Thermal Decomposition of Metal Nitrate Carbonate and Hydroxides Chemistry Lesson 56 part c
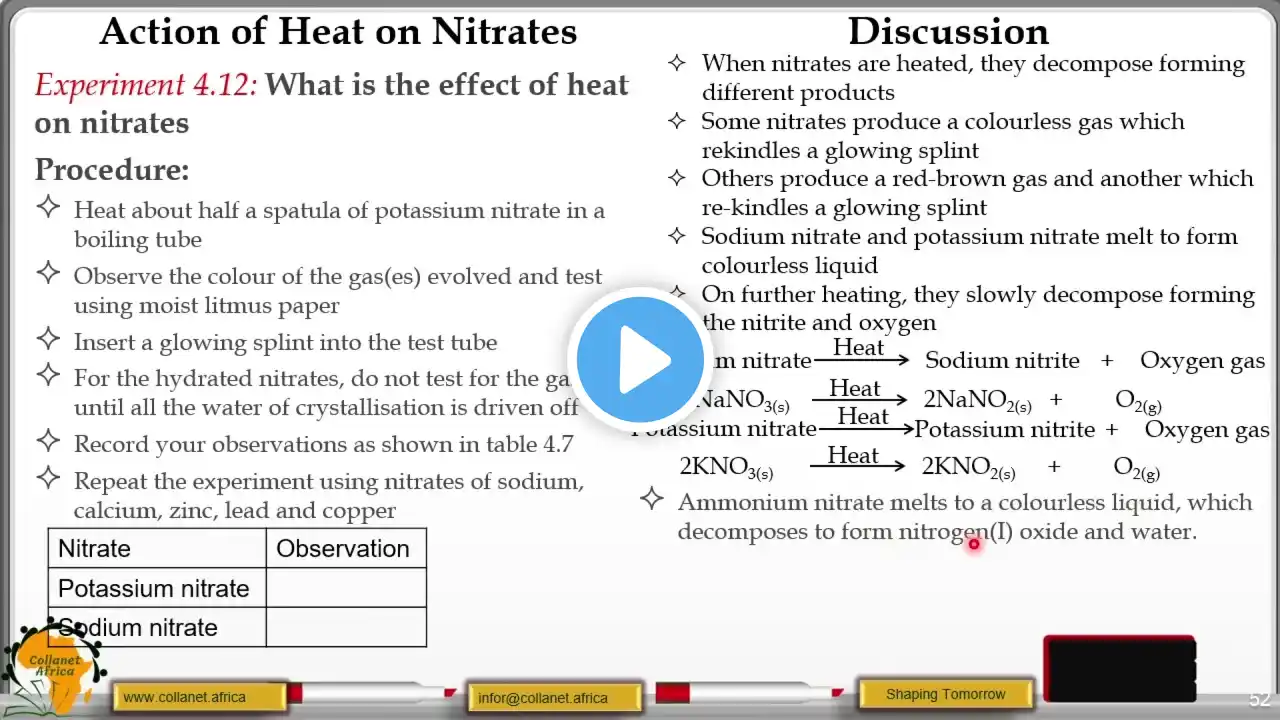
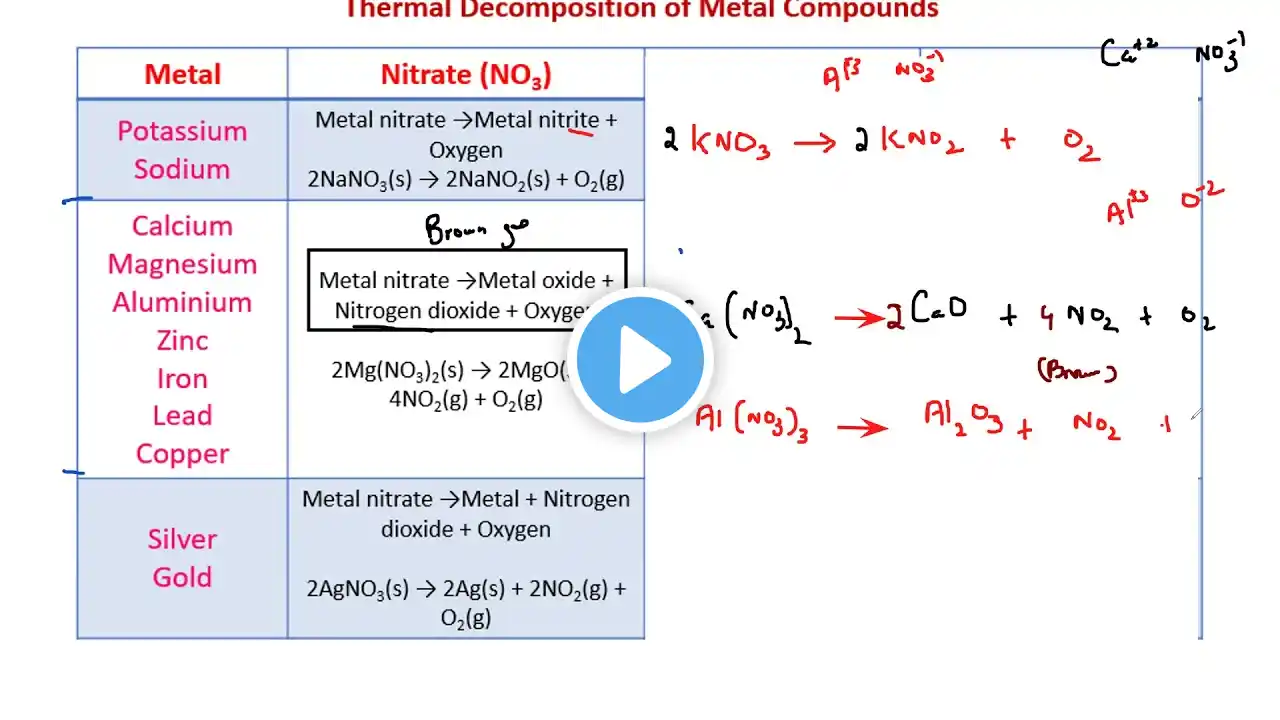
10 Metals 10.1 Properties of metals Core •• List the general physical properties of metals •• Describe the general chemical properties of metals, e.g. reaction with dilute acids and reaction with oxygen •• Explain in terms of their properties why alloys are used instead of pure metals •• Identify representations of alloys from diagrams of structure 10.2 Reactivity series Core •• Place in order of reactivity: potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron, (hydrogen) and copper, by reference to the reactions, if any, of the metals with: –– water or steam –– dilute hydrochloric acid and the reduction of their oxides with carbon •• Deduce an order of reactivity from a given set of experimental results Supplement •• Describe the reactivity series as related to the tendency of a metal to form its positive ion, illustrated by its reaction, if any, with: –– the aqueous ions –– the oxides of the other listed metals •• Describe and explain the action of heat on the hydroxides, carbonates and nitrates of the listed metals •• Account for the apparent unreactivity of aluminium in terms of the oxide layer which adheres to the metal 10.3 Extraction of metals Core •• Describe the ease in obtaining metals from their ores by relating the elements to the reactivity series •• Describe and state the essential reactions in the extraction of iron from hematite •• Describe the conversion of iron into steel using basic oxides and oxygen •• Know that aluminium is extracted from the ore bauxite by electrolysis •• Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of recycling metals, limited to iron/steel and aluminium Supplement •• Describe in outline, the extraction of zinc from zinc blende •• Describe in outline, the extraction of aluminium from bauxite including the role of cryolite and the reactions at the electrodes 10.4 Uses of metals Core •• Name the uses of aluminium: –– in the manufacture of aircraft because of its strength and low density –– in food containers because of its resistance to corrosion •• Name the uses of copper related to its properties (electrical wiring and in cooking utensils) •• Name the uses of mild steel (car bodies and machinery) and stainless steel (chemical plant and cutlery) Supplement •• Explain the uses of zinc for galvanising and for making brass •• Describe the idea of changing the properties of iron by the controlled use of additives to form steel alloys