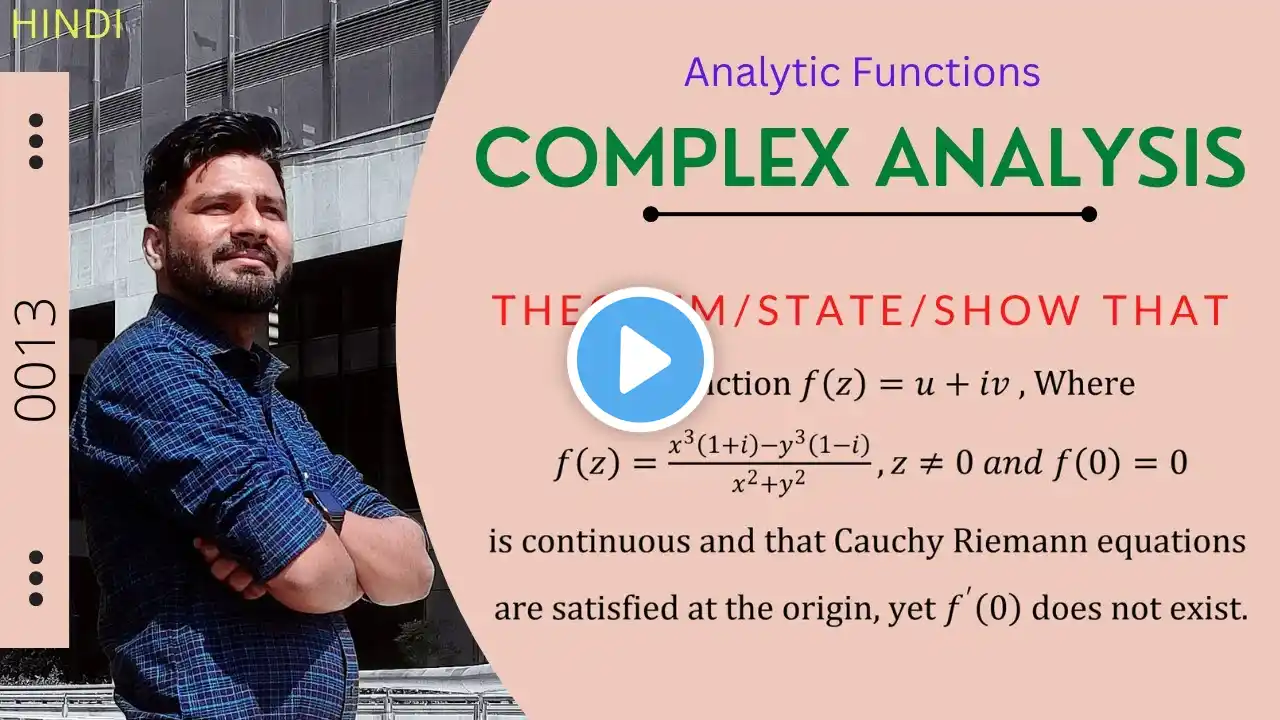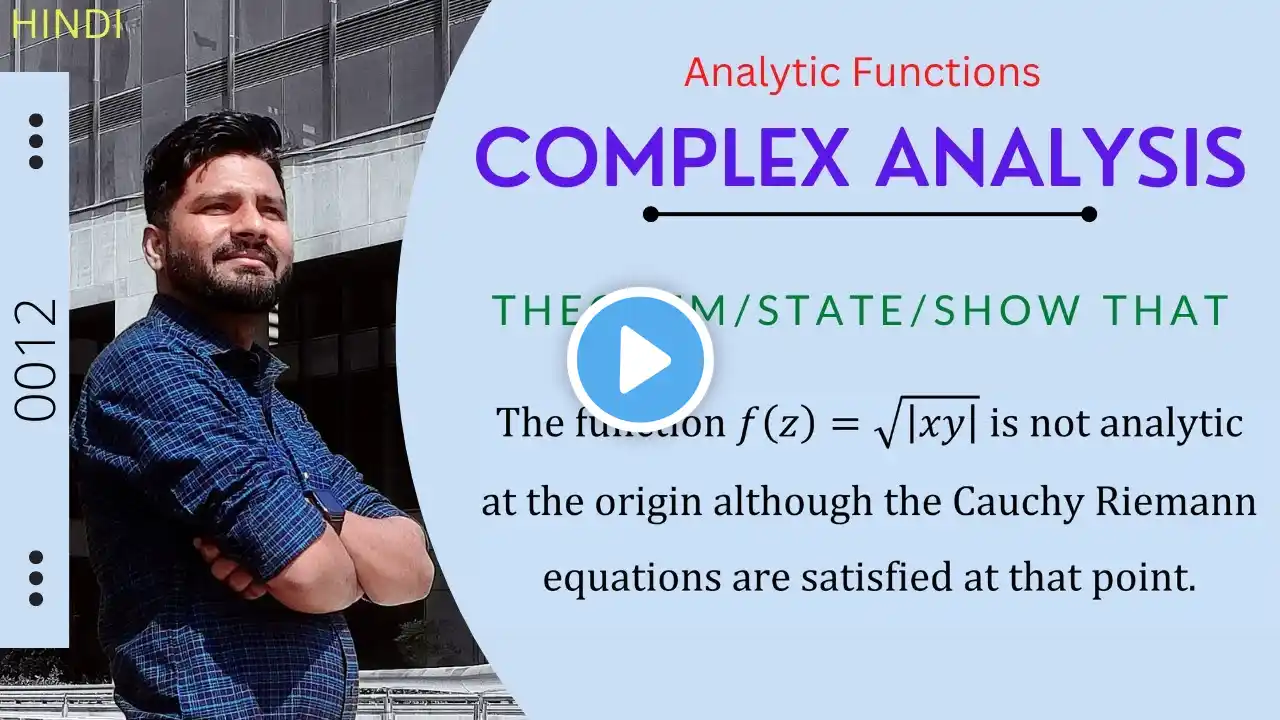
Show f(z) = √|xy| is not analytic at origin although the C-R equations are satisfied at that point.
Complex Analysis Theorem from Analytic function Statement/Theorem /Prove that :- Show that the function f(z) = sqrt(|xy|) or √|xy| is not analytic at the origin although the Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfied at that point. Solution. Let f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) =√|xy| Here u(x,y)= √|xy| and v(x,y)=0 At the origin zₒ=(0,0), (∂u/∂x) = lim ₓ→ₒ {u(x, 0) - u(0, 0)}/x ⇒ (∂u/∂x)= (0 - 0)/x ⇒(∂u/∂x) = 0 and (∂v/∂y) = lim ᵧ→ₒ {v(0, y) - v(0, 0)}/y ⇒(∂v/∂y)= (0 - 0)/y ⇒(∂v/∂y) = 0 Here , ∵(∂u/∂x) = 0 and (∂v/∂y) = 0 ∴(∂u/∂x) = (∂v/∂y) Hence Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfied at the origin zₒ=(0,0). Now by property of differentiability... f'(0)=lim z→o {f(z)-f(0)}/z ⇒f'(0)=lim z→o {√|xy|-0}/(x+iy) ⇒f'(0)=lim z→o √|xy|/(x+iy) Now let a line y=mx, z→o we get ⇒f'(0)=lim z→o √|mx²|/(x+imx) Simplify ⇒f'(0)=lim z→o √|m|/(1+im) Here f'(0) is dependent on slop m thus the limit is not unique ∴ differentiability is not exist so that f(z) is not Analytic function at the origin zₒ=(0,0). Hence Proved...!!! . . . . . . . . Kindly join us for CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) for Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-ship COMMON SYLLABUS FOR PART 'B' AND 'C' MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE . . . . . All BSc, B.Tech, MSc, MA Mathematics students join with us A great platform to get knowledge in Mathematics and science... Stay tuned....for detailed videos on whole SYLLABUS with topic wise... . . . . . . . #complexanalysis #csirnet #analyticfunction . Videos links 🔥🔥🔥 1) • Coming Soon With A New Concept of Learning... 2) • Continuity is necessary but not sufficient... 3) • Cauchy-Riemann Equation : (C-R Equation ) ... 4) • The Sufficient Condition for an Analytic F... 5) • The Polar Form of Cauchy-Riemann equation ... 6) • The Real Valued function of a complex vari... 7) • If n is real, r^n(cosnθ+isinnθ) is Analyti... 8) • Φ(x,y) & ψ(x,y) are satisfied Laplace eq'n... 9) • Laplace’s Equation: f(z)= u+iv Analytic fu... 10) • Analytic Function: Show that f(z) = z̄ is ... 11) • Real & Imaginary part of an Analytic funct... Play List ( Complex Analysis) 👉 • Complex Analysis