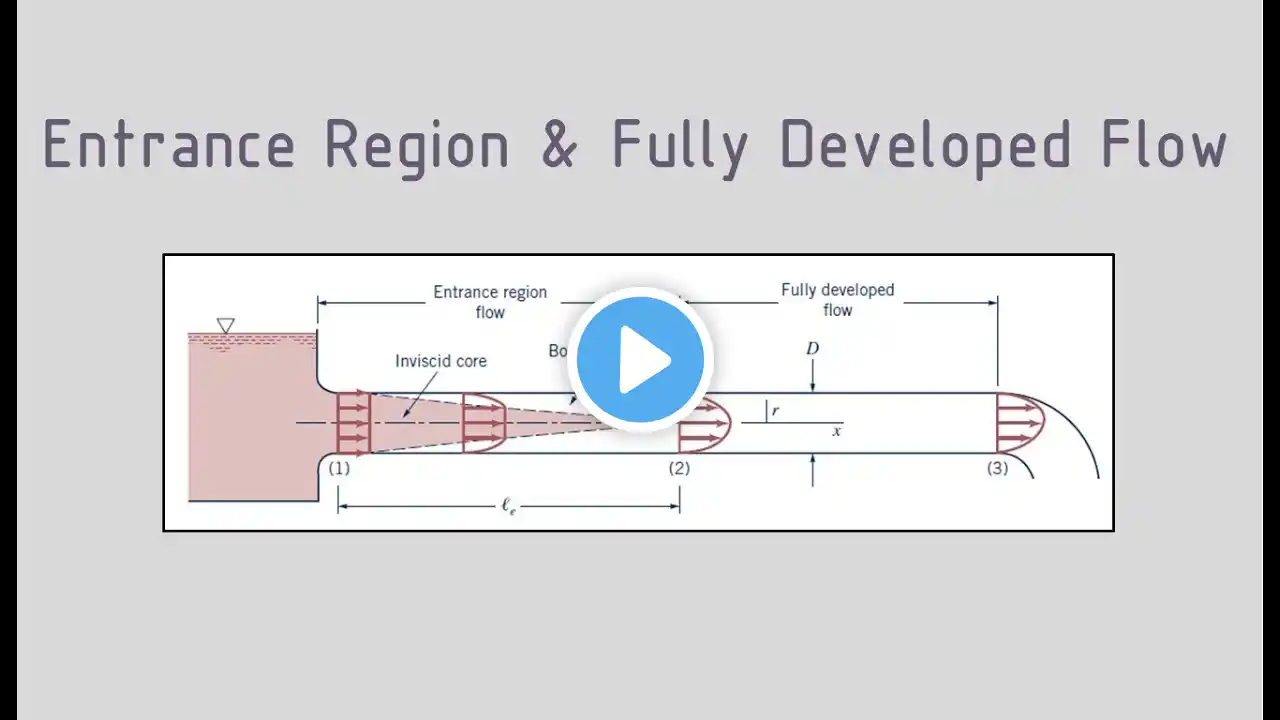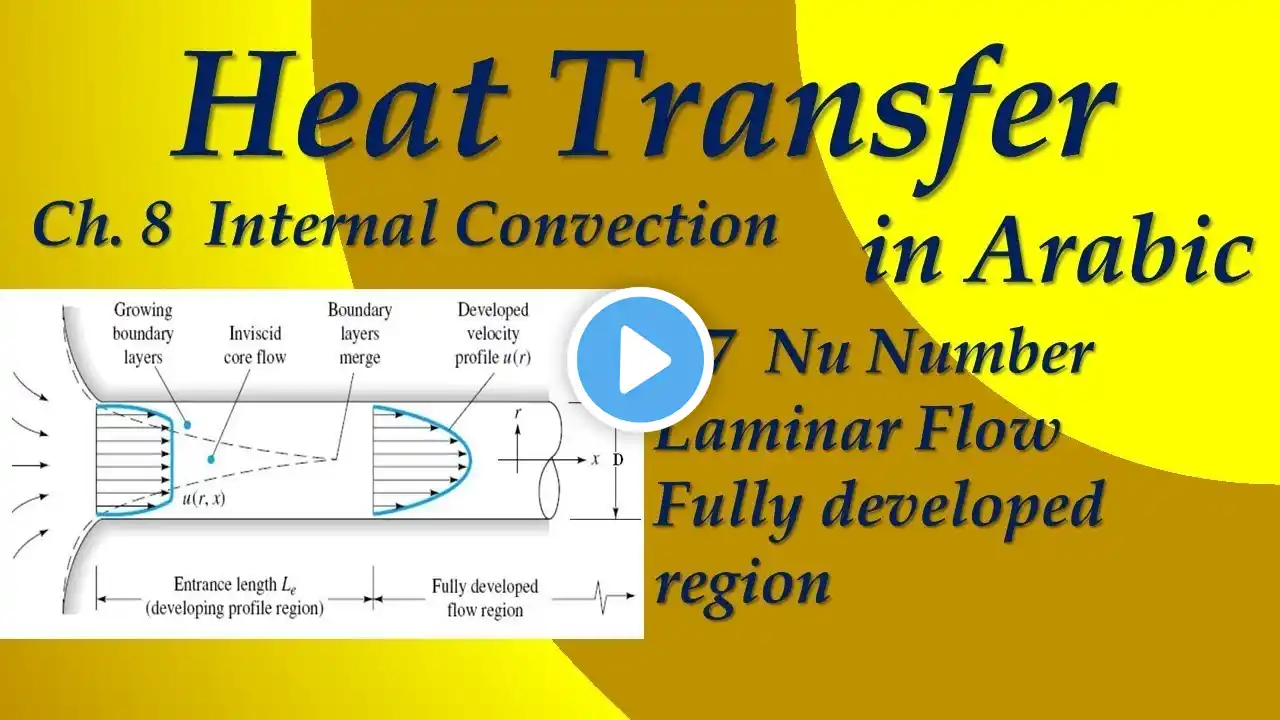
8.7 Nu Number | Laminar Flow | Fully developed region |
Ch. 6: Introduction to Convection (3 Lectures). 6.1.1 The Velocity Boundary Layer, 6.1.2 The Thermal Boundary Layer (equation 6.5, the convection problem), Local and Average heat transfer Coefficients, 6.2.3 The Problem of Convection, 6.3.1 Laminar and Turbulent Velocity Boundary Layers, 6.6 Physical Interpretation of the Dimensionless Parameters: (only Re, Nu, and Pr) Not included: 6.1.3 The Concentration Boundary Layer, 6.2.2 Mass Transfer, 6.3.2 Laminar and Turbulent Thermal and Species Concentration Boundary Layers, 6.4 The Boundary Layer Equations, 6.5 Boundary Layer Similarity: The Normalized Boundary Layer Equations, 6.7 Boundary Layer Analogies, 6.7.2 Evaporative Cooling Ch. 7: External Flow (3 Lectures). 7.1 The Empirical Method, 7.2 The Flat Plate in Parallel Flow: an ability to use equations: 7.20, 7.23, 7.29, and 7.30; Laminar Flow over an Isothermal Plate: an ability to use equations: 7.34, 7.36 (Turbulent Flow); 7.34, 7.40 (Mixed Boundary layer); 7.4. The Cylinder in Cross Flow: an ability to use equations: 7.52, 7.54. 7.5; The sphere: an ability to use equations 7.56 & 7.57 Reading by student: 7.2.5 Flat Plates with Constant Heat Flux Conditions, 7.3 Methodology for a Convection Calculation, 7.4.1 Flow Considerations (The Cylinder in Cross Flow) Not included: 7.2.4 Unheated Starting Length, 7.6 Flow across banks of Tubes, 7.7 Impinging Jets, 7.8 Packed Beds Ch. 9: Free convection (2.5 Lectures). 9.1 Physical Considerations. 9.5 The Effects of Turbulence. 