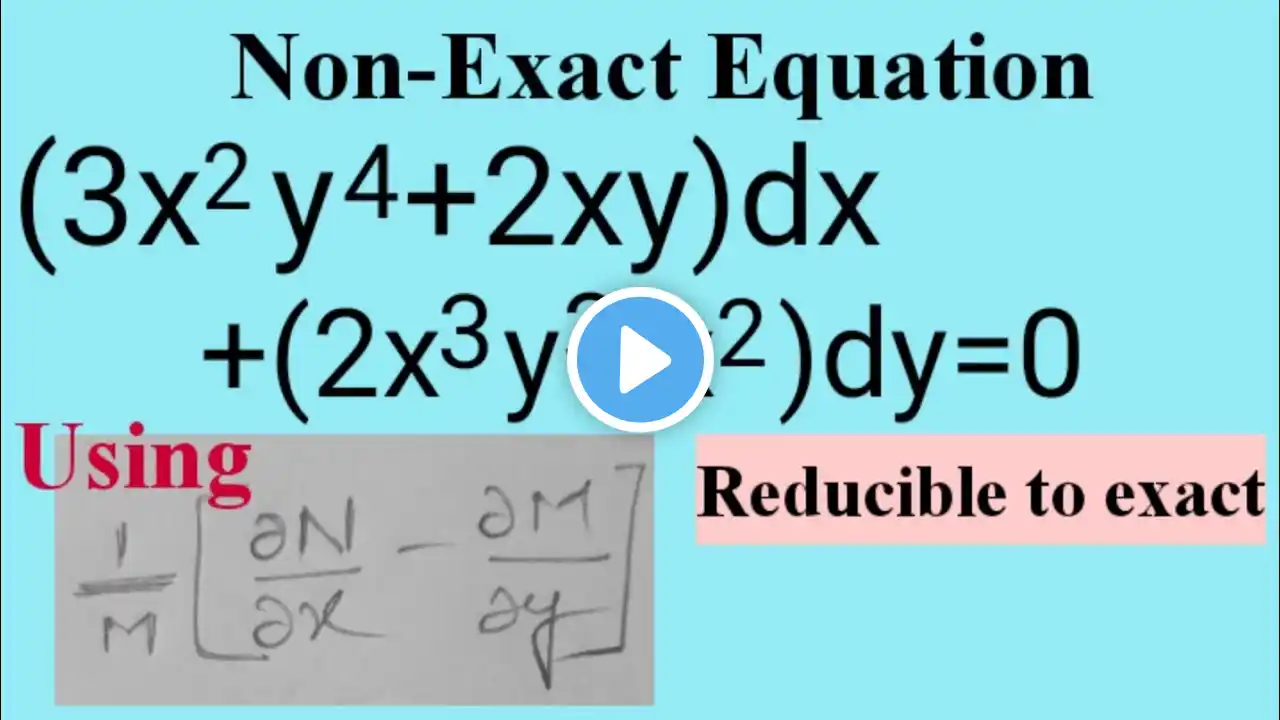(y+y^3/3+x^2/2)dx+1/4(x+xy^2)dy=0 #NonExact L597 @MathsPulseChinnaiahKalpana
#nonexactequation #reducibletoexact Hello, People! Here is a video of solving non-exact equation, by reducing the given equation exact form. Have a little patience and watch the video till end. My hearty thanks to all the subscribers, supporters, viewers and well-wishers❤ With Love, Chinnaiah Kalpana🍁 Note: If (1/N)[(partial derivative of M w.r.t. y) - (partial derivative of N w.r.t. x)] = f(x) [i.e., a function of x only] (or) k [real number] , then exp(∫f(x)dx) (or) exp(∫kdx) is an integrating factor of Mdx+Ndy=0. exp(log f(x)) = f(x) & exp(k logx) = exp[log(x^k)] = x^k where k is constant. Working rule to solve Mdx+Ndy=0: 1. General equation is Mdx+Ndy=0 ......(i) Observe (partial derivative of M w.r.t. y) ≠ (partial derivative of N w.r.t. x), then (i) is Non-Exact. 2. Find (1/N)[(partial derivative of M w.r.t y) - (partial derivative of N w.r.t x)] and observe it as a function of x alone = f(x) or a real constant k. 3. Then exp(∫f(x)dx) or exp(∫kdx) is an Integrating factor of (i). 4. Multiplying (i) with I.F. to transform it into an exact equation of (i), M1dx+N1dy=0 ...(ii) 5. Solve (ii) to get the general solution of (i). For more such videos 👇 • Differential Equations- Engineering Mathem... Stay tuned to 'Maths Pulse'. Get rid of 'Maths Phobia'. Have a happy learning! #differentialequations #mathspulse #chinnaiahkalpana #nonexactproblems #engineeringmathematics #bscmaths #maths #math