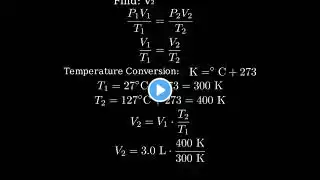
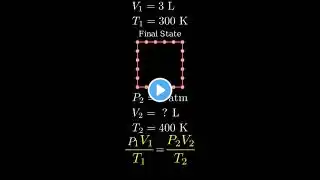
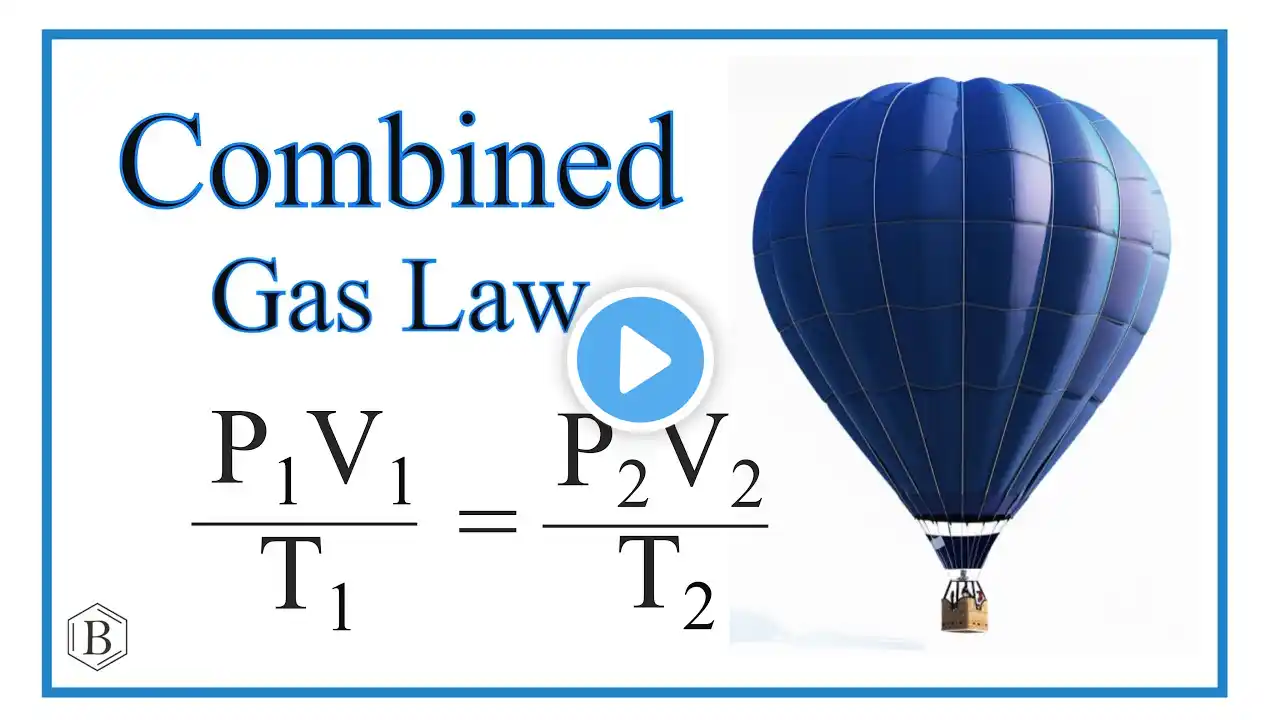
Combined Gas Law Practice Problem: Find New Volume
In this video, we'll tackle a combined gas law practice problem. We're given a gas sample with an initial volume, pressure, and temperature (in Celsius), and we'll calculate its new volume when the pressure and temperature change. Problem: A sample of gas has a volume of 15.0 L at a pressure of 1.00 atm and a temperature of 27.2 degrees Celsius. What is the new volume if the pressure is raised to 1580 mmHg and the temperature is raised to 356.2 K? This is a classic example of how to apply the combined gas law, derived from the ideal gas law, when you're given initial pressure, volume, and temperature, and asked to find the new volume under changed conditions. We'll walk through the solution step-by-step, including the necessary temperature conversion, ensuring you understand the process.