Excel Shorts #10 Rank formula with absolute value #excel #exceltips
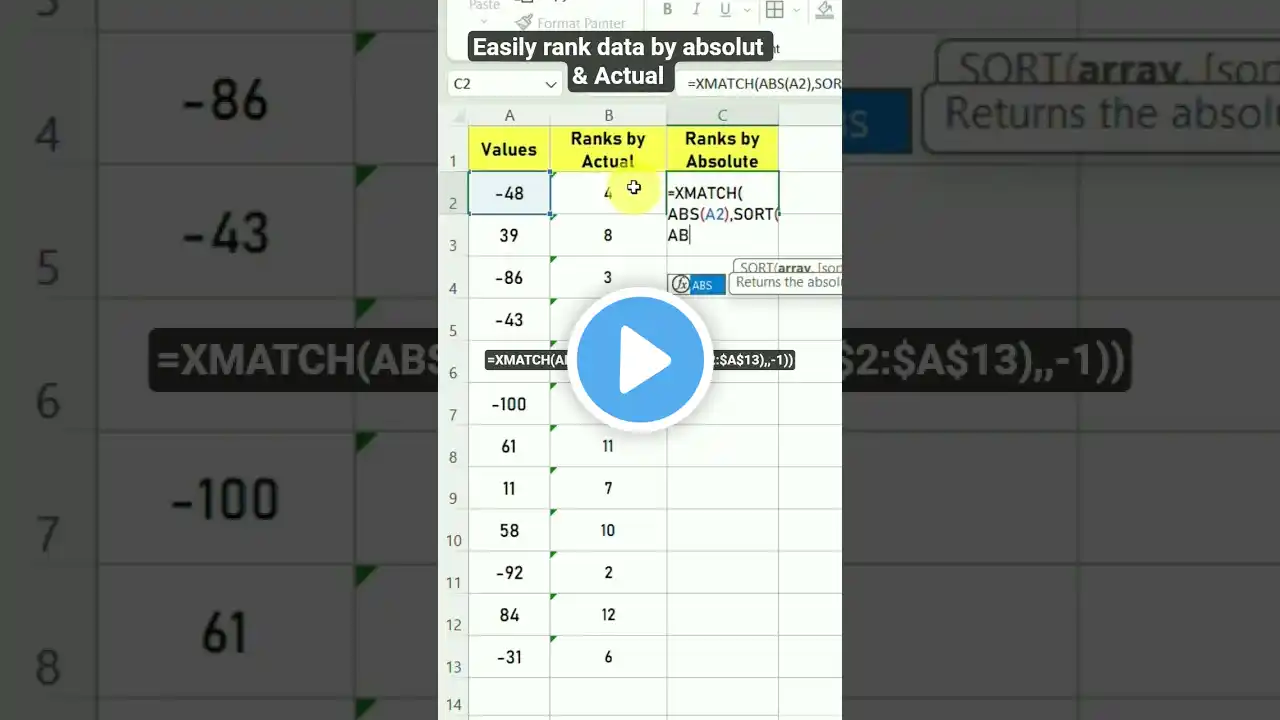
Ranking data by absolute value in Excel is a valuable technique, especially in statistical analysis, financial modeling, and comparative data reporting. It helps highlight the most significant changes or values, regardless of whether they are positive or negative. While Excel offers built-in functions like RANK, RANK.EQ, and RANK.AVG, these functions evaluate actual values — which means negative numbers are treated as smaller, even if their magnitude is larger. This makes it difficult to rank based on impact or deviation. For example, in financial variance reports or risk assessments, a value of –100 may be more significant than +50, but Excel’s standard ranking functions will rank +50 higher. To address this, we need to rank data based on their absolute values — essentially ignoring the sign and focusing purely on the size of the number. This guide walks you through several efficient techniques to rank data by absolute value using: Helper columns Array formulas ABS() function SORT and RANK together Dynamic solutions with LET and LAMBDA (Excel 365) Each method is explained step-by-step, with examples to help you apply it to real-world scenarios. Whether you’re building dashboards, analyzing performance, or preparing business reports, these solutions will save time and improve accuracy. Let’s explore how to implement absolute value ranking in Excel — from basic formulas to advanced, dynamic approaches.