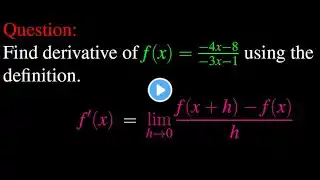
How to compute derivatives using the limit definition
The problem we have to solve here is about computing derivative using the limit definition. This type of questions usually appears in the first midterm exam in calculus 1. We need to find the derivative of the rational function { , minus 4 x , minus 8 } over { , minus 3 x , minus 1 }. Recall that the derivative is defined as the limit of a difference quotient. Then, We define the derivative of f of x as the limit of f of x plus h, minus f of x over h as h goes to zero. Consequently, f prime of x is the limit as h goes to zero of the fraction { , minus 4 x , minus 4 h , minus 8 } over { , minus 3 x , minus 3 h , minus 1 } minus the fraction { , minus 4 x , minus 8 } over { , minus 3 x , minus 1 } over h. This expression is obtained by replacing f of x+h, and f of x by their respective values. It is clear that we need to simplify this expression using basic algebraic techniques. In order to simplify this expression we first need to reduce the difference of fractions to the same denominator. To do so, we multiply the numerator of the first fraction, the quantity , minus 4 x , minus 4 h , minus 8 , with the denominator of the second fraction, the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 1 ; and we also have to multiply the denominator of the first fraction , minus 3 x , minus 3 h , minus 1 with the numerator of the second fraction , minus 4 x , minus 8 . Then we take the difference of these products to obtain the new numerator of the reduced fraction. As for the denominator of our reduced fraction, we just multiply the denominators of both original fraction, namely the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 3 h , minus 1 , with the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 1 . We expand each of those product on the numerator of the top fraction. This numerator is the difference of the quantity 12 x square + 12 h x + 4 x + 4 h + 24 x + 8 and the quantity 12 x square + 12 x h + 4 x + 24 x + 24 h + 8 . Note that it is very important to put each of these quantity into parenthesis. The next key step is the remove those parenthesis and adjust the signs accordingly. In fact, it there is a negative sign infront of a parenthesis, when removing that parenthesis we have to change the sign of each term in that expression. Thus, , the new numerator is the expression 12 x square + 12 h x + 4 x + 4 h + 24 x + 8 plus the expression , minus 12 x square , minus 12 x h , minus 4 x , minus 24 x , minus 24 h , minus 8 . Note that, we have fully expanded our new numerator, we now need to simplify its expression by cancelling all terms that appear with their opposite. The simplified numerator is the quantity , minus 20 h . Therefore, , after simplification, we obtain , f prime of x is the limit as h goes to zero of the quotient of fractions; the expression , minus 20 h over the product of the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 3 h , minus 1 times the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 1 everything divided by the fraction h over 1 . Now, in order to simplify a fraction of fractions, we just need to multiply the top fraction with the inverse of the bottom fraction. The whole expression is just a product of two fractions, now we can try to see if there are common factors between numerators and denominators of both fractions. It is evident to see that the common factor here is the term h. Then, , we simplify the common factor h, our new expression is the fraction with numerator , minus 20 , and denominator the product of the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 3 h , minus 1 with the quantity , minus 3 x , minus 1 . as a result, , we take the limit as h goes to 0. This is just done by replacing h with zero on the simplified expression. Therefore, the derivative f prime of x is equal to { , minus 20 } over { 9 x square + 6 x + 1 } Thank you for viewing this video. Please like the video and subscribe to our Channel. We have an extensive collection of calculus-related videos covering limits, derivatives, integration and many other calculus topics



















