Vasa previa //Types //pathophysiology//Symptoms// Risk factors// Diagnosis// Management
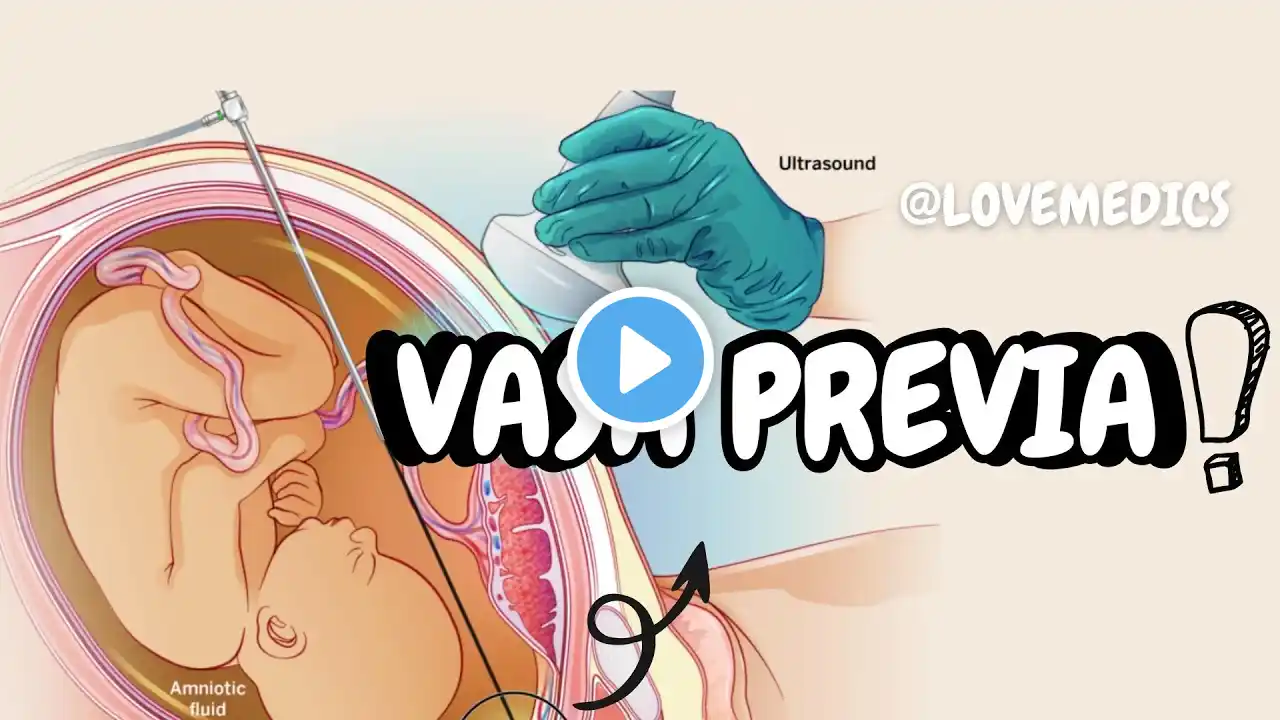
@lovemedics Vasa previa Vasa previa meaning: Vasa - Fetal blood vessel previa- Before / Obstructing the way vessels in the way, before the baby" Vasa previa _ Define Vasa previa is a rare but serious obstetric condition where fetal blood vessels -run through the membranes (amnion and chorion), -unprotected by the umbilical cord or placenta and -cross or are very close to the internal cervical os (the opening of the cervix). Types of vasa previa Vasa previa is classified into 2 main types based on the origin & path of the unprotected fetal vessels Type I Vasa Previa: velamentous cord insertion. Type 11 vasa previa: Two lobes (accessory/bilobed placenta) Type 111 vasa previa: Rare/Unclassified Type Associated with low-lying Type I Vasa Previa: Insertion abnormalitY Velamentous cord insertion. Fetal blood vessels travel from the cord to the placenta across the internal os, within the membranes & without protection from Wharton’s jelly Type II Vasa Previa: Two lobes (accessory/bilobed placenta) succenturiate or bilobed placenta. Fetal vessels run between two lobes of the placenta (main & accessory lobe), & they cross over the cervical os. Types III - vasa previa Rare/Unclassified Types (less commonly mentioned) Proposed as a classification for cases that don't fit into Type I or II. Associated with low-lying placentas or abnormal placental development. Abnormal branching of fetal vessel excit and reenter the placenta with normal umbilical cord Risk factors of vasa previa: Velamentous cord insertion (umbilical cord inserts into membranes instead of the placenta) Succenturiate lobe of placenta (accessory placental lobe) Placenta previa Multiple pregnancies IVF pregnancies Previous uterine surgery /procedure Pathophysiology of Vasa previa: Abnormal Placental Anatomy Unprotected Vessels Rupture of Membranes Massive Fetal Hemorrhage Fetal Hypoxia and Death Why is vasa previa dangerous for fetus ? The vessels are part of the fetal circulation, not maternal. These vessels are vulnerable to rupture, especially when the membranes rupture during labor. If the vessels rupture, it can lead to rapid fetal blood loss and fetal death if not managed immediately. Clinical findings of vasa previa: Painless vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimester (often at membrane rupture). Fetal distress or Bradycardia due to blood loss. Abnormal fetal heart rate Absence of maternal signs of shock Diagnosis of vasa previa @Antepartum: Transvaginal Color Doppler Ultrasound: Gold standard. Shows fetal vessels crossing the internal os. Color Doppler helps confirm that these vessels are fetal (pulsatile flow synchronous with fetal heart rate). Transabdominal Ultrasound: May initially suggest vasa previa. Less sensitive; transvaginal scan is usually done to confirm. @intrapartum Usually discovered after rupture of membranes: a. Classic triad: Painless vaginal bleeding. Fetal distress (bradycardia, sinusoidal heart rate pattern). Ruptured membranes. b. Apt Test (rarely used today): Distinguishes fetal from maternal blood. Management of vasa previa in antenatal period: Confirm diagnosis by 20–24 weeks with color Doppler ultrasound. Hospitalization: At 30–32 weeks for close monitoring. Corticosteroids: Administer betamethasone at 28–32 weeks to promote fetal lung maturity. Delivery with vasa previa: Elective cesarean section at 34–36 weeks, before labor or membrane rupture. Avoid digital vaginal exams or artificial rupture of membranes. Emergency management of vasa previa: If vasa previa is undiagnosed and presents with: Vaginal bleeding after membrane rupture Fetal bradycardia/distress Immediate emergency C-section is indicated to prevent fetal death. Resuscitate newborn if fetal hemorrhage occurs (may need transfusion). What does the term “vasa previa” mean? Define vasa previa How many main types of vasa previa are commonly classified? what is Type I vasa previa? what is Type II vasa previa? What is a succenturiate lobe? What is Type III vasa previa associated with? What is the initial anatomical abnormality in the pathophysiology of vasa previa? What causes fetal hypoxia in vasa previa? What leads to massive fetal hemorrhage in vasa previa? What is the most common symptom of vasa previa before diagnosis? What type of bleeding is seen in vasa previa — painful or painless? What fetal heart pattern may be seen due to vasa previa? What is the gold standard imaging for diagnosing vasa previa? What feature on color Doppler suggests fetal origin of the vessels? Which type of ultrasound is more sensitive: transabdominal or transvaginal? What is the classic triad of vasa previa seen during labor? What test distinguishes fetal from maternal blood? Why are corticosteroids given in vasa previa? What is the immediate step if vasa previa is suspected intrapartum? What emergency measure might be needed for the newborn after delivery?


