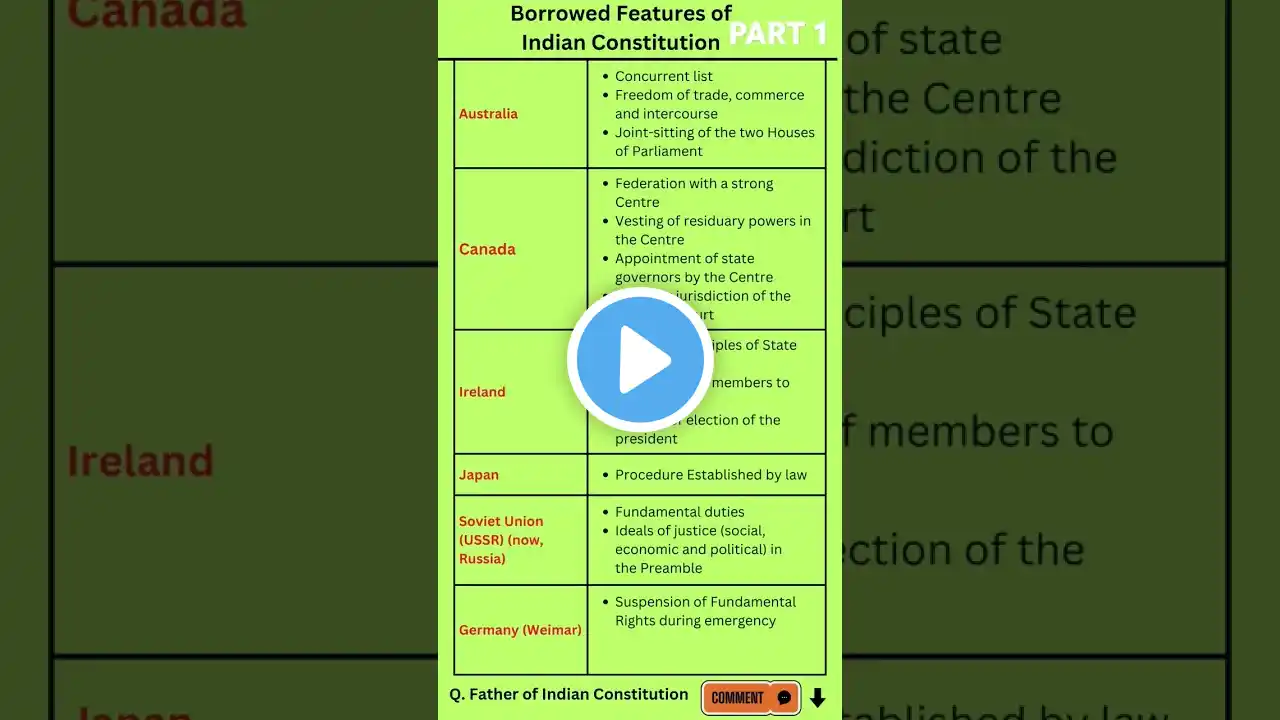
Salient Features of the Constitution Malayalam | laxmikant polity malayalam | kerala PSC , UPSC
In this video, we explore the salient features of the Indian Constitution, one of the most significant documents in shaping the governance of India. The Constitution lays down the framework for a democratic, socialist, secular republic, ensuring justice, equality, and liberty for all citizens. Understanding these features is crucial for aspirants of UPSC, KAS, and PSC exams as they form the foundation for a deeper understanding of India's political system. Key Features Covered: Preamble – India as a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, and Democratic Republic. Lengthiest Written Constitution – The longest constitution in the world. Federal System with Unitary Bias – Division of powers between the central and state governments. Parliamentary System – A system of government where the executive is accountable to the legislature. Fundamental Rights – Guarantees individual freedoms and rights. Directive Principles of State Policy – Guiding principles for governance. Fundamental Duties – Duties of citizens for national harmony. Secular State – Equal treatment of all religions by the state. Independent Judiciary – Ensures protection of rights and upholding the rule of law. Single Citizenship – A unified system of citizenship for all Indian citizens. Universal Adult Franchise – Right to vote for all citizens aged 18 and above. Emergency Provisions – Allows the central government to exercise extraordinary powers in crises. Amendability – Procedure to amend the Constitution to adapt to changing times. Bicameral Legislature – The central legislature consisting of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. Special Provisions – Provisions for specific states and regions to cater to their unique needs. Why It’s Important: The Indian Constitution is the cornerstone of India's political structure. Understanding its features is vital for civil services exams like UPSC, KAS, and PSC, as it helps in building a comprehensive knowledge of India's governance system. #IndianConstitution #SalientFeatures #UPSC #KAS #PSC #IndianPolitics #ParliamentarySystem #FundamentalRights #Democracy #SocialJustice #ConstitutionalLaw