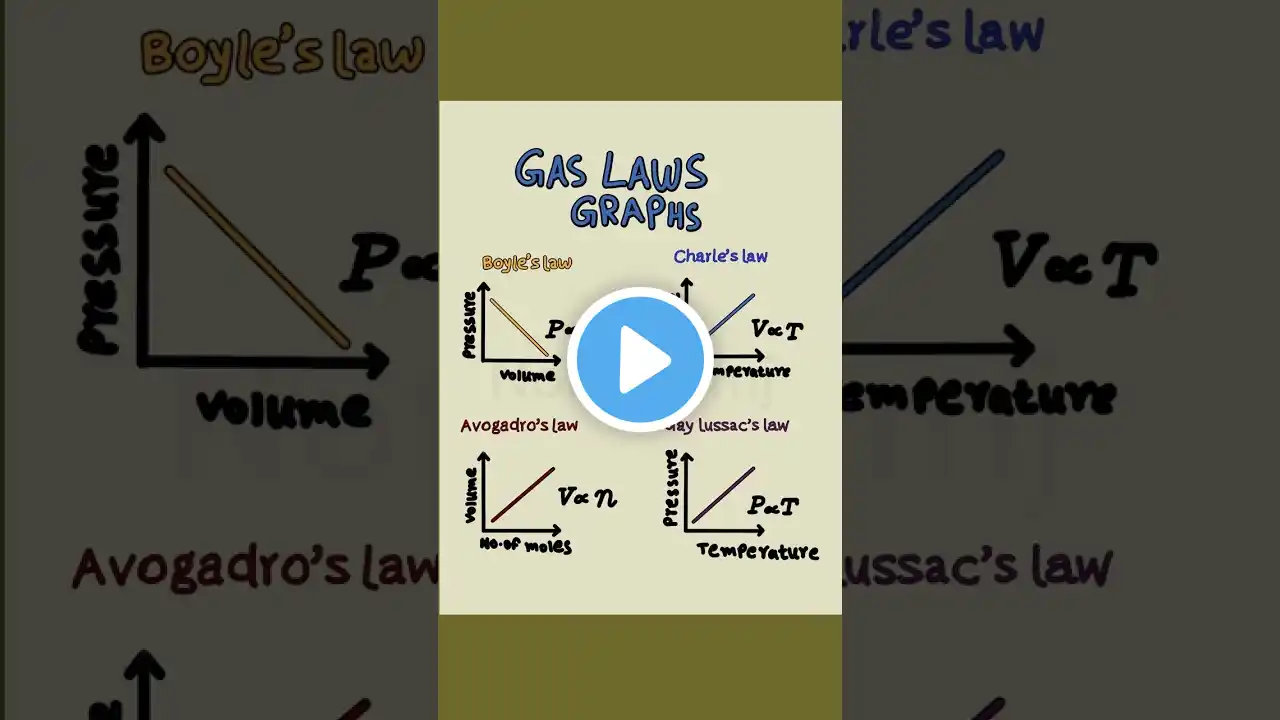
Gas Laws Explained: Boyle, Charles, Gay‑Lussac and the Combined Law
Explore the fundamental gas laws that govern how pressure, volume, and temperature interact in everyday phenomena. This video breaks down the core concepts and shows how they apply to real‑world examples such as hot‑air balloons, soda cans, syringes, and scuba tanks. *What you’ll learn* The basic properties of gases and how particle collisions create pressure. Boyle’s Law (pressure ↔ volume at constant temperature) with a syringe demonstration. Charles’s Law (volume ↔ temperature at constant pressure) illustrated by a balloon in changing temperatures. Gay‑Lussac’s Law (pressure ↔ temperature at constant volume) using an aerosol can and a sealed jar. The Combined Gas Law, which links all three variables for more complex scenarios, demonstrated with a scuba diving tank and a weather balloon calculation. *Why it matters* Understanding these relationships helps explain everyday observations—from why tires feel flat on a cold morning to how weather balloons expand at altitude. The video also provides quick knowledge checks to reinforce each law. Watch to see clear analogies, step‑by‑step problem solving, and practical tips for applying gas laws in both classroom problems and real life.