Birt Hogg Dube Syndrome ; Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
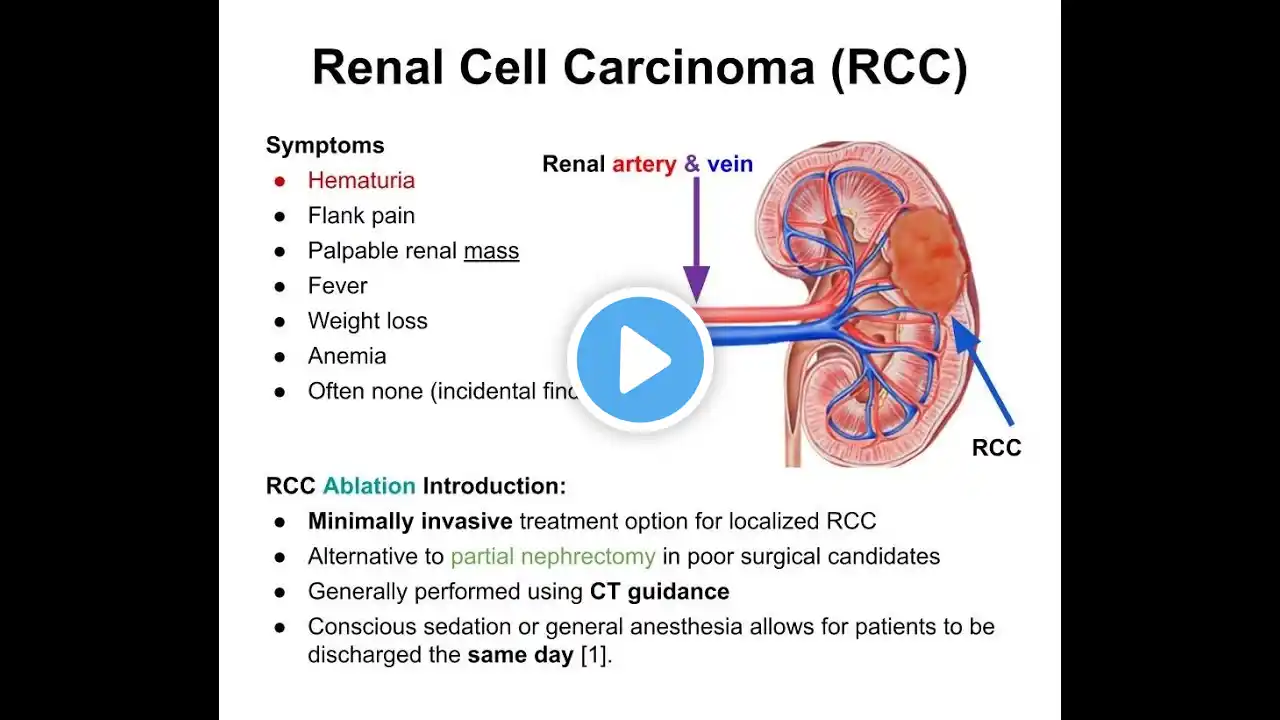
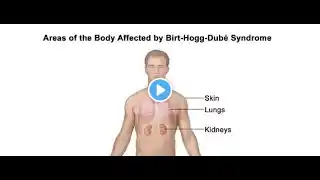
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome (BHD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the development of benign skin tumors, lung cysts, and an increased risk of kidney tumors. Here are some key points about BHD: Overview Genetic Cause: BHD is caused by mutations in the folliculin (FLCN) gene, which is thought to be a tumor suppressor gene. Inheritance: It follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning a person only needs to inherit one copy of the mutated gene from one parent to develop the disorder. Symptoms Skin Lesions: The most common manifestation is the development of fibrofolliculomas, which are benign tumors of the hair follicles, typically appearing on the face, neck, and upper chest. Lung Cysts: Many individuals with BHD develop lung cysts, which can lead to spontaneous pneumothorax (collapsed lung). Kidney Tumors: There is an increased risk of developing kidney tumors, including chromophobe renal cell carcinomas and oncocytomas. Diagnosis Genetic Testing: A definitive diagnosis is made through genetic testing to identify mutations in the FLCN gene. Imaging: Imaging studies such as CT scans and ultrasounds can help detect lung cysts and kidney tumors3. Management Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the kidneys and lungs using medical imaging is recommended. Surgical Removal: Fibrofolliculomas can be removed surgically if they cause cosmetic concerns or other issues. Treatment of Complications: Spontaneous pneumothorax and kidney tumors are treated according to standard medical practices. Prognosis General Outlook: The prognosis for individuals with BHD varies depending on the presence and severity of complications. Early detection and management can help improve outcomes. #BirtHoggDubeSyndrome