9.6.1 Empirical Correlations: The Vertical Plate (9.26 and 9.27). 9.6.3 The Long Horizontal Cylinder. 9.6.4. Spheres (9.35). 9.9Combined Free and Forced Convection Reading by student (optional): 9.7 Free Convection within Parallel Plate Channels, 9.8 Empirical Correlations: Enclosures Not included: 9.2 The Governing Equations for Laminar Boundary Layers, 9.3 Similarity Considerations, 9.4 Laminar Free Convection on a Vertical Surface, 9.10 Convection Mass Transfer Ch. 8: Internal Flow (5 Lectures). 8.1 Hydrodynamic Considerations, 8.2 Thermal Considerations, 8.3 The Energy Balance (8.34, 8.38, 8.40, 8.41a&b, 8.43, 8.45a&b, 8.46a&b), 8.4 Laminar Flow in Circular Tubes: Thermal Analysis and Convection Correlations: Only an ability to use 8.53, 8.55, 8.56, 8.57, and 8.58. 8.4.3 Temperature-Dependent Properties, 8.5 Convection Correlations: Turbulent Flow in Circular Tubes (8.60, 8.61, 8.61), 8.6 Convection Correlations: Noncircular Tubes and the Concentric Tube Annulus (8.66, Table 8.1 & 8.2). Reading by student: 8.7 Heat Transfer Enhancement, 8.10 Summary (except anything related to concentration mass transfer) Not included: 8.8 Flow in Small Channels, 8.9 Convection Mass Transfer. Ch. 11: Heat Exchangers (4 Lectures). 11.1 Heat Exchanger Types. 11.2 The Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient. 11.3 Heat Exchanger Analysis: the Log Mean Temperature Difference (NO DERIVATION; just an ability to use LMTD method). 11.4 Heat Exchanger Analysis: The Effectiveness–NTU Method; ((NO DERIVATION; just an ability to use effectiveness method).11.5 Heat Exchanger Design and Performance Calculations Reading by student: 11.6 Additional Considerations, 11.7 Summary.