Confidence Intervals Class 5 | Finding CI for Proportions using Binomial Distribution
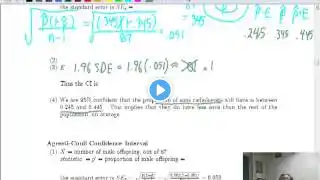
#StatisticsMadeEasy#ConfidenceIntervals#NormalDistribution#ExamPreparation#actuarialscience#binomialdistribution Video Summary: Confidence Intervals & Normal Distribution Explained! 🔹 Introduction to Normal Distribution Covers one-sample and two-sample normal distributions. Importance of understanding formulas for open-book exams and real-world applications. 🔹 Essential Probability Distributions Explanation of Binomial and Poisson distributions and when to use them. Why 80-90% of statistical problems rely on just a few key distributions. Understanding the role of parameters like mean and probability (p). 🔹 Applying the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) How CLT helps in approximating binomial distributions with normal distributions for large samples. Key takeaway: Use normal approximation when the sample size is large! For small samples: Direct probability calculations are required. 🔹 Step-by-Step Confidence Interval Calculation ✅ Example: Estimating Mortality Rate Given: A binomially distributed sample where deaths are counted. Finding: A 90% confidence interval for the mortality rate. Key observation: Understanding the difference between "mean" and "rate" is crucial! 🔹 Formulas & Problem-Solving Approach Identifying whether the question asks about the mean or probability (p). When sigma (σ) is unknown, using an alternative approach for confidence intervals. The five most commonly used formulas in hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. 🔹 Understanding Small Sample Confidence Intervals Example problem: Survey data where 7 out of 8 people favor a decision. Small sample size means Central Limit Theorem cannot be applied. Direct binomial probability calculations are needed. 🔹 Introduction to Numerical Analysis & Bisection Method 💡 Why Do We Need Numerical Methods? Some equations cannot be solved algebraically, so we use numerical techniques. Applications in weather prediction, actuarial science, and finance. 🟢 Step-by-Step Explanation of the Bisection Method 1️⃣ Identify two values where the function changes sign (one positive, one negative). 2️⃣ Take the midpoint and check its sign. 3️⃣ Repeat the process, continuously halving the interval. 4️⃣ This method always converges to a root, ensuring accuracy. 🔹 Applying the Bisection Method in Statistics Finding probabilities using binomial distributions when direct formulas don’t apply. Example problem: Estimating the probability of success in a given scenario. Key idea: Using the numerical method to approximate unknown probabilities. 🔹 Final Insights on Statistical Confidence Intervals Two major approaches: ✅ Using the Central Limit Theorem for large samples. ✅ Direct calculations for small samples. Applying confidence intervals to one-sample and two-sample scenarios. Practical exam tips for solving confidence interval problems efficiently! 📌 This video provides a step-by-step breakdown of confidence intervals, probability distributions, and numerical methods—perfect for students preparing for exams or anyone interested in statistical applications! 🚀📊