Cirrhosis causes symptoms by (#NGST) diagnosis treatment pathology #NUSRING STUDY
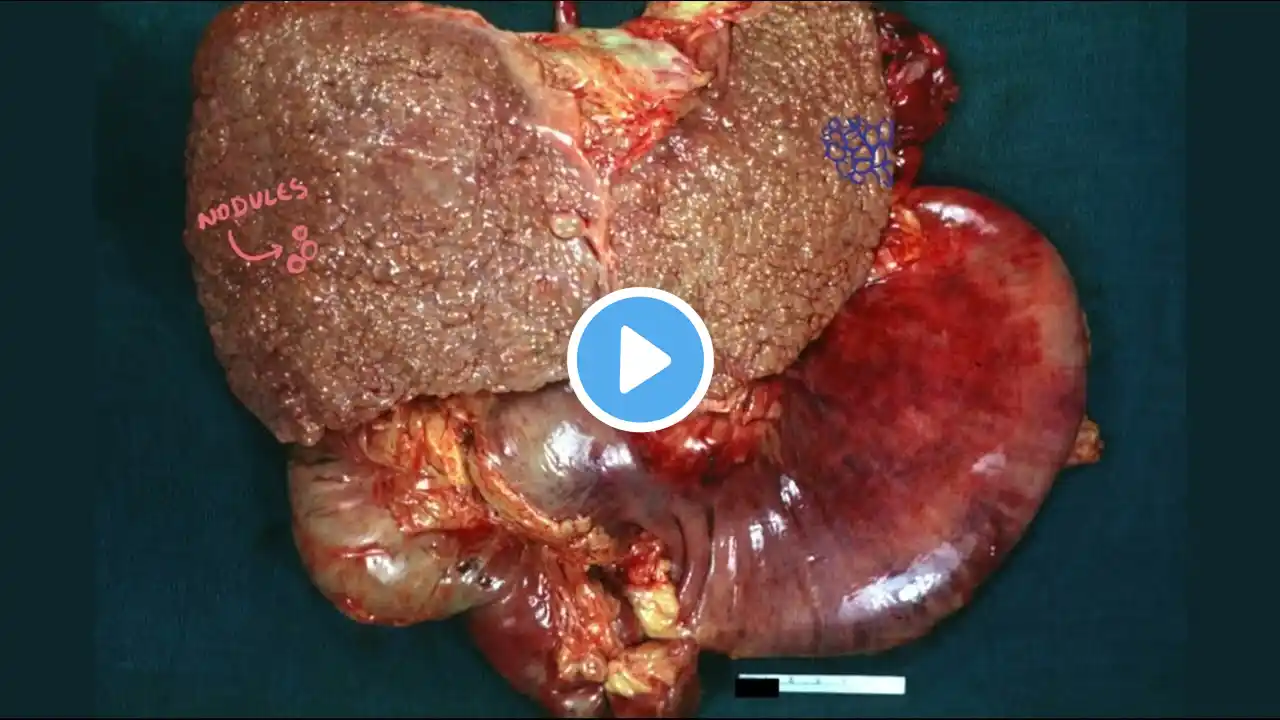
"This video also translet into text if you want notes then you read this given below 👇👇👇👇" Finally, the liver helps in making clotting factors or proteins that help coagulate your blood, so when you aren’t producing these coagulation factors, you can develop issuesrelated to your ability to coagulate blood, which you need in order to stop blood loss after an injury. To recap the general symptoms of cirrhosis, early on, with a small amount of scarring and fibrosis, we call it compensated cirrhosis, meaning the liver can still do a lot of its job. In this case, somebody with cirrhosis might not have any symptoms, or have nonspecific symptoms like weight loss, weakness, or fatigue. Later on, though, with extensive scarring, the liver progresses to decompensated cirrhosis, and can’t function properly. At this point many of the described symptoms start to develop, like jaundice and pruritus or itchy skin, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy leading to confusion, and easy bruising from low coagulation factors. For diagnosis, the “gold standard” is a liver biopsy, taking a tiny sample of the liver tissue examine under a microscope. Common lab findings include elevated serum bilirubin, as well as elevated liver enzymes like aspartate aminotransferase, (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), where AST is usually more elevated than ALT, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, and thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count.As to treatment, generally the scarring in cirrhosis is irreversible, so first of allit’s important to prevent continued liver damage by identifying the underlying causeand treating that, for example stopping alcohol consumption or antiviral treatment for those with hepatitis C. With advanced cirrhosis, though, where the liver stops functioning, a liver transplant might be needed. Alright, as a quick recap, cirrhosis is when inflammation and liver damage causes the liver to become fibrotic and develop scar tissue. Causes include things like excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged viral attack like from hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. Over time as the liver becomes less functional, symptoms like jaundice, ascites, easy bruising, and hepatic encephalopathy develop. Diagnosis is often done with a biopsy or through lab tests, and treatment for advanced cirrhosis is to treat the underlying cause, but sometimes a liver transplant is required.