The Ideal Gas Law Explained | Boyle’s, Charles’, Gay-Lussac’s & Avogadro’s Laws Made Simple
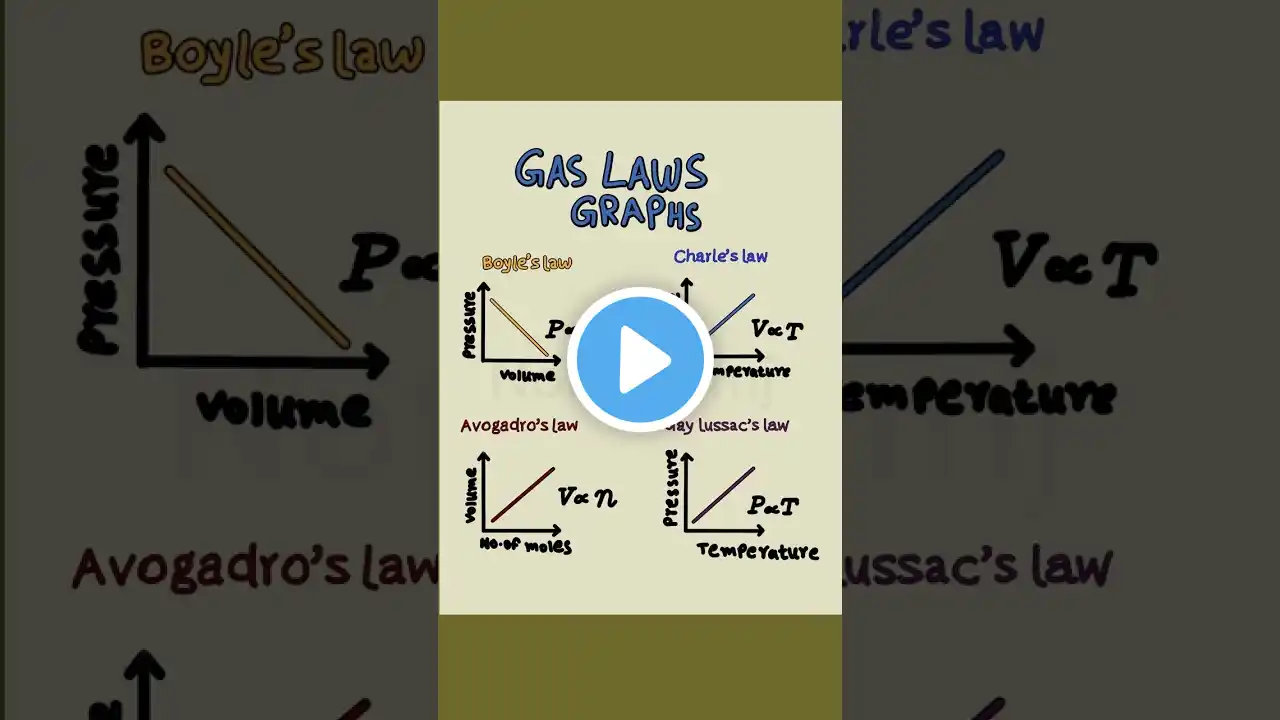
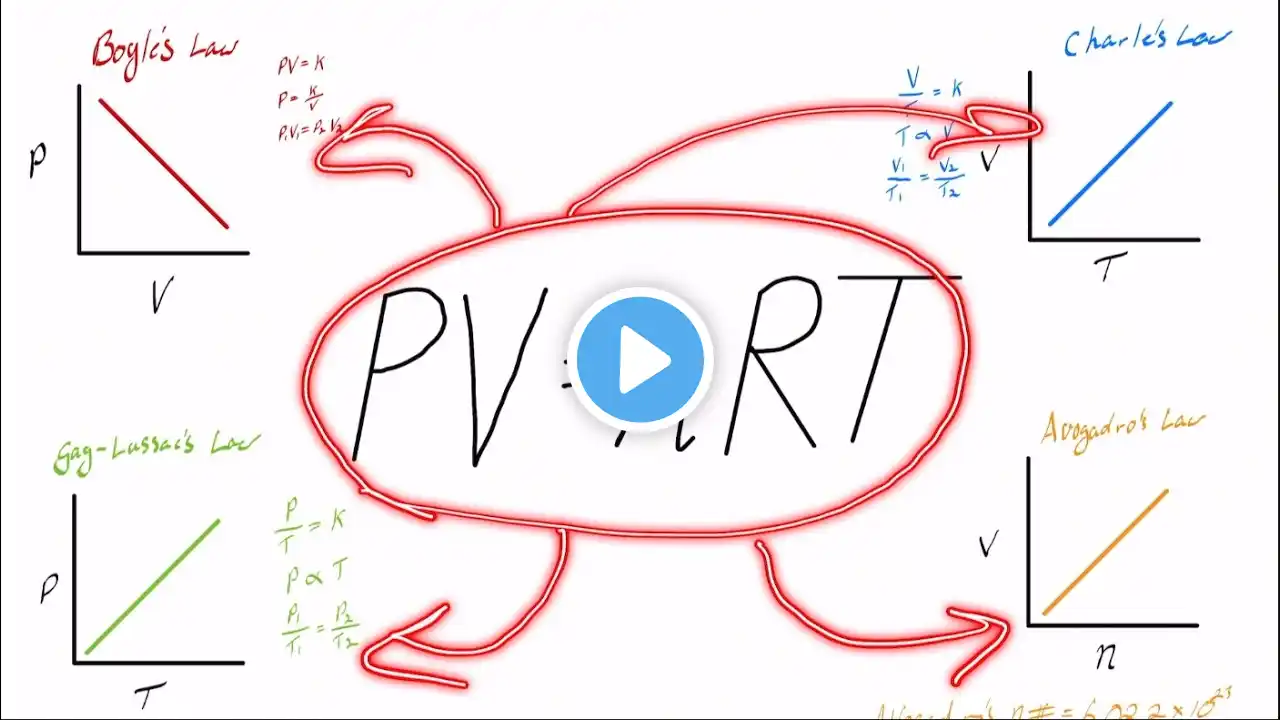
Hey Everyone! In this video, we break down the Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT) — one of the most fundamental equations in physics, chemistry, and medical physiology. You’ll learn how it describes the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount of gas, and how we can derive four essential gas laws from it: Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law, Gay-Lussac’s Law, and Avogadro’s Law. 📘 What You’ll Learn: 🔹 1. The Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT) What each variable represents: Pressure (P), Volume (V), Moles (n), Gas Constant (R), Temperature (T). How constants influence the relationships between gas variables. 🔹 2. Boyle’s Law (P₁V₁ = P₂V₂) Describes the inverse relationship between pressure and volume when temperature is constant. Clinical example: How lung volume changes with intrathoracic pressure during breathing. Real-world example: Calculating how much oxygen remains in a gas cylinder based on pressure. 🔹 3. Charles’ Law (V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂) Shows a direct relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure. Applications: Gas expansion in cylinders and the function of mercury thermometers. 🔹 4. Gay-Lussac’s Law (P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂) Explains how pressure increases with temperature in a fixed-volume container. Clinical relevance: Safety of gas storage and explosion risk at high temperatures. 🔹 5. Avogadro’s Law (V ∝ n) Connects the number of gas moles to volume at constant temperature and pressure. Defines a mole and introduces Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10²³). Demonstrates that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules. 🧩 Key Takeaways: PV = nRT unifies all the gas laws under one framework. Each derived law isolates two variables while holding others constant. These concepts are essential in respiratory physiology, anesthesia, and gas storage safety. 🎯 Relevant For: Medical and physiology students Chemistry and physics learners Anesthesia and respiratory physiology revision Students preparing for the Primary Exam or similar assessments Contents: 0:20 Ideal Gas Law 1:02 Boyle's Law 2:53 How to use Boyle's Law to calculate amount of gas in a pressurised container 5:09 Charle's Law 8:05 Gay-Lussac's Law 9:41 Avogadro's Law #physiology #gaslaws #anesthesiaexam