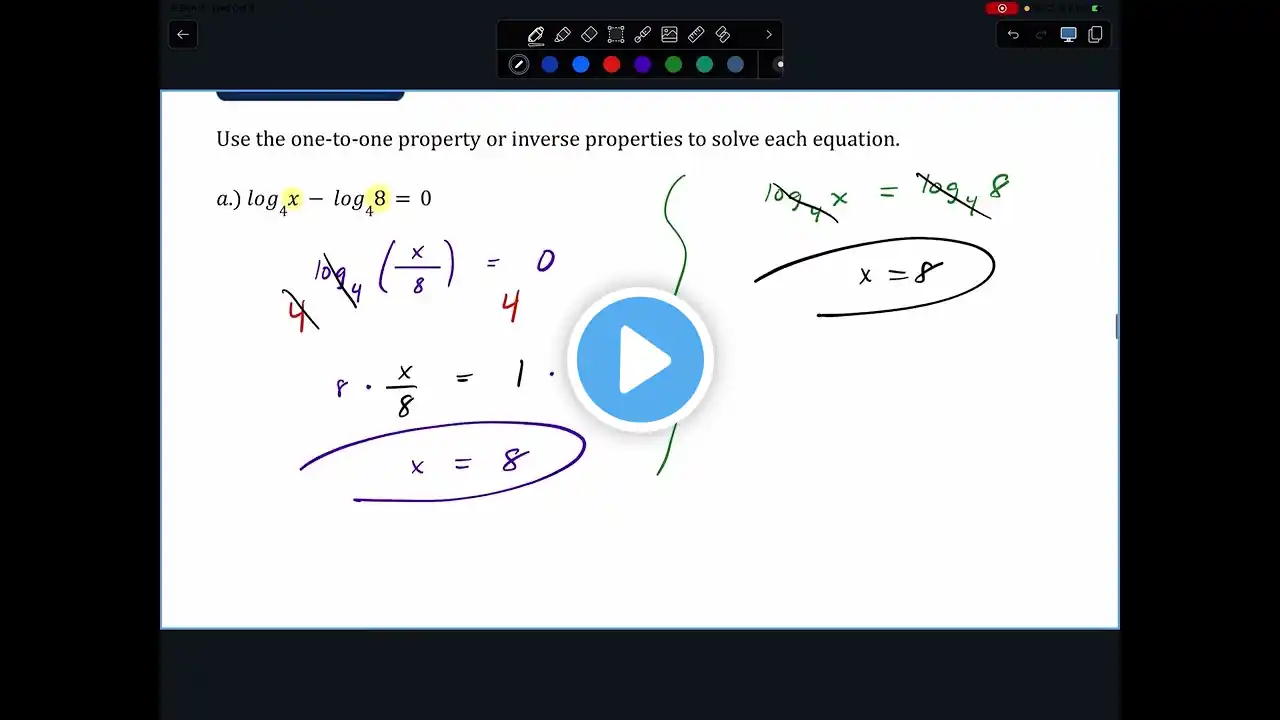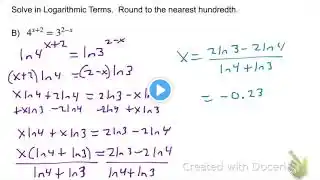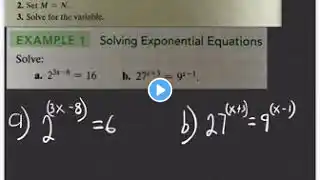
PreCalc 1 (3.4) Exponential & Logarithmic Equations Part A
Exponential functions are the first focus, with the goal of learning how to solve equations for these functions, and then moving on to logarithmic equations 00:29. There are two methods for solving exponential equations, with the first method involving setting the exponents equal to each other if the bases are the same 01:42. The second method involves using the power rule and taking the natural log of both sides of the equation to solve for the variable, as seen in the example of solving for x in the equation 4 to the power of x equals 15 08:35. The inverse operations of ln and e have a cancellation effect, and ln of e is equal to 1 17:07. To solve for x in the equation 0.6x = ln of 6, divide both sides by 0.6 to isolate x 17:50. When solving exponential equations, it's essential to avoid rounding answers and instead keep them exact to maintain mathematical accuracy 18:08. To solve for x in the equation 5^x - 2 = 4^(2x + 3), take the natural logarithm of both sides and apply the power rule to simplify 19:00. After applying the power rule and distributing, the equation can be rearranged to isolate x by factoring out x and dividing both sides by the resulting coefficient 23:05.