Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens? (a) Water (b) Glass (c) Plastic
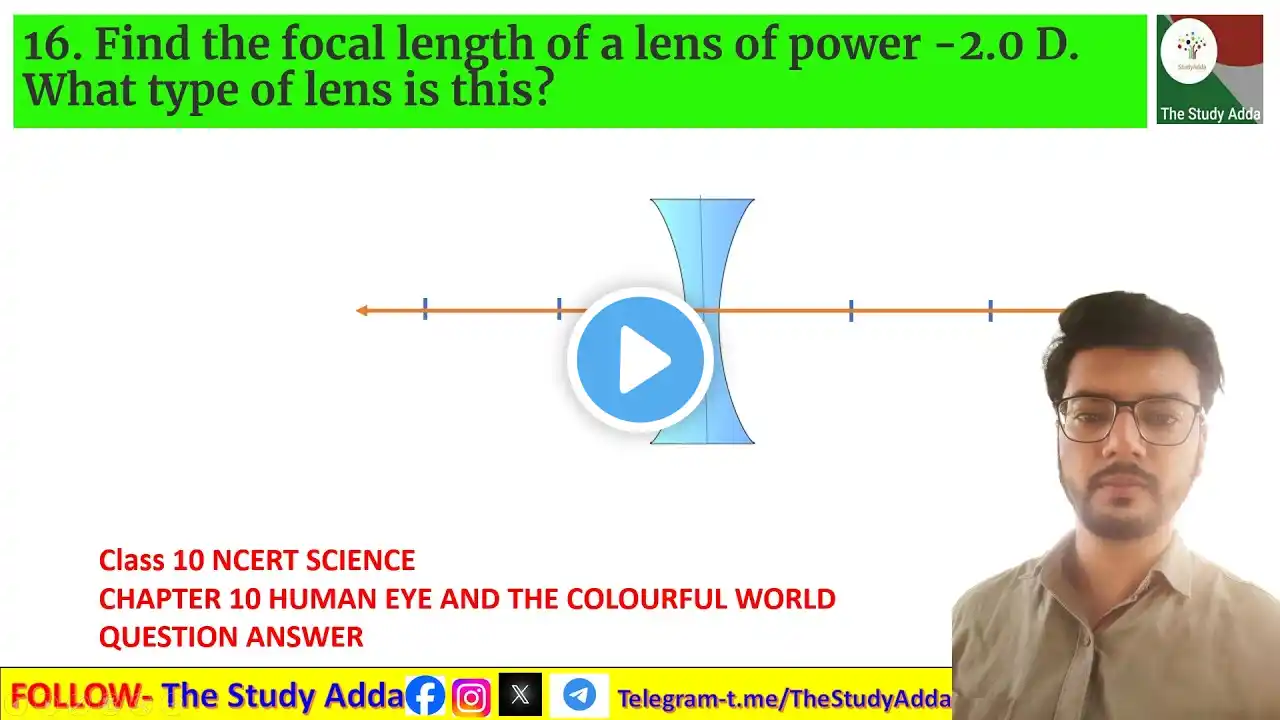
1. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens? (a) Water (b) Glass (c) Plastic (d) Clay 1. निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा पदार्थ लेंस बनाने के लिए उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता है? (a) पानी (b) कांच (c) प्लास्टिक (d) मिट्टी 1. nimnalikhit mein se kaun-sa padaarth lens banaane ke lie upayog nahin kiya ja sakata hai? (a) paanee (b) kaanch (ch) plaastik (d) mittee You can contact with us - www.facebook.com/thestudyadda www.instagram.com/thestudy01 Telegram- https://t.me/TheStudyAdda Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction EXPLANATION OF NCERT EXERCISE QUESTIONS PLAYLIST Chapterwise solution - • Video PLAYLIST of question answer - • Video In this session we will be starting with the chapter "metals and non metals?". We will cover the In-between Question/Answers and exercise questions. ✔️ Class: 10th ✔️ Subject: Chemistry ✔️ Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction CLASS 10th NCERT CHAPTER & EXERCISE QUESTION & ANSWER अध्याय 10 प्रकाश परावर्तन और अपवर्तन 10वीं एनसीईआरटी अध्याय और अभ्यास प्रश्न और उत्तर, एनसीईआरटी अभ्यास प्रश्नों की व्याख्या एनसीईआरटी अध्याय और अभ्यास प्रश्न और उत्तर कक्षा 10वीं एनसीईआरटी विज्ञान adhyaay 10 prakaash paraavartan aur apavartan kaksha 10veen enaseeeeaaratee adhyaay aur abhyaas prashn aur uttar, enaseeeeaaratee abhyaas prashnon kee vyaakhya enaseeeeaaratee adhyaay aur abhyaas prashn aur uttar kaksha 10veen enaseeeeaaratee vigyaan Disclaimer: "This video is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to infringe on any copyrights. If you believe that this video has used any copyrighted material in a way that constitutes copyright infringement, please contact us at cand we will take appropriate action." 1. Define the principal focus of a concave mirror. 2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length? 3. Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object. 4. Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles? 1. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm. 2. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located? 1. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why? 2. Light enters from air to glass, having a refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1. 3. Find out, from the table, the medium having the highest optical density. Also, find the medium with the lowest optical density. 4. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given in the table. Material medium Refractive index Material medium Refractive index Air 1.0003 Canada Balsam 1.53 Ice 1.31 – – Water 1.33 Rock salt 1.54 Alcohol 1.36 – – Kerosene 1.44 Carbon disulphide 1.63 Fused quartz 1.46 Dense flint glass 1.65 Turpentine oil 1.47 Ruby 1.71 Benzene 1.50 Sapphire 1.77 Crown glass 1.52 Diamond 2.42 5. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement? 1. Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens. 2. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens. 3. Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m. 1. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens? (a) Water (b) Glass (c) Plastic (d) Clay 2. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object? (a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature (b) At the centre of curvature (c) Beyond the centre of curvature (d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus. 3. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object? (a) At the principal focus of the lens (b) At twice the focal length (c) At infinity (d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus. 4. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be (a) both concave (b) both convex (c) the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex (d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave