Effect of Osmosis on bacterial cell
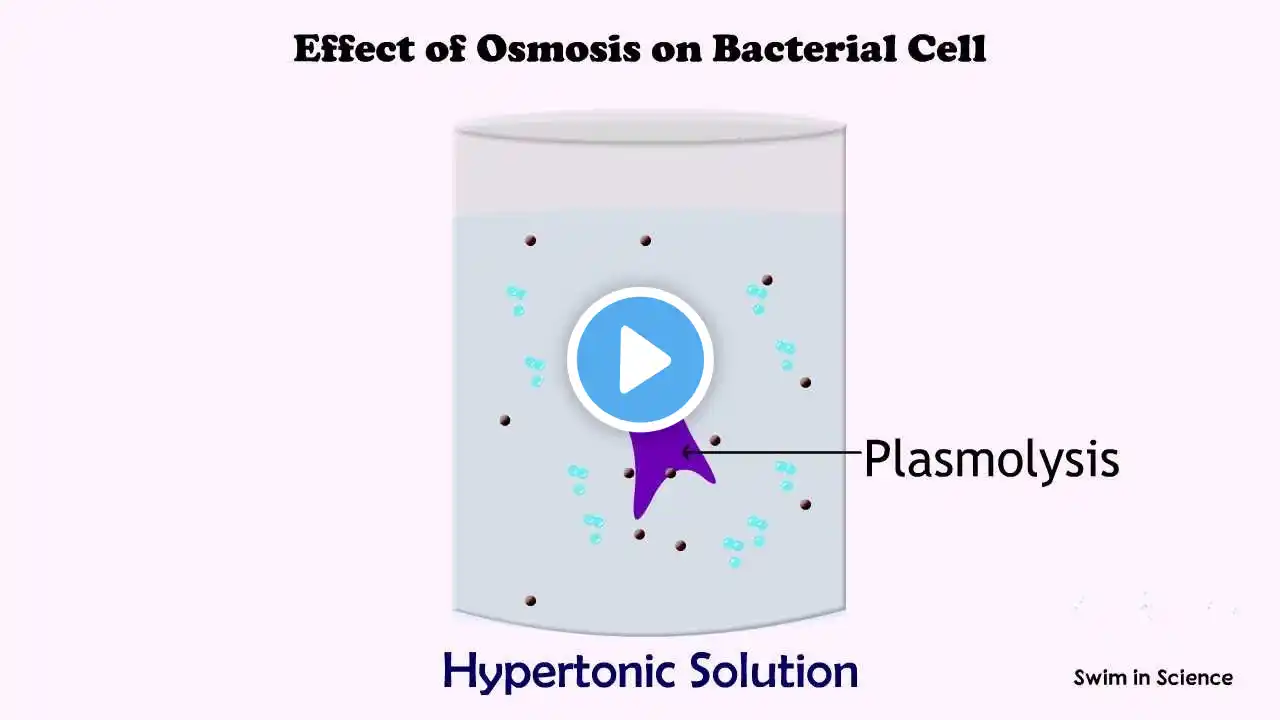
Welcome to Swim in Science #swiminscience #sowmyanrao #sowmyanagaraj The movement of solvent (water) from a low solute concentration to a higher solute concentration through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis. The flow of this solution stops when equilibrium is achieved on both sides of the membrane. The minimum pressure required to avoid a solution flowing through a semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure. Bacterial cells have semipermeable membranes which allow the movement of water whereas, salts cannot pass through it. Three terms are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell: 1. Hypertonic solution: A solution with high osmotic pressure in which the solute concentration is higher than that of a cell. 2. Isotonic solution: A solution with equal osmotic pressure in which solute concentration is same as that of a cell. 3. Hypotonic solution: A solution with low osmotic pressure in which the solute concentration is lower than that of a cell. What happens when a cell is placed in these solutions? Hypertonic solution If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move out of the cell (exosmosis). Water is lost from the cell resulting in dehydration, shrinkage of the plasma membrane and eventual death. This is a process known as plasmolysis. The addition of salt to fruits/fishes as a method of preservation causes a hypertonic condition resulting in shrinkage and eventual death of microbial cells. Saltwater gargling for sore throat is also based on the same principle. Some bacteria can withstand hypertonic environments and are called osmotolerant. Eg: S. aureus. Some bacteria specifically require an environment with a high concentration of sodium chloride. These organisms are called halophiles. Ex. Halobacterium spp. Isotonic solution If a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net water movement, so there is no change in the size of the cell. We use physiological saline (0.9% of NaCl solution) in the biological experiment to make a bacterial suspension. It is an isotonic solution that maintains the proper size and shape of bacterial cells. Hypotonic solution: If a cell is placed in a hypotonic environment, water will move inside the cell (endosmosis). The cells swell and eventually burst. The process is called. osmotic lysis Most bacteria, algae and fungi have rigid cell walls that allow them to tolerate a hypotonic environment. References https://www2.hawaii.edu/~johnb/micro/... https://www.khanacademy.org/science/a.... https://pediaa.com/difference-between.... https://byjus.com/biology/difference-.... https://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/lab... BGM: Weekend by LesFM | https://lesfm.net/acoustic-background... Music promoted by https://www.chosic.com/ Creative Commons CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/...










