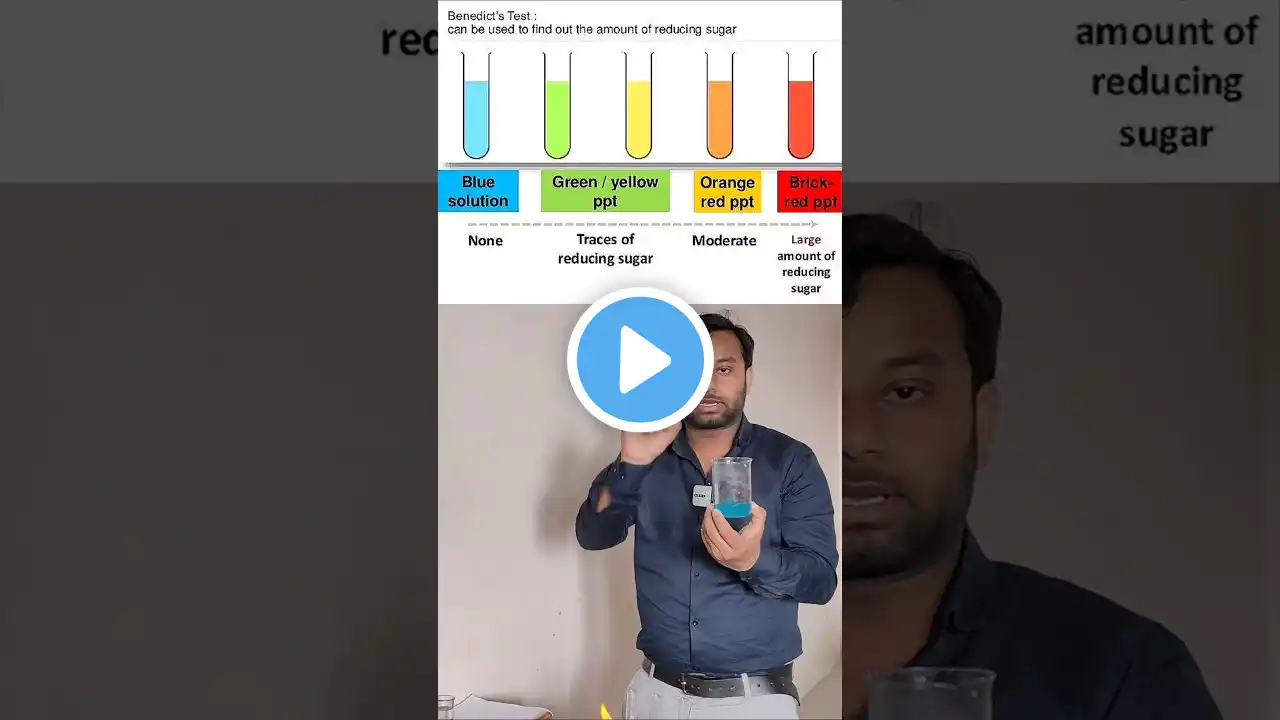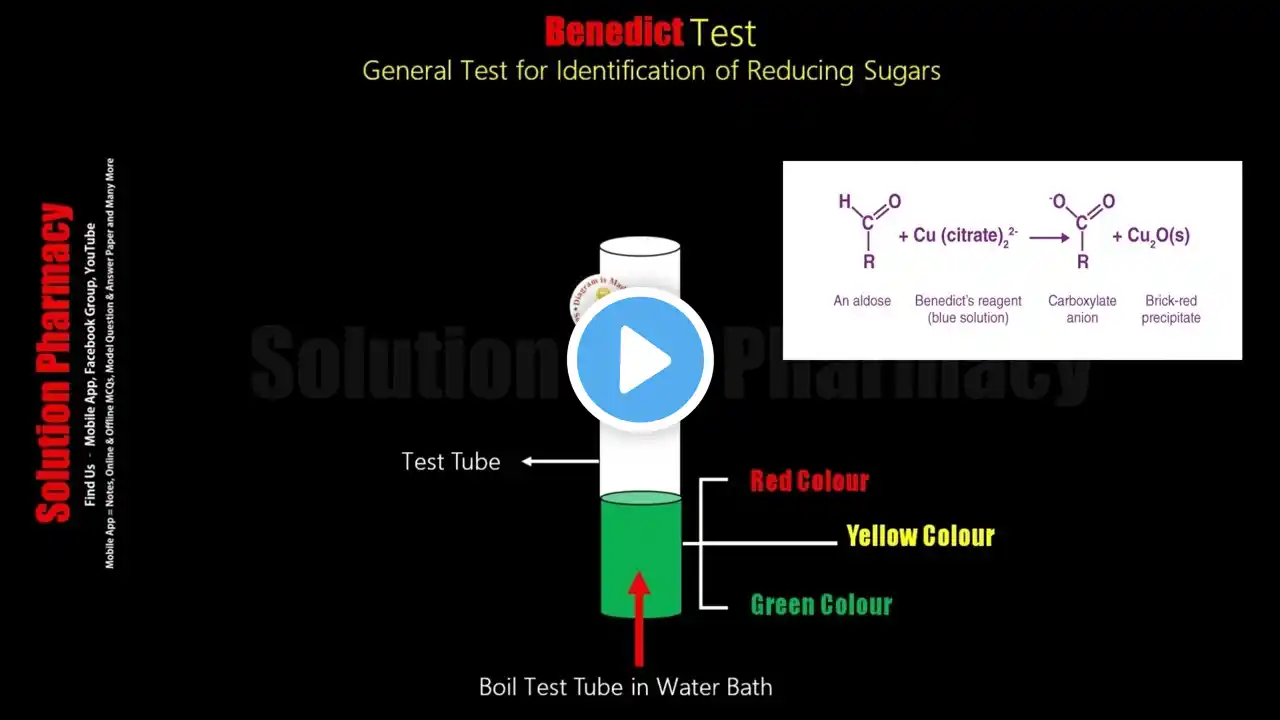
Benedict's Test | Test for Reducing Sugar | Biochemical test for Carbohydrate |Animation Video Hindi
Download the "Solution Pharmacy" Mobile App to Get All Uploaded Notes, Model Question Papers, Answer Papers, Online Tests and other GPAT Materials - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... 1. Determination of Sugar in Urine = Benedict Test | Detection of Sugar in Urine | Diabetes Mellitus • Determination of Sugar in Urine | Benedict... 2. Benedict Reagent = Preparation and Use in Estimation of Carbohydrate (HINDI) By Solution Pharmacy • Benedict Reagent = Preparation & Use in Es... 3. Benedict Test | Test for Reducing Sugar | Biochemical Test for Carbohydrate | Animated Video English • Benedict Test | Test for Reducing Sugar | ... Benedict's Test Benedict’s test is a chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars in a given analyte. Therefore, simple carbohydrates containing a free ketone or aldehyde functional group can be identified with this test. Benedict’s reagent (also known as Benedict’s solution), is a complex mixture of sodium citrate, sodium carbonate, and the pentahydrate of copper(II) sulfate. When exposed to reducing sugars, the reactions undergone by Benedict’s reagent result in the formation of a brick-red precipitate, which indicates a positive Benedict’s test. An