Muscle Contraction Mechanism Explained | Molecular & Chemical Basis for UG & PG Biology Students.
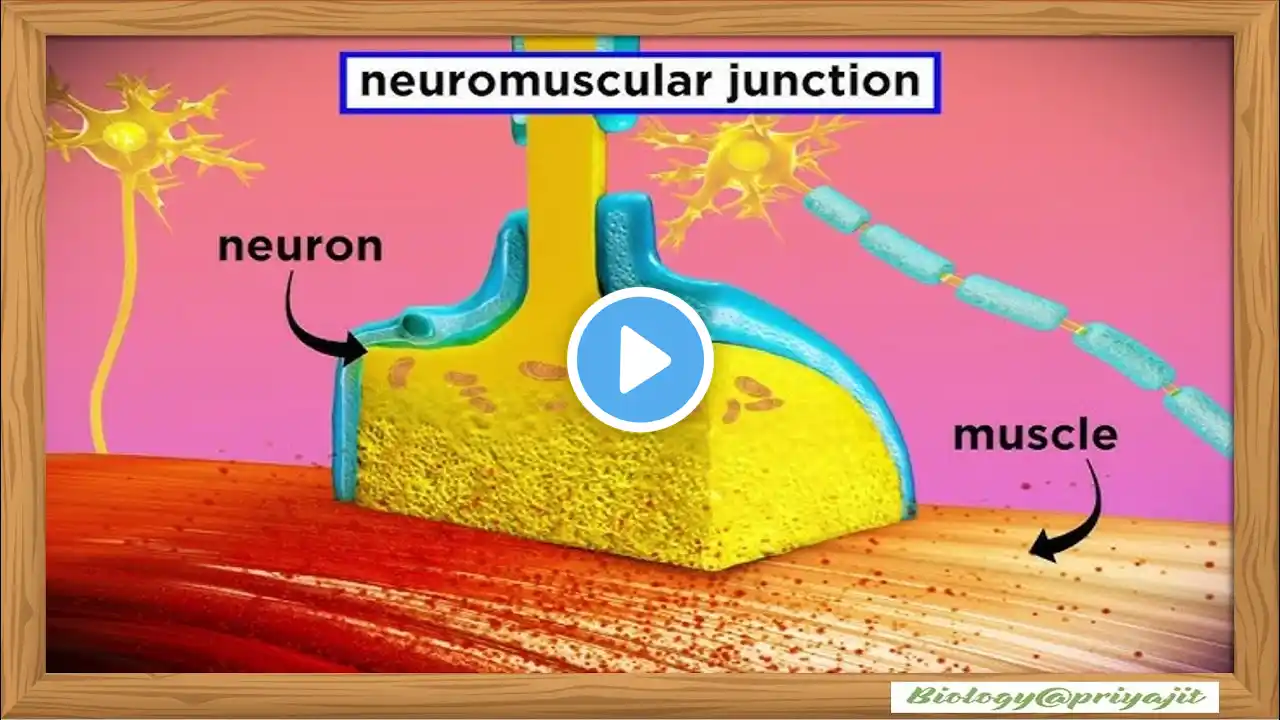
In this video, we explain the mechanism of muscle contraction in detail, covering both the molecular and chemical basis. Learn how actin, myosin, troponin, tropomyosin, ATP, and calcium ions work together in the sliding filament theory to produce muscle contraction. This lecture is designed for UG (Undergraduate) and PG (Postgraduate) biology students, NEET aspirants, and medical/paramedical learners. By the end of this session, you will clearly understand: Ultrastructure of skeletal muscle. Role of ATP and calcium in muscle contraction. Sliding filament theory. Molecular interactions of actin and myosin. Chemical basis of contraction & relaxation. General Mechanism of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Skeletal muscle contraction initiation and execution occur in the following steps. An action potential (AP) travels along a motor nerve to its endings on muscle fibers. At each motor nerve ending, the nerve secretes acetylcholine (ACh). ACh acts locally on the muscle fiber membrane to open ACh-gated cation channels. The opening of ACh-gated channels allows large quantities of sodium (Na) ions to diffuse to the interior of the muscle fiber membrane. This action causes a local depolarization, leading to the opening of voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels, which initiates an AP at the membrane. The AP depolarizes the muscle membrane, causing the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) to release large quantities of Ca ions stored within the reticulum. The Ca ions produce attractive forces to act between actin and myosin filaments, causing them to slide alongside each other leading to the contractile process. After a fraction of a second, the Ca ions are pumped back into the SR by a Ca-membrane pump and remain stored in the SR until a new muscle AP occurs. The removal of Ca ions from the myofibrils causes muscle contraction to cease. Some main concepts that you will learn in this video are How Muscle Contracts, Control of muscle Contraction, Energy of Muscle contraction, Structure of Thin and Thick Filament, Stimulation Muscle to contract, Providing Energy for muscle contraction, Some important keywords or tags to search this topic #MuscleContraction #MusclePhysiology #Sarcomere #MotorUnit #ActinMyosin #ExcitationContractionCoupling #MuscleFiber #NeuromuscularJunction #MuscleContractionProcess #MuscleContractionTypes #MuscleContractionMechanism


