Components of #Building with Standard #Dimensions | #Shorts #Construction #CivilEngineering
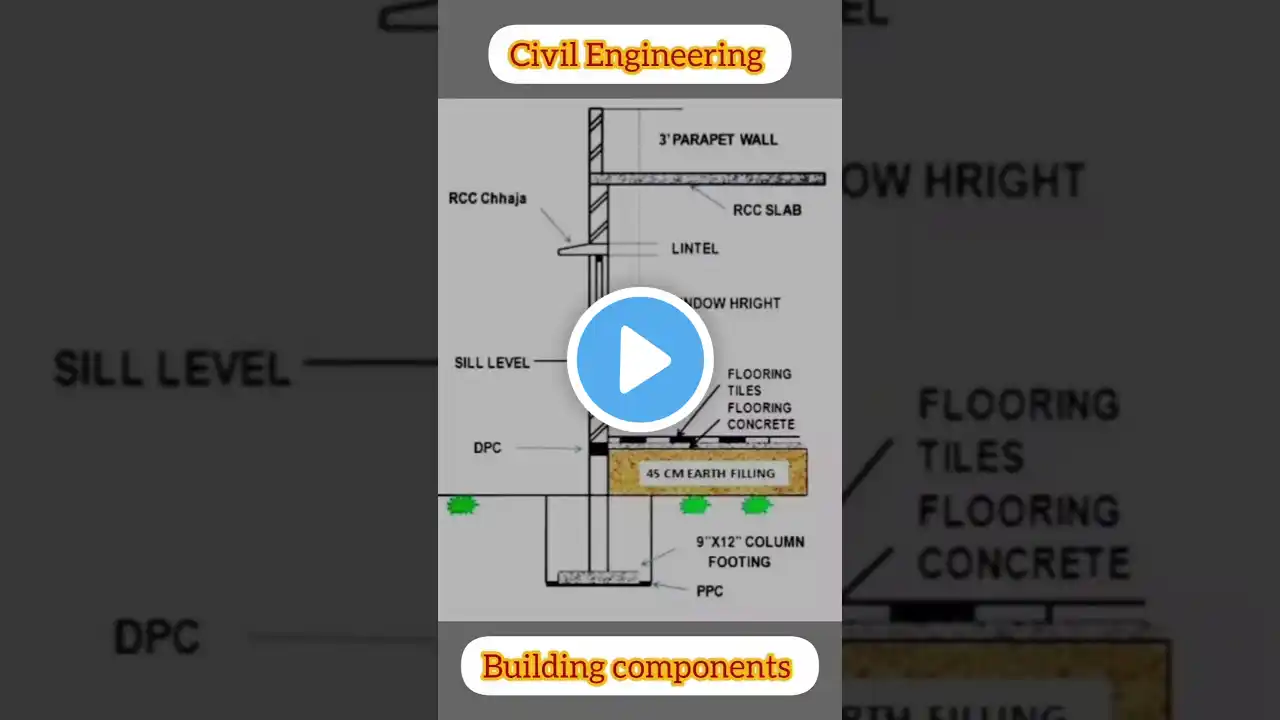
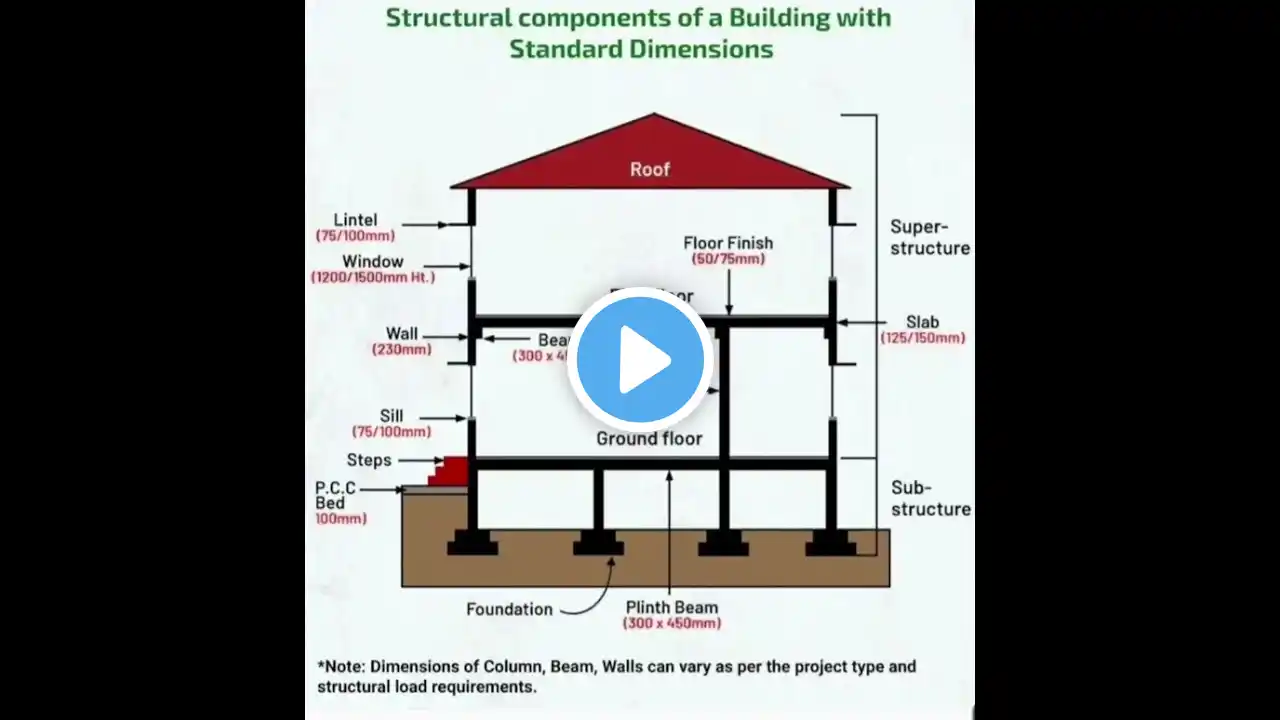
🏛️ 𝗖𝗢𝗠𝗣𝗢𝗡𝗘𝗡𝗧𝗦 𝗢𝗙 𝗕𝗨𝗜𝗟𝗗𝗜𝗡𝗚 𝗪𝗜𝗧𝗛 𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗡𝗗𝗔𝗥𝗗 𝗗𝗜𝗠𝗘𝗡𝗦𝗜𝗢𝗡𝗦 🏛️ Welcome to this comprehensive guide on "Components of a Building with Standard Dimensions!" 🌟 In construction, each building component plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity, safety, and functionality of a structure. Knowing these components and their standard dimensions is crucial for architects, engineers, and builders. 📽️ ═════════•°•🏛 °•═════════ 🔶 𝗙𝗼𝘂𝗻𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 🔶 The foundation is the base of any building, providing stability and support. It transfers the building's load to the ground safely. Standard dimensions vary depending on the type of foundation and the load-bearing requirements. 📌 Standard Depth: Minimum depth of 1.5m below ground level for residential buildings. 📌 Width of Footing: Generally 2-3 times the width of the wall it supports. 📌 Types of Foundations: Isolated Footing, Raft Foundation, Pile Foundation, and Strip Foundation. 🔷 𝗖𝗼𝗹𝘂𝗺𝗻𝘀 🔷 Columns are vertical structural members that bear loads from the roof, slabs, and beams and transfer them to the foundation. 📌 Minimum Size: Commonly 230mm x 230mm for small structures. 📌 Spacing: Typically 3m to 4.5m apart in regular structures. 📌 Reinforcement: Depends on load requirements, commonly using 4 to 6 rebars of 12mm diameter for standard columns. ═════════•°•📏 °•═════════ 🔶 𝗕𝗲𝗮𝗺𝘀 🔶 Beams are horizontal structural elements that support loads from slabs and transfer them to columns. 