image detailing the changes in the color of Benedict’s reagent (from clear blue to brick-red) that are triggered by exposure to reducing sugars is provided below. Principle of Benedict’s Test When a reducing sugar is subjected to heat in the presence of an alkali, it gets converted into an enediol (which is a relatively powerful reducing agent). Therefore, when reducing sugars are present in the analyte, the cupric ions (Cu2+) in Benedict’s reagent are reduced to cuprous ions (Cu+). These cuprous ions form copper(I) oxide with the reaction mixture and precipitate out as a brick-red-colored compound. Benedict’s Test Procedure 1. Take 2 ml of the test sample must be mixed with 2 ml of Benedict’s reagent 2. Heat the content of the test tube in a bath of boiling water for 3 to 5 minutes. 3. The development of a brick-red colored precipitate of cuprous oxide confirms the presence of reducing sugars in the test sample. Interpreting of the Results Color of the Precipitate and approx of Reducing Sugar a. Green 0.5% b. Yellow 1% c. Orange 1.5% d. Red 2% Get in touch with the solution by just clicking the following links- Facebook Group- / solutionpharamcy Mobile App - https://play.google.com/store/apps/de... New Channel (Pharmacy Dictionary) / @pharmacydictionary E-Mail for official and other work - [email protected] #solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #Pharmacognosyvideos #GPAT