Docker Hub → Auto Push EC2 → Auto Deploy 0 manual steps after setup Perfect for real-time DevOps and production workflows. ❤️ Thank You This is a long but very clear tutorial so everyone can practice. Please Like, Comment your doubts & Subscribe for more hands-on DevOps videos.