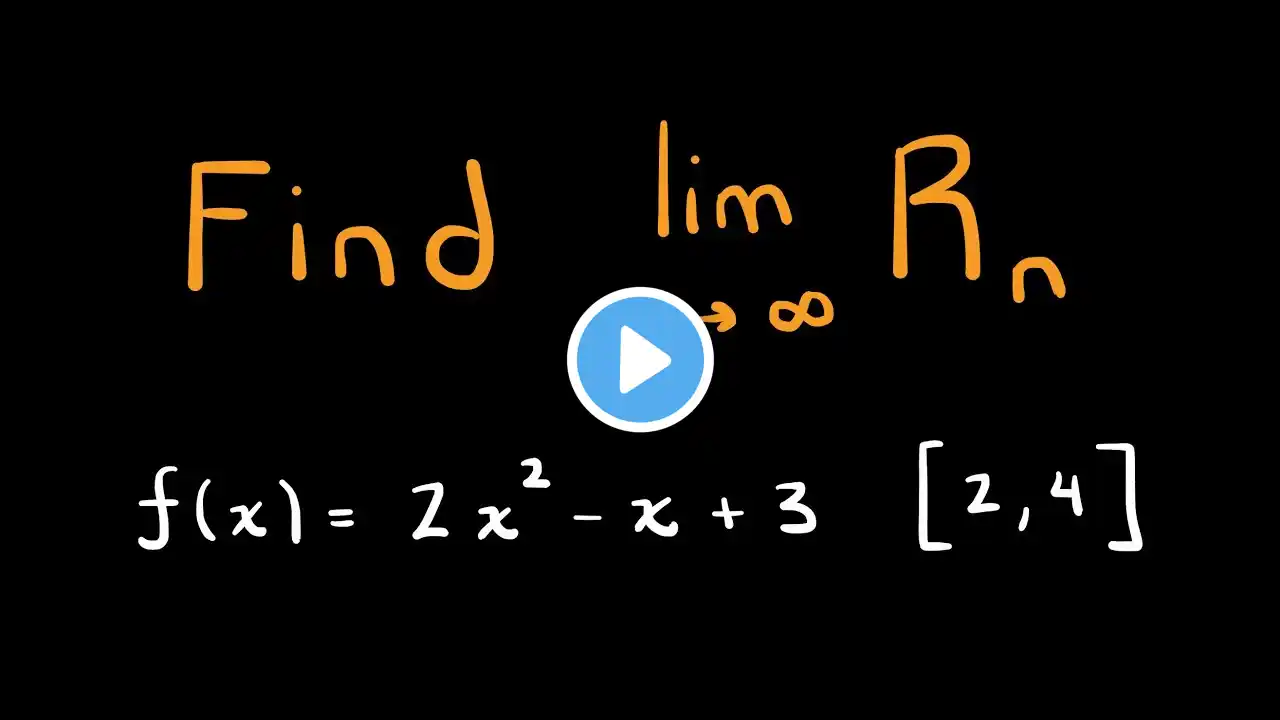Exact Area Under a Curve from Left, Right, and Midpoint Riemann Sums | Integral Calculus
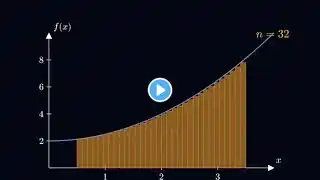
In this video, we explain how the area under a curve can be found exactly by taking limits of left, right, and midpoint Riemann sums. Starting from area approximations with rectangles, we increase the number of rectangles and see how these sums converge to a single exact value for non-negative continuous functions. Timestamps: 0:00 - Limit of left, right, and midpoint approximations explained 3:04 - Power sum formulas 4:58 - Example involving limit of Riemann sums If you would like to support the channel (much appreciated!) and/or download annotated lecture notes from any video, click here: / mathswithmoh