Constitutional Amendments Explained | Article 368 | UPSC SSC State PCS#IndianConstitution
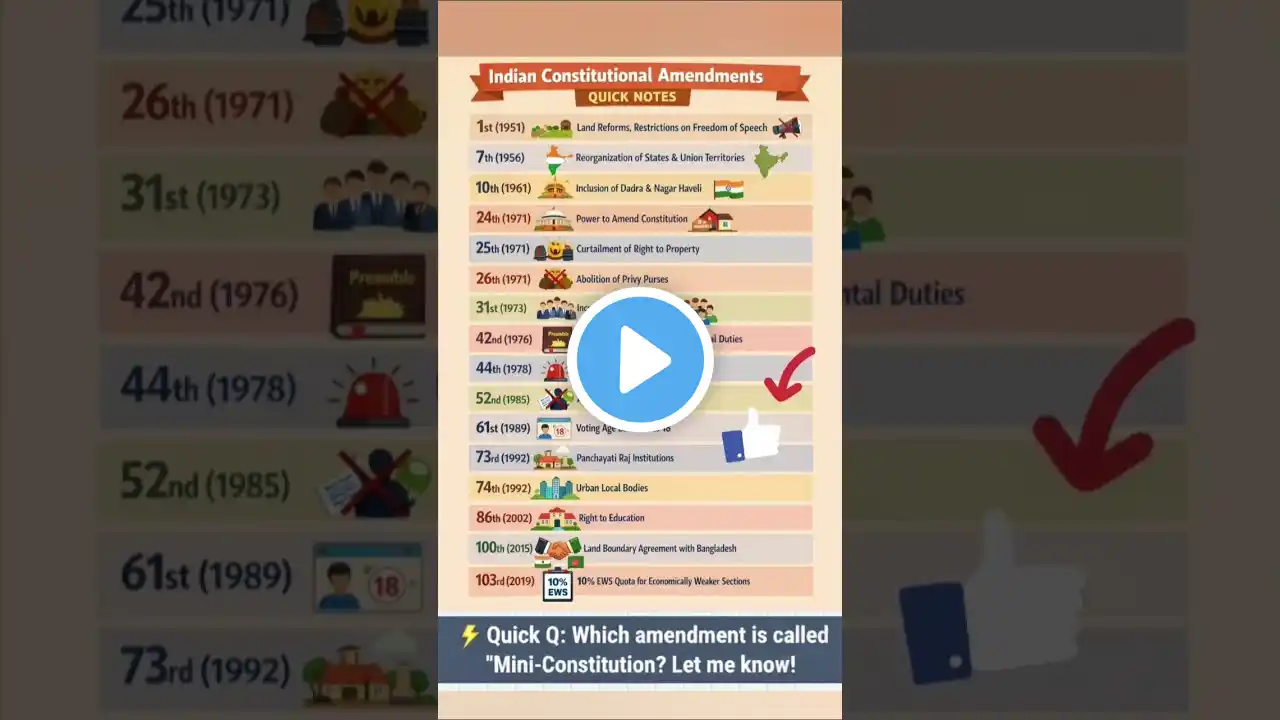
CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENTS – EXAM NOTES 🇮🇳 1. Meaning Amendment = Formal change in the Constitution. Ensures flexibility with stability. 2. Constitutional Provision Article 368 → Power & procedure of amendment Amendment power lies with Parliament. 3. Types of Amendments (MOST IMPORTANT) 🔹 A. Simple Majority (Outside Article 368) Same as passing an ordinary law No special procedure Examples: Formation of new states (Art. 2, 3) Citizenship provisions Salaries & allowances of officials 👉 Asked frequently in SSC 🔹 B. Special Majority Requires: 2/3rd members present & voting More than 50% of total membership Used for: Fundamental Rights Directive Principles Most constitutional provisions 👉 Most amendments fall under this category 🔹 C. Special Majority + State Ratification Requires: Special majority in Parliament Ratification by at least 50% of states Used for: Election of President Centre–State relations Supreme Court & High Courts Seventh Schedule 👉 UPSC favorite 4. Important Amendments (HIGH-YIELD) Amendment Year Key Feature 1st 1951 Reasonable restrictions on FRs 7th 1956 Reorganization of states 24th 1971 Parliament can amend FRs 42nd 1976 Mini Constitution 44th 1978 Right to Property removed 61st 1988 Voting age → 18 73rd 1992 Panchayati Raj 74th 1992 Urban Local Bodies 86th 2002 Right to Education (Art. 21A) 101st 2016 GST 103rd 2019 10% EWS reservation 5. 42nd Amendment (VERY IMPORTANT) Called Mini Constitution Added words: Socialist Secular Integrity Strengthened Centre Added Fundamental Duties 👉 UPSC + State PCS favorite 6. Basic Structure Doctrine Parliament cannot amend the Basic Structure Introduced in Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973) Includes: Supremacy of Constitution Rule of Law Judicial Review Federalism Democracy Secularism 👉 Frequently asked in UPSC Prelims & Mains 7. Key Exam Facts Indian Constitution is partly rigid, partly flexible Amendment Bill: Can be introduced in either House No joint sitting allowed President must give assent (24th Amendment) 8. Prelims One-Liners Article 368 → Amendment procedure Right to Property → Legal Right (Art. 300A) Voting age → 61st Amendment GST → 101st Amendment EWS quota → 103rd Amendment



















