Types Of Bones Based on Shapes || Long, Short, Flat, Irregular, Sesamoid || Radiology Tech || Hindi
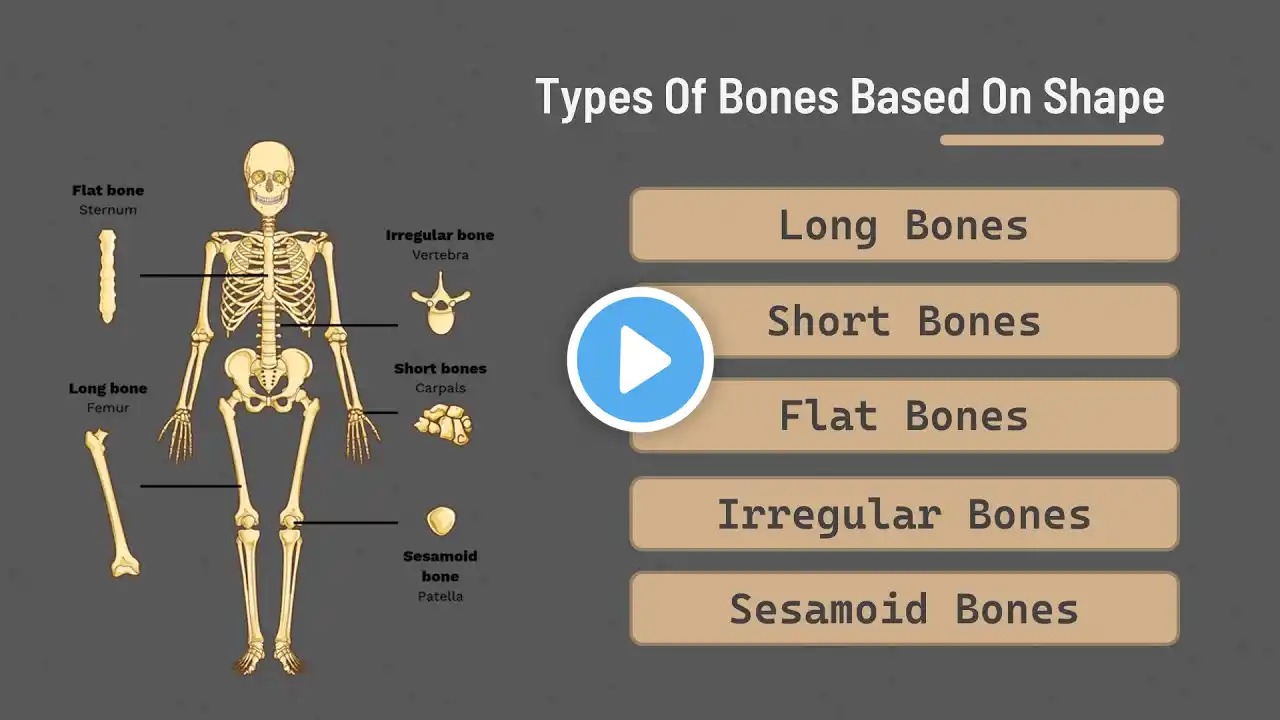
Let’s explore the fascinating world of human bones based on their shapes. Our skeletal system is a marvel of engineering, and understanding the different types of bones helps us appreciate its complexity. In this video, we’ll delve into the various bone shapes and their functions: Long Bones: These bones are longer than they are wide. Examples include the femur (thigh bone), humerus (upper arm bone), and tibia (shin bone). Long bones provide support, leverage for movement, and house bone marrow for blood cell production. Short Bones: Short bones are approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. Found in the wrists (carpals) and ankles (tarsals). Short bones contribute to stability and allow fine movements. Flat Bones: Flat bones are thin and often curved. Examples include the ribs, sternum, scapula (shoulder blade), and parts of the skull (such as the frontal bone). Flat bones protect internal organs and provide attachment sites for muscles. Irregular Bones: Irregular bones have no characteristic shape. They vary in structure and function. Examples include the vertebrae, facial bones, and hip bones (os coxae). Sesamoid Bones: Sesamoid bones are small, round bones embedded within tendons. The patella (kneecap) is a well-known sesamoid bone. Sesamoid bones protect tendons and improve joint mechanics.