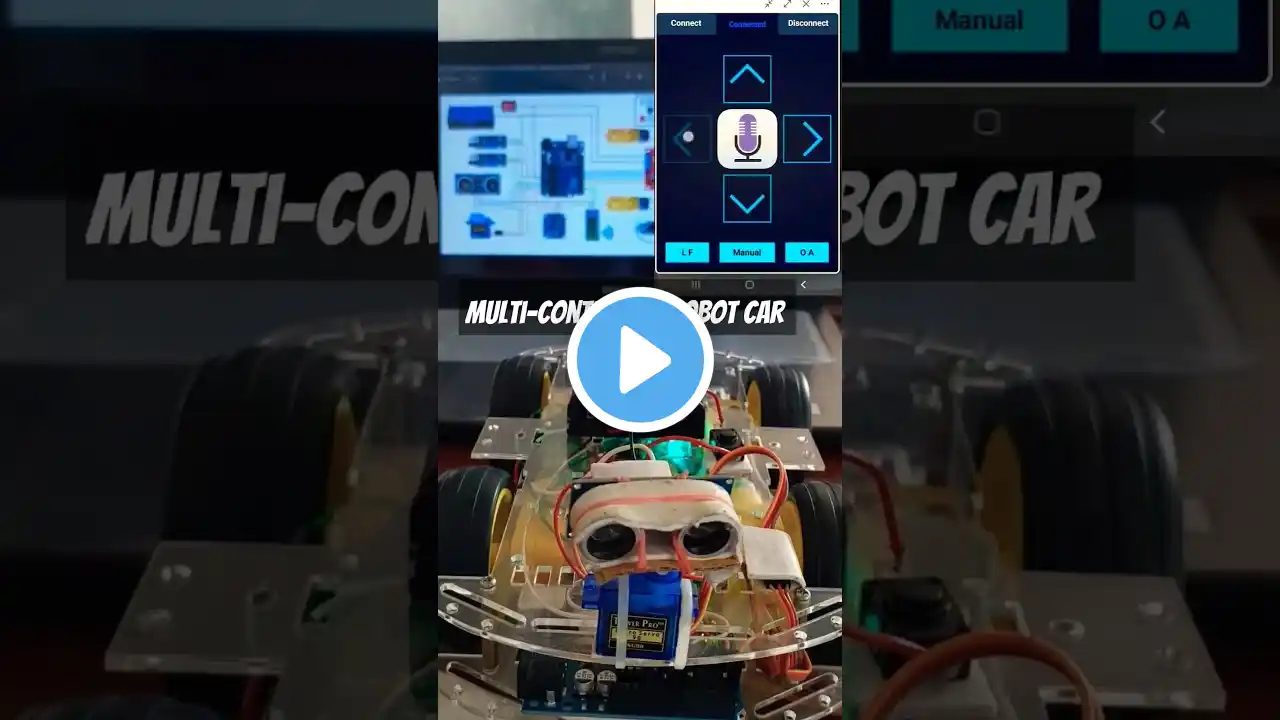
Remote🦾Control robot car🚕and Obstacle Avoiding Robot car #arduinoprojects #shorts
How to make Remote control car and Obstacle Avoiding Robot car? Arduino project Creating a remote control robot car with Arduino Uno that can perform obstacle avoidance, line following, and voice control, along with control via a mobile app, is an exciting project. It involves various sensors, motor drivers, and communication modules. Here's a high-level overview of how you can create such a versatile robot: Materials You'll Need: Arduino Uno (or compatible board) Motor driver module (e.g., L298N or L293D) Wheels, motors, and chassis for the robot Ultrasonic distance sensor (HC-SR04) for obstacle avoidance IR sensors for line following (e.g., IR modules or reflectance sensors) Microphone module for voice control (e.g., MAX4466) Bluetooth module (e.g., HC-05 or HC-06) for mobile app control Battery or power supply for the robot Jumper wires, resistors, and connectors Mobile device with Bluetooth capabilities Motor driver, IR sensor, and microphone shields (if needed) Step-by-Step Instructions: Build the Robot Chassis: Assemble the robot chassis, mount the wheels, motors, and motor driver module. Ensure proper connections between the motors and the motor driver. Line Following Sensors: Attach IR sensors underneath the robot to detect the line on the ground. Wire them to your Arduino Uno. Obstacle Avoidance Sensor: Mount the ultrasonic distance sensor on the front of the robot to detect obstacles. Connect it to the Arduino. Voice Control Module: Connect the microphone module to the Arduino for voice input. You may need additional components (like an amplifier) for better voice recognition. Bluetooth Module: Connect the Bluetooth module to the Arduino for mobile app control. This will allow you to send commands to the robot via a smartphone app. Write Arduino Code: Develop the Arduino code to integrate all functionalities. You'll need libraries for motor control, IR sensor readings, ultrasonic sensor readings, voice recognition (e.g., EasyVR or other voice recognition libraries), and Bluetooth communication. Test Individual Functions: Before combining everything, test each function individually: Ensure the line following sensors can detect and follow lines. Verify the obstacle avoidance system can detect and react to obstacles. Test the voice control module for accurate recognition. Make sure the Bluetooth module can receive and interpret commands from the mobile app Combine Functions: Merge the code for all functions, allowing the robot to switch between line following, obstacle avoidance, and voice control modes. Mobile App: Create a mobile app using a platform like MIT App Inventor or a programming language suitable for app development. Implement a user-friendly interface for controlling the robot. Bluetooth Pairing: Pair the mobile app with the Bluetooth module on the robot. Testing: Test your robot in different scenarios. Ensure that it follows lines, avoids obstacles, and responds to voice commands as expected. Adjust code and sensor placements as needed for better performance. Fine-Tuning and Optimization: Continuously fine-tune your robot's behavior and voice recognition accuracy. Optimize the code for efficiency. Safety and Precautions: When testing, ensure your robot operates safely and doesn't damage itself or the surroundings. This project combines various complex components and requires significant coding and testing. Be prepared to iterate on the design and code to achieve the desired functionality. Additionally, consider power management to ensure your robot has a suitable runtime. Robo star pr @robostarpro.2680 #science #engineering #robotics #robot #engineeringprojects #iit #arduinoprojects #iot #ultrasonicsensor #scienceproject #students #youtubeshorts #shortvideo #reels #viralshorts #trendingshorts #technology #innovation thank you _