Mechanism of Sorting and Regulation in Intracellular Transport | CSIR Life Sciences
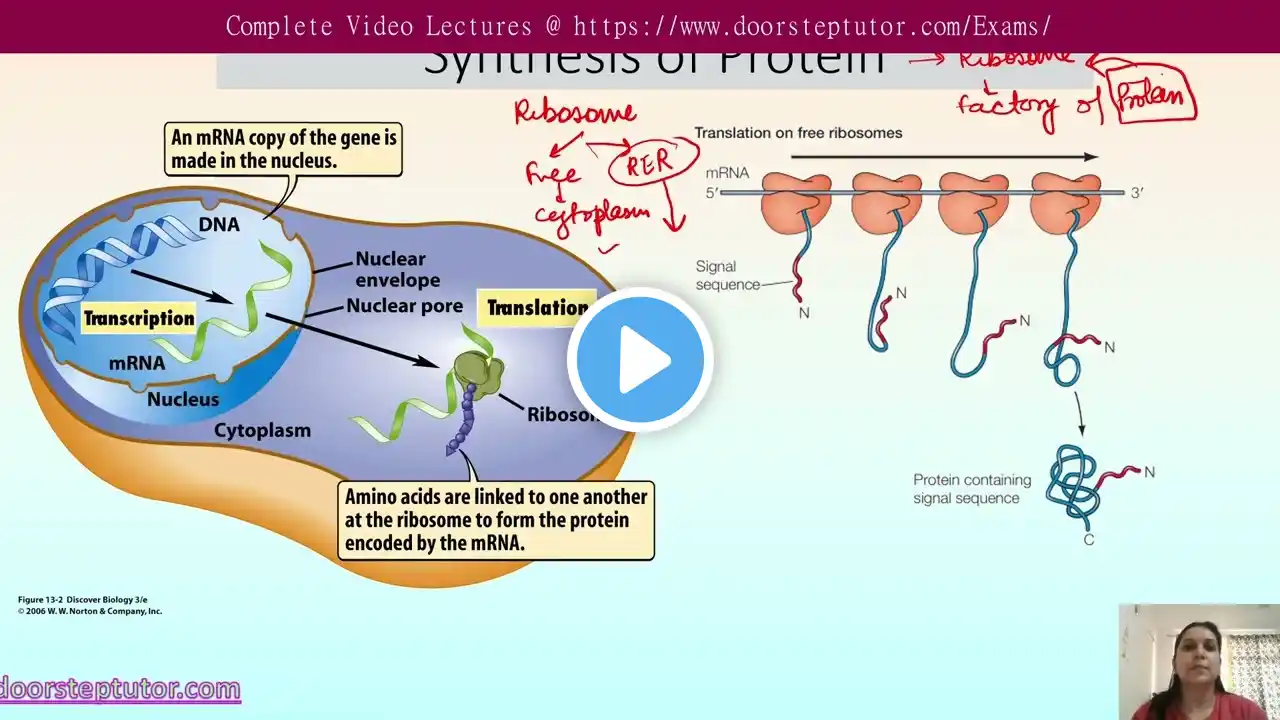
CSIR NET Preparation: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/C... IAS Mains: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/I... GATE: https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/G... NTA NET Paper 1 Lectures - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/U... NTA NET Paper 1 Mock papers - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/U... NTA NET Paper 1 Practice questions - https://www.doorsteptutor.com/Exams/U... NTA NET Paper 1 Postal Course - https://www.examrace.com/NTA-UGC-NET/... NCERT, Yojana, Kurukshetra, Down to Earth, Science, Social Studies and More interesting topics subscribe at Examrace: / examrace NCERT, Yojana, Kurukshetra, Down to Earth, Science, Social Studies and More interesting topics subscribe at ExamraceHindi: / examracehindi For classes nursery to class 5 videos subscribe to FunProf: / funprof For Science Class 11-12 and important topics subscribe to DoorStepTutor: / doorsteptutor The topology of a protein in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) refers to how the protein is oriented or positioned within the ER membrane. Proteins in the ER membrane can have different topologies depending on their function, structure, and the number of transmembrane segments they contain. Here are some common topologies of proteins in the ER: Type I Single-Pass Transmembrane Protein: These proteins have a single transmembrane domain (TM) that anchors them in the lipid bilayer. The N-terminus is located in the cytoplasm, and the C-terminus is in the ER lumen. Signal sequence (N-terminus) Cleaved Sequence Present Stop Signal Present Translocon stopped Diffuse Laterally and Anchored in Lipid bilayer Translation continues Eg : LDL Receptor,Insulin Receptor Type II Single-Pass Transmembrane Protein: Similar to Type I, these proteins have a single TM domain. (N) terminus is exposed on the cytosolic side. C-terminus on the non-cytosolic side. Single non-cleavable internal sequence. The transmembrane sequence exits the translocon to anchor the protein in the lipid bilayer and the remainder of the polypeptide chain is translocated into the ER as translation proceeds. Eg: Transferrin receptor, Golgi galactosyl transferase However, the N-terminus is located in the ER lumen, and the C-terminus is in the cytoplasm. TYPE III Single Pass Transmembrane Similar to Type I No cleavable signal sequence Like Type II single cleavable internal signal sequence Eg: Cyt P〰450 Multi-Pass Transmembrane Protein: These proteins have multiple TM domains that traverse the lipid bilayer several times. Spans the membrane multiple times Its amino (N) terminus and C-terminus either on same side or different orientation Even number Alpha helices- both N and C-terminus same side Eg: CFTR, GLUT 1 Translation proceeds until a second transmembrane sequence is encountered. This causes the polypeptide chain to form a loop within the lumen of the ER; translation continues in the cytosol.