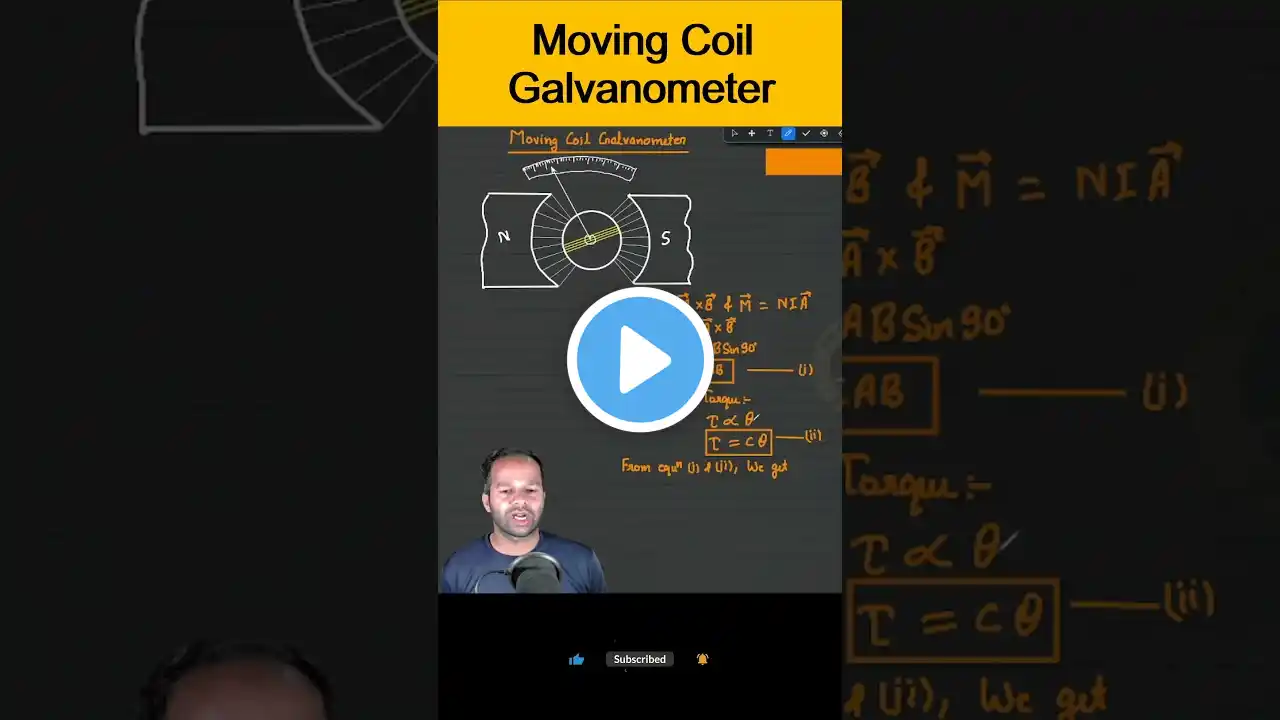
Moving coil Galvanometer, principle, construction, working|12th Physics|CBSE/ISC #education#physics
Moving coil Galvanometer, principle, construction, working, Current sensitivity, voltage sensitivity byg|12th|12th physics|Derivation|CBSE|ISC#cbse #12thphysics #study #education #physics #trending #science Link for all important derivation for 12th Physics - # • 12th physics (all important derivation) Link for all important derivation Shorts for revision for 12th Physics - • 12yh Physics (All important derivation) sh... Link for telegram group- Concept Dost - Mayank Saxena Group for notes and competition exam notes, short notes pdf etc https://t.me/conceptdost Welcome to Concept Dost ! A moving coil galvanometer is a device that measures electric current. It consists of a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field. When current flows through the coil, it experiences a torque, causing it to rotate. This rotation is proportional to the current, making it a useful tool for measuring and detecting small electrical currents. *Principle:* The moving coil galvanometer operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When current flows through the coil (usually made of a few turns of fine wire), it produces a magnetic field. The coil is positioned within the field of a permanent magnet. According to Ampere's law, a torque is exerted on the coil, causing it to rotate. *Construction:* 1. *Coil:* Typically, a lightweight coil of wire is wound on a delicate frame or spindle. 2. *Magnet:* A permanent magnet generates a uniform magnetic field, and the coil is positioned within this field. 3. *Suspension System:* The coil is suspended using a thin fiber or metallic suspension, allowing it to rotate freely. *Working:* When current flows through the coil, the interaction between the magnetic field produced by the current and the external magnetic field results in a torque. This torque causes the coil to rotate. The deflection of the coil is proportional to the current passing through it. *Current Sensitivity:* Current sensitivity is a measure of how much the coil deflects for a given amount of current. It is often expressed in terms of deflection per unit current (e.g., degrees per microampere). *Voltage Sensitivity:* Voltage sensitivity is related to current sensitivity but considers the relationship between coil deflection and applied voltage across the galvanometer. It is expressed as deflection per unit voltage (e.g., degrees per millivolt). Electromagnetic induction Coil of wire Torque Permanent magnet Suspension system Deflection Current sensitivity Voltage sensitivity Calibration Ampere's law Ampere's Law, Right-hand rule, Magnetic field, Lorentz force, Fleming's left-hand rule, right hand palm rule Magnetic flux, Permeability, Current density, Biot-Savart Law, Magnetic induction, Torque on current carrying loop magnetic dipole Torque moving coil galvanometer #trending , #Viral, #YouTub, #Entertainment #Music, #Gaming, #Travel, #Food, #Comedy #DIY #physicswallah #Lifestyle, #Fitness, #Fashion, #Tech, #News, #Tutorials, #reviews #inspiration #funny About myself- Mayank saxena P.G.T. (Physics) Inspire scholar-2013-2018