Allocate Memory Dynamically for Large Text Files in C
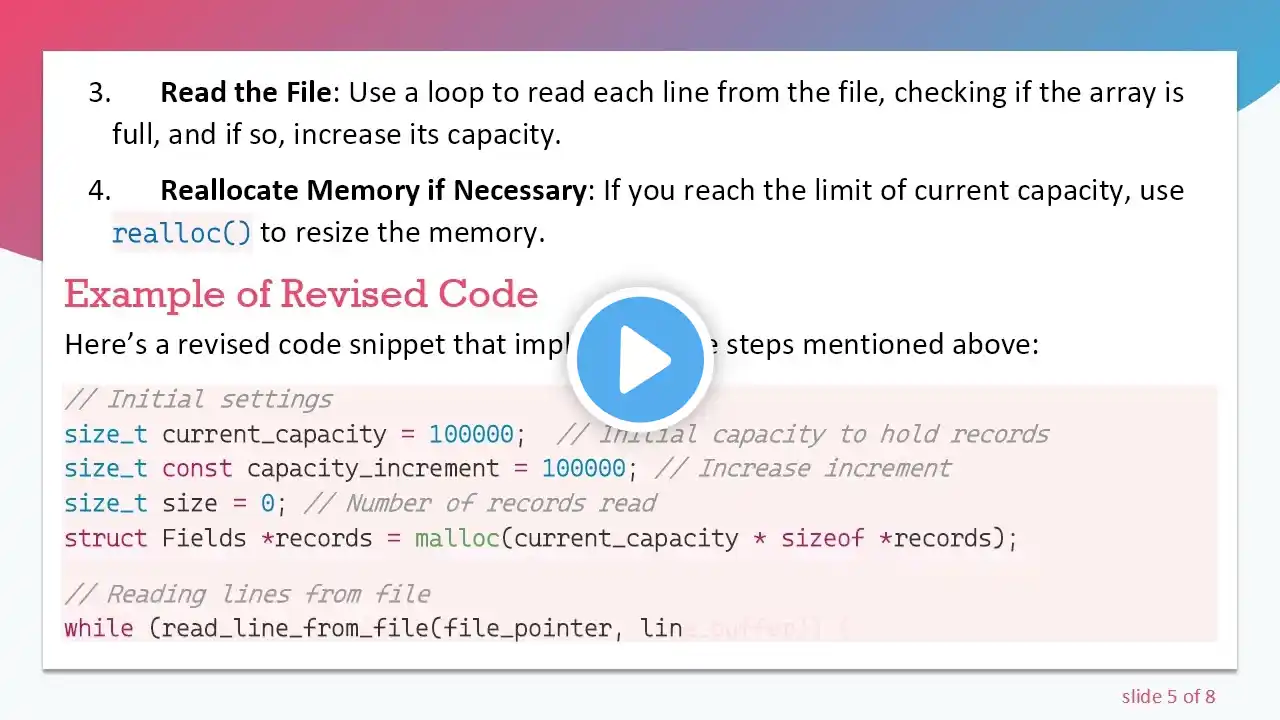
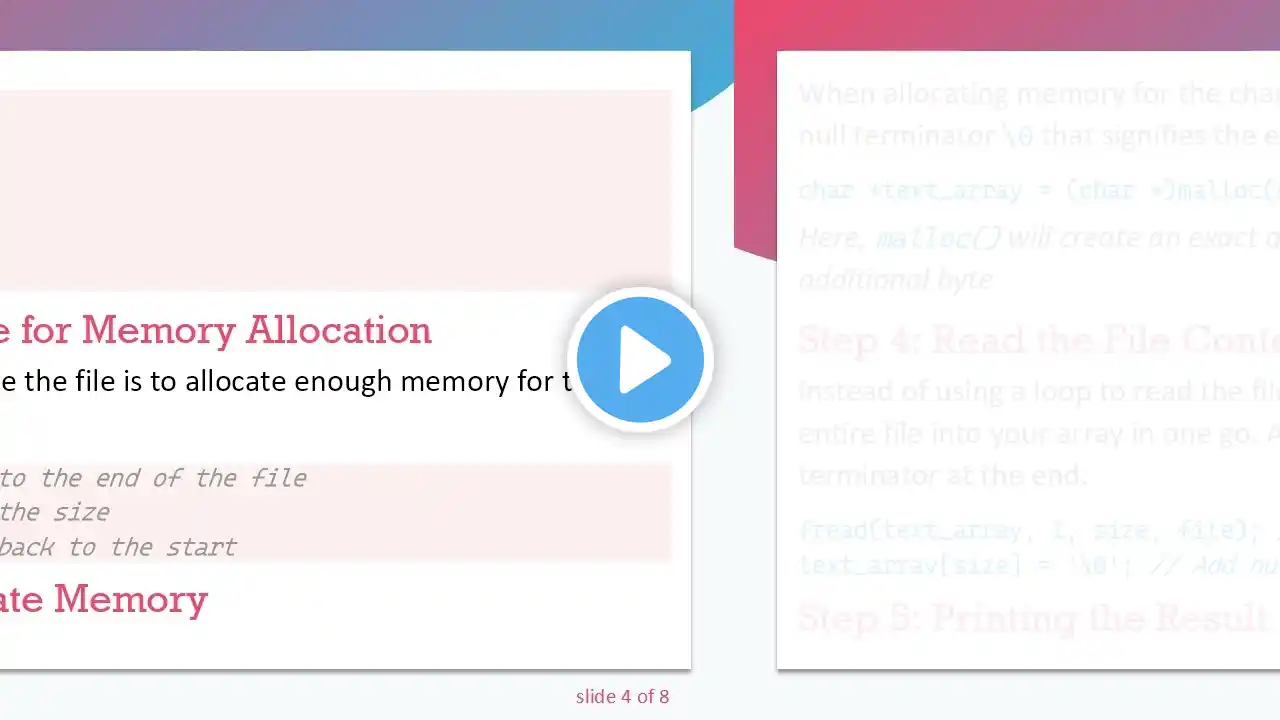
Learn how to dynamically allocate memory to an array and read a large text file in C for efficient text processing. --- This video is based on the question https://stackoverflow.com/q/63353054/ asked by the user 'PetrifiedPenguin' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/14085178/ ) and on the answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/63353211/ provided by the user 'Barmar' ( https://stackoverflow.com/u/1491895/ ) at 'Stack Overflow' website. Thanks to these great users and Stackexchange community for their contributions. Visit these links for original content and any more details, such as alternate solutions, latest updates/developments on topic, comments, revision history etc. For example, the original title of the Question was: Dynamically allocating memory to an array and reading a large text file Also, Content (except music) licensed under CC BY-SA https://meta.stackexchange.com/help/l... The original Question post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license, and the original Answer post is licensed under the 'CC BY-SA 4.0' ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/... ) license. If anything seems off to you, please feel free to write me at vlogize [AT] gmail [DOT] com. --- Dynamically Allocating Memory to an Array and Reading a Large Text File in C If you've ever tried to handle large text files with C, you might have stumbled upon issues with memory allocation and string manipulation. Many programmers face challenges when working with dynamic memory and file I/O, which can lead to unexpected errors and behaviors. Do you find yourself feeling overwhelmed when trying to read a large text file and storing it in memory for further processing? If so, you’re not alone! In this post, we'll break down the solution to ensure that you can effectively allocate memory and read a large text file in C without any hassle. Understanding the Problem The task at hand involves reading a large text file, which is often comparable in size to a novel, and storing its content in a