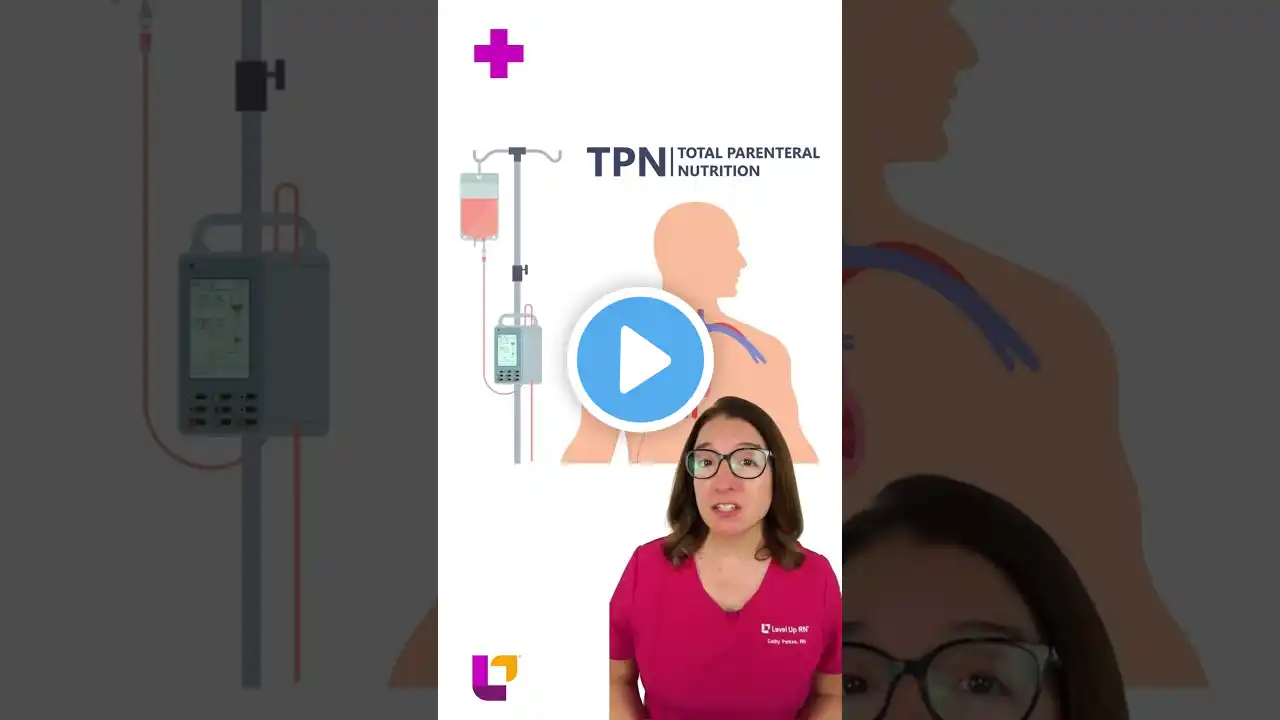
ENTERAL vs. PARENTERAL NUTRITION #nursingschool
If a patient is unable to intake food by mouth, there are two ways they can receive nutrition: enterally or parenterally. 👉 Enteral Nutrition:→ Provided directly via GI tract→ Indications: Patients in need of nutrition with a functioning GI tract ⭐️Enteral Routes: Nasogastric (NG) tube Orogastric (OG) tube Gastrostomy tube (G-tube) Jejunostomy tube (J-tube) 👉 Parenteral Nutrition:→ Provided IV, bypasses GI tract→ Indications: Patients in need of nutrition without a functioning GI tract Types of Parenteral Nutrition: 1️⃣ Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition (PPN):→ No central access needed, given through a peripheral line→ Only provides partial nutrient needs, short-term use only 2️⃣ Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN):→ Provides full nutrient needs, long-term use→ Requires central access, higher risk of CLABSI (central line-associated bloodstream infection) 💬 Comment below if you’d like to see more videos about this topic! #nursingschool #nursingstudent