📌 Standard Dimensions: Commonly 230mm x 300mm or 230mm x 450mm for residential buildings. 📌 Clear Span: Typically between 3m to 5m. 📌 Reinforcement: Main reinforcement bars are usually 12mm to 16mm in diameter. 🔷 𝗦𝗹𝗮𝗯𝘀 🔷 Slabs are flat, horizontal components forming the floors and ceilings of a building. They play a key role in distributing loads to the beams and columns. 📌 Thickness: Generally ranges from 100mm to 150mm for residential floors. 📌 Span-to-Depth Ratio: A standard ratio of 30 to 40 for reinforced concrete slabs. 📌 Reinforcement: Main bars 8mm to 12mm in diameter, spaced at 150mm to 200mm. ═════════•°•🏗 °•═════════ 🔶 𝗪𝗮𝗹𝗹𝘀 🔶 Walls enclose and divide spaces within a building. They are either load-bearing or non-load-bearing. 📌 Thickness for Load-Bearing Walls: Commonly 230mm for brick walls. 📌 Thickness for Partition Walls: Typically 100mm to 150mm. 📌 Height: Standard height is around 3m for residential structures. 🔷 𝗥𝗼𝗼𝗳𝘀 🔷 The roof protects the building from weather elements and provides an aesthetic appeal. Roof design and dimensions vary based on style and climate. 📌 Slope: Depends on the type, with standard slopes ranging from 15° to 30° for pitched roofs. 📌 Thickness: Varies from 100mm for flat concrete roofs to 50mm for tiled roofs. ═════════•°•📐 °•═════════ 🔶 𝗗𝗼𝗼𝗿𝘀 & 𝗪𝗶𝗻𝗱𝗼𝘄𝘀 🔶 Doors and windows are essential for accessibility, light, and ventilation within a building. 📌 Standard Door Dimensions: Commonly 900mm x 2100mm for main doors. 📌 Standard Window Dimensions: Usually 1200mm x 1200mm for residential buildings. 📌 Sill Level: Typically 600mm to 900mm from the floor level for windows. 