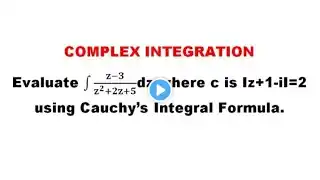
Evaluate ∫(2z-1)/(z(z-3)(z+1))dz using cauchy Residue theorem where C is the circle x^2+y^2=4
Laplace Transform: • M3 / Laplace Transform Laplace Inverse: • M3 / Laplace Inverse FOURIER SERIES: • M3 / FOURIER SERIES Complex Variables: • M3(Comp/IT) M4(Mech/Civil)Complex Variables Probability: • M3(Comp/IT) M4(Mech/ Civil)Probability Statistics:-: • M4(Mech/Civil)M3(Comp/ IT)Statistics:- Matrices(Eigenvalues &Eigen vectors): • M3(Mech/Civil) M4(Comp/IT)Matrices(Eigenva... Complex Integration: • M4(Comp/IT/AI/Mech/ Civil)Complex Integration Cauchy's Integral Theorem: • M4(Comp/IT/AI/Mech/ Civil)Cauchy's Integra... Residues: • M4(Comp/IT/AI/Mech/ Civil)Residues Taylor's and Lourent's Series: • M4(Comp/IT/AI/Mech/ Civil)Taylor's and Lou... Sample Tests(Small and Large ): • M4(Mech /Civil)/M4(Comp/IT)Sample Tests(Sm... Evaluate ∫(2z-1)/(z(z-3)(z+1))dz using cauchy Residue theorem where C is the circle x^2+y^2=4 Your Queries 🔎 residue theorem cauchy's residue theorem cauchy residue theorem cauchy residue theorem examples cauchys residue theorem cauchy residue theorem solved problems cauchy residue theorem problems residue theorem examples cauchy residue theorem proof application of cauchys residue theorem residue theorem complex analysis cauchy residue theorem complex analysis residue theorem proof cauchy's residue theorem proof cauchys residue theorem proof Residues in complex analysis How to calculate residue in complex analysis Using residue theorem evaluate Residue theorem engineering mathematics