Electric Circuits Questions Cambridge IGCSE O level Physics 0625 0972 5054 Lesson 63 part b
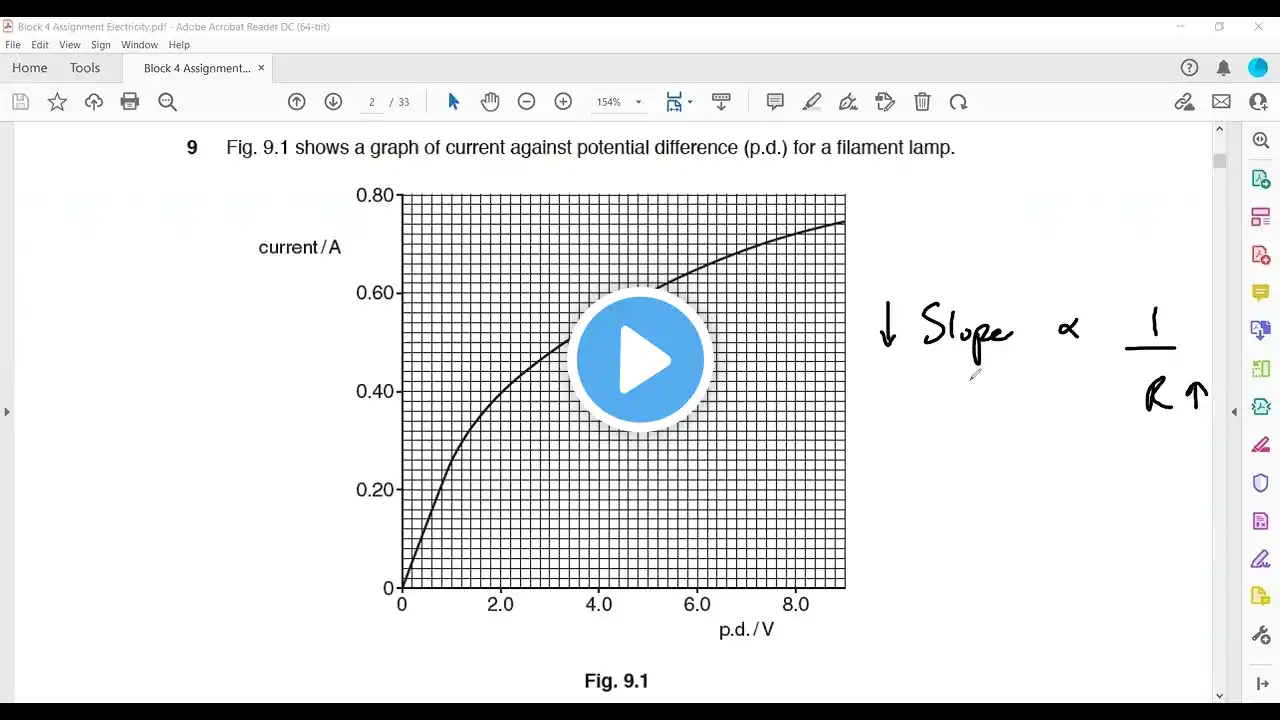
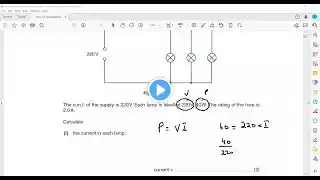
4.3 Electric circuits 4.3.1 Circuit diagrams Core •• Draw and interpret circuit diagrams containing sources, switches, resistors (fixed and variable), heaters, thermistors, light-dependent resistors, lamps, ammeters, voltmeters, galvanometers, magnetising coils, transformers, bells, fuses and relays Supplement •• Draw and interpret circuit diagrams containing diodes 4.3.2 Series and parallel circuits Core •• Understand that the current at every point in a series circuit is the same •• Give the combined resistance of two or more resistors in series •• State that, for a parallel circuit, the current from the source is larger than the current in each branch •• State that the combined resistance of two resistors in parallel is less than that of either resistor by itself •• State the advantages of connecting lamps in parallel in a lighting circuit Supplement •• Calculate the combined e.m.f. of several sources in series •• Recall and use the fact that the sum of the p.d.s across the components in a series circuit is equal to the total p.d. across the supply •• Recall and use the fact that the current from the source is the sum of the currents in the separate branches of a parallel circuit •• Calculate the effective resistance of two resistors in parallel 4.3.3 Action and use of circuit components Core •• Describe the action of a variable potential divider (potentiometer) •• Describe the action of thermistors and lightdependent resistors and show understanding of their use as input transducers •• Describe the action of a relay and show understanding of its use in switching circuits Supplement •• Describe the action of a diode and show understanding of its use as a rectifier •• Recognise and show understanding of circuits operating as light-sensitive switches and temperature-operated alarms (to include the use of a relay)