Ideal Gases | A2 Level | Physics | Jawad Tariq | SLATE
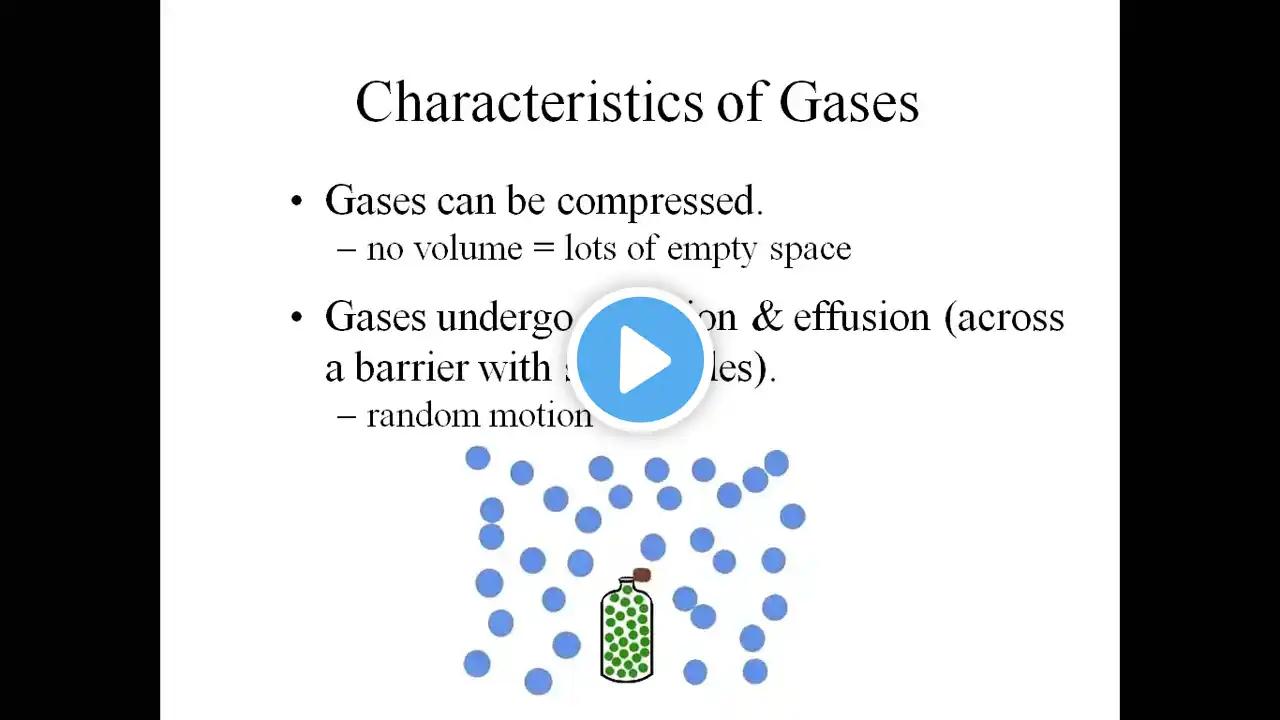
#igcse #cambridge #slate #slatepakistan Ideal Gases – O/A Level Physics Overview An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that interact only when they collide elastically. It obeys the ideal gas equation, which is: 𝑃 𝑉 = 𝑛 𝑅 𝑇 PV=nRT Where: 𝑃 P = Pressure (Pa) 𝑉 V = Volume (m³) 𝑛 n = Number of moles 𝑅 R = Universal gas constant (8.31 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹) 𝑇 T = Temperature (K) Key Assumptions of an Ideal Gas: Gas particles have negligible volume compared to the volume of the container. No intermolecular forces between particles. Collisions between particles and with the container walls are perfectly elastic (no energy loss). Particles are in constant, random motion. These assumptions help simplify the behavior of gases, especially under low pressure and high temperature, where real gases behave more ideally. Ideal Gases | A2 Level | Physics | Jawad Tariq | SLATE This video is likely a helpful visual explanation of the Ideal Gas concepts at A-Level, presented by Jawad Tariq from SLATE.