molecular basis of inheritance/#shorts #study #class12biology #motivation #viral
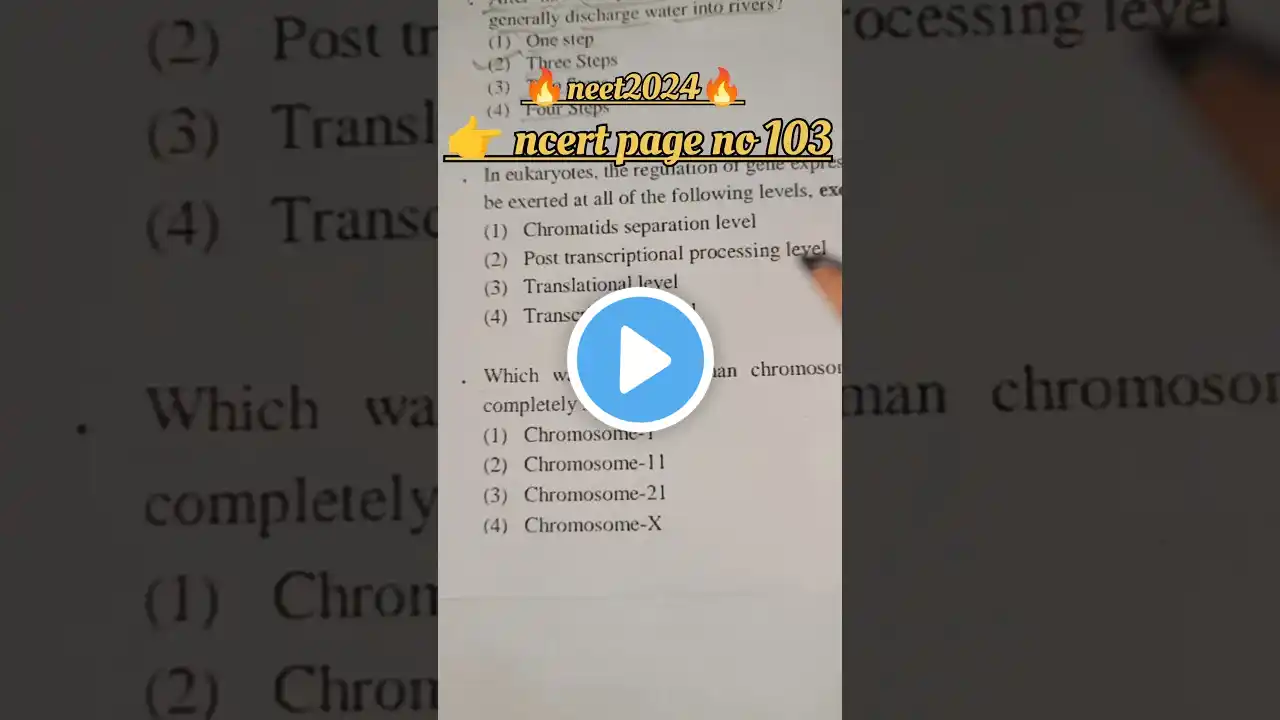
1. Genetic Material (DNA & RNA) DNA is the genetic material in most organisms (proved by Hershey & Chase experiment). RNA acts as genetic material in some viruses (like TMV) and as messenger in others. 2. DNA Structure (Watson & Crick model) Double helix made of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains. Backbone: sugar (deoxyribose) + phosphate. Bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G). Base pairing: A–T (2 H-bonds), G–C (3 H-bonds). 3. Packaging of DNA DNA wraps around histone proteins → nucleosome → chromatin. Chromatin further coils to form chromosomes. 4. Replication of DNA Semi-conservative (proved by Meselson & Stahl). Enzymes: DNA helicase (unwinds helix), DNA polymerase (synthesizes new strand), Ligase (joins Okazaki fragments). 5. Transcription (DNA → RNA) DNA acts as template to form RNA. RNA polymerase binds to promoter → synthesizes mRNA using complementary base pairing. In eukaryotes, hnRNA undergoes splicing, capping & tailing → forms mature mRNA. 6. Genetic Code Triplet code (3 bases = 1 codon = 1 amino acid). Universal, unambiguous, and degenerate. Start codon: AUG (Methionine). Stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA. 7. Translation (Protein Synthesis) mRNA provides code, tRNA brings amino acids, ribosomes act as site. Codon–anticodon pairing ensures correct sequence. Polypeptide chain forms → folds into functional protein. 8. Regulation of Gene Expression Operon model (Lac operon in E. coli): Structural genes (Z, Y, A), promoter, operator, and regulator gene. When lactose is present, it inactivates repressor → genes express to produce enzymes for lactose metabolism. 9. Human Genome Project (HGP) Aimed to sequence the entire human DNA. Found ~20,000–25,000 genes. Most of the DNA is non-coding (“junk DNA”). 10. DNA Fingerprinting Uses VNTR (Variable Number of Tandem Repeats) sequences. Developed by Alec Jeffreys. Applications: paternity tests, crime investigation, genetic diversity studies. --- 👉 In short: The molecular basis of inheritance explains how DNA stores, replicates, transmits, and expresses genetic information through replication, transcription, translation, and regulation of genes.