Stability of four wheel drive in curved path: example problem
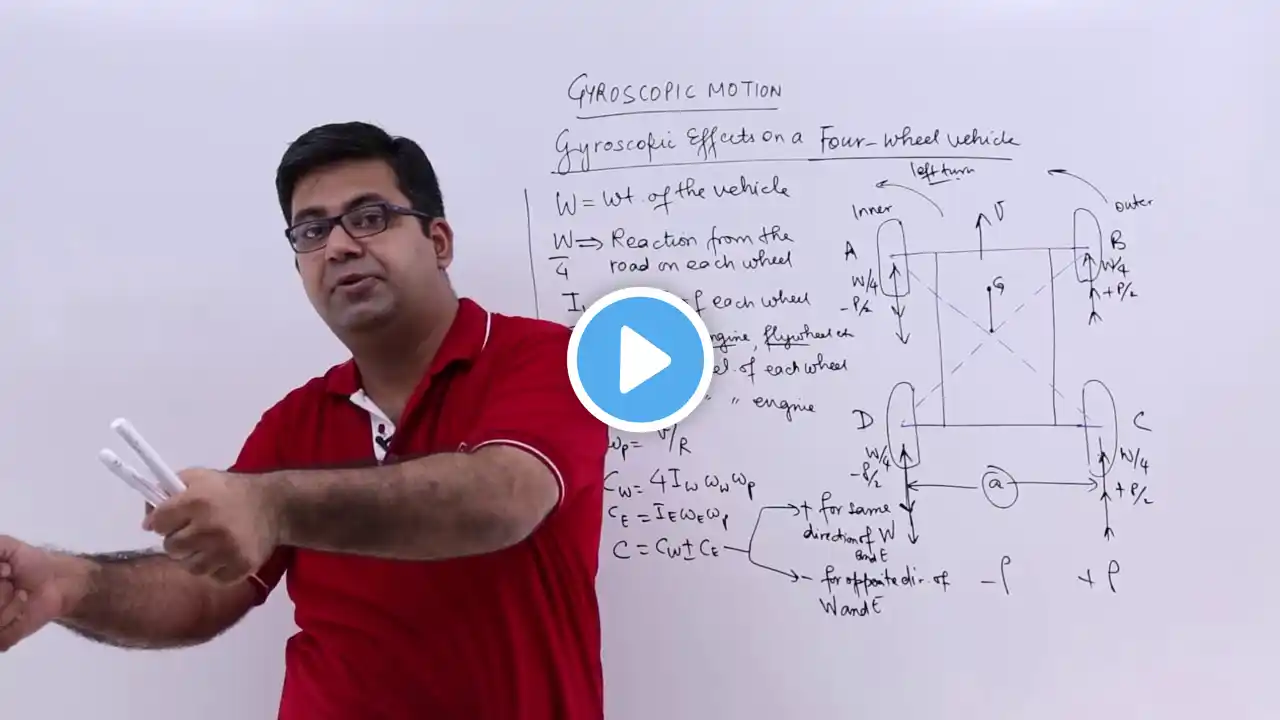
Following problem related to gyroscopic effect, and centrifugal effect on a four wheel drive taking a turn is explained. A four wheeled motor car of mass 2000 kg has a wheel base 2.5 m, track width 1.5 m and height of centre of gravity 500 mm above the ground level and lies at 1 metre from the front axle. Each wheel has an effective diameter of 0.8 m and a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg-m2. The drive shaft, engine flywheel and transmission are rotating at 4 times the speed of road wheel, in a clockwise direction when viewed from the front, and is equivalent to a mass of 75 kg having a radius of gyration of 100 mm. If the car is taking a right turn of 60 m radius at 60 km/h, find the load on each wheel.