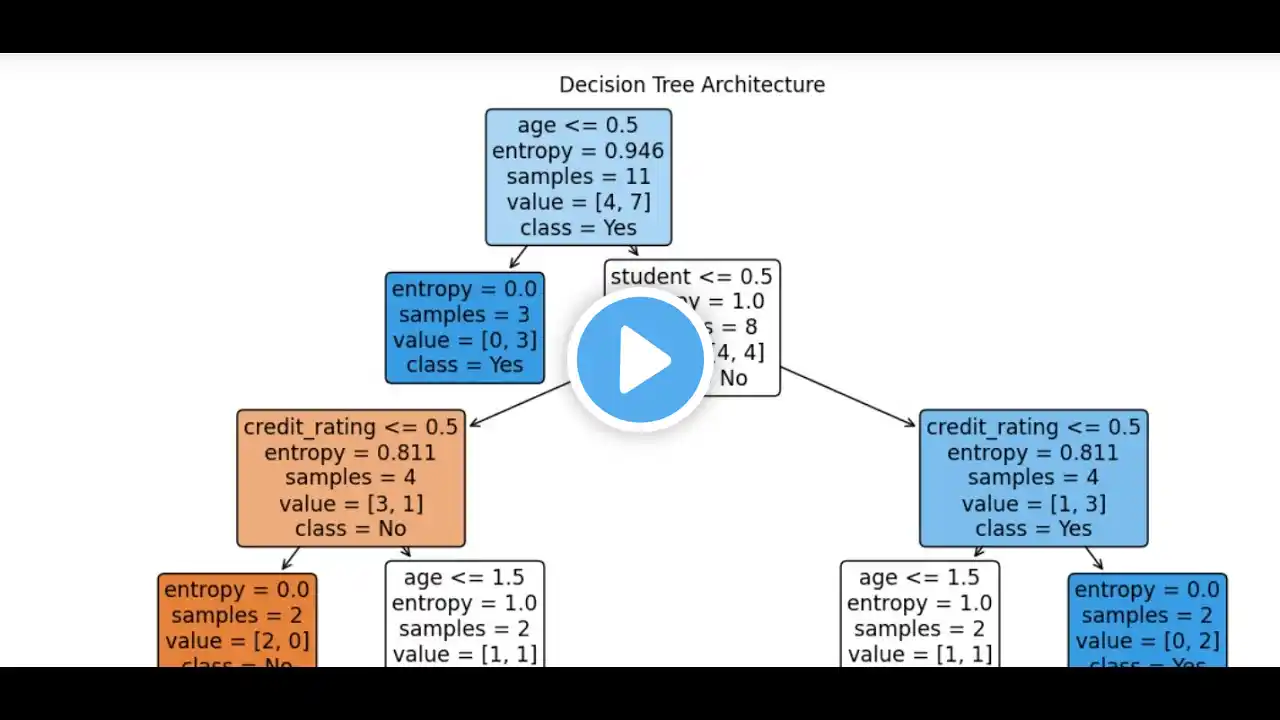
Introduction to Decision Tree | Implementing Decision Tree from Scratch using entropy
#decisiontree #ml #CART algorithm #entropy #informationgain A Decision Tree is a popular machine-learning tool for predicting outcomes (classification) or values (regression). It works by breaking down data into smaller groups based on specific characteristics. Key Parts: 1. Root Node: The starting point, representing the entire dataset. 2. Internal Nodes: Where the data is split based on a specific condition (e.g., "Is age over 30?"). 3. Leaf Nodes: The final points, show the predicted outcome or value. How it Works: 1. Splitting: The algorithm chooses the best characteristic and value to split the data. 2. Recursive Splitting: This process is repeated, dividing the data into smaller groups until a stopping point is reached. 3. Prediction: For classification: Follow the decisions from the root to a leaf node to classify a new instance. For regression: The predicted value is the average of the target variable in the leaf node.