dynamically allocated array. The objective is to manipulate this array later, but challenges arise when the content gets garbled or shows unexpected results. Analyzing the provided code reveals a few common pitfalls that need to be addressed for successful execution. The Solution To achieve your goal, follow the structured steps outlined below. We'll start with how to correctly allocate memory, read in the text, and manage null-termination for proper string handling. Step 1: Open the File Begin by opening the file using fopen(). Ensure to check if the file opens successfully: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Step 2: Determine File Size for Memory Allocation Next, you'll need to find out how large the file is to allocate enough memory for the array: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Step 3: Dynamically Allocate Memory When allocating memory for the character array, remember to add an extra byte for the null terminator \0 that signifies the end of a string in C: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Here, malloc() will create an exact array based on the detected file size, plus one additional byte. Step 4: Read the File Content Instead of using a loop to read the file line by line, you can leverage fread() to read the entire file into your array in one go. After reading in the content, ensure you place a null terminator at the end: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Step 5: Printing the Result Finally, print the content of text_array directly. There’s no need to loop through each character as we've already managed the string formatting with \0: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Complete Working Example Bringing it all together, here’s the corrected code: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Conclusion With this guide, you should now have a clear understanding of how to manage dynamically allocated memory in C to read large text files. Always remember to take care of memory management practices, ensuring you free any allocated memory after its use. This method not only improves your coding efficiency but also adds robustness to your applications. Happy coding!