🔷 𝗦𝘁𝗮𝗶𝗿𝘀 🔷 Stairs connect different floors in a building and must adhere to specific dimensions to ensure safety and comfort. 📌 Tread Size: Standard treads are 250mm to 300mm in depth. 📌 Riser Height: Usually between 150mm to 180mm. 📌 Width: For residential stairs, a standard width is 900mm to 1000mm. ═════════•°•🌟 °•═════════ 🔶 𝗢𝘁𝗵𝗲𝗿 𝗕𝘂𝗶𝗹𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗼𝗻𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 🔶 Besides the primary structural elements, various other components contribute to a building's safety, comfort, and efficiency. 📌 Lintels: Provided above doors and windows for load distribution, typically 100mm to 150mm thick. 📌 Chajjas: External projections for sunshade and rain protection, with a standard width of 600mm. 📌 Parapet Walls: Guard walls on the roof, generally 100mm to 150mm thick and 900mm high. 🔷 𝗜𝗺𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗦𝘁𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗮𝗿𝗱 𝗗𝗶𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 🔷 Standard dimensions ensure uniformity, safety, and ease of construction. They also help maintain structural integrity and prevent issues related to load distribution, stability, and aesthetics. ═════════•°•🛠 °•═════════ 📢 𝗤𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 & 𝗙𝗲𝗲𝗱𝗯𝗮𝗰𝗸 💬 Got any questions about the components of a building or their standard dimensions? Let us know in the comments! 💬👇 If you enjoyed the video, give it a thumbs up and share it with others who might find it helpful. Don’t forget to subscribe for more civil engineering insights! 🚀🔔 ═════════•°•🏛 °•═════════ 📌 #BuildingComponents #StandardDimensions #CivilEngineering #ConstructionBasics #MirzaJahanzaibZameer