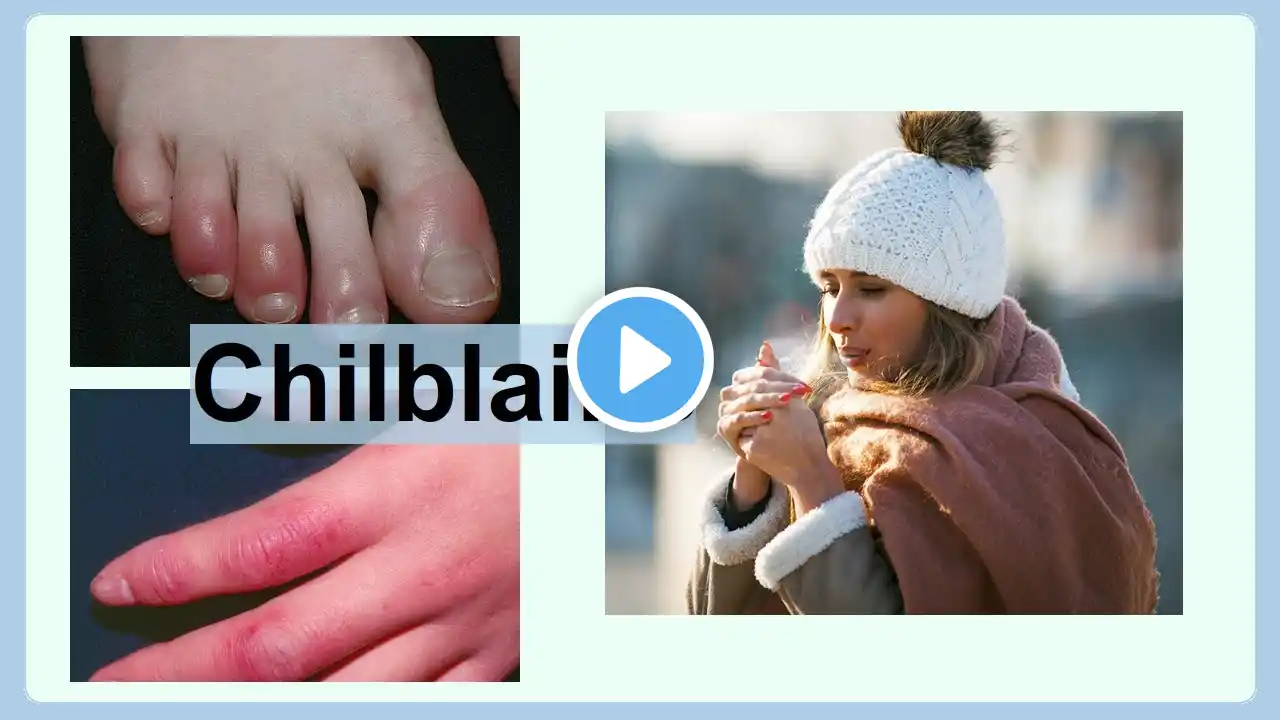
chilblains
(pernio, perniosis) Cold-induced inflammatory cutaneous lesions, occurring to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet. (Symptoms) • When blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, it results in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters. • The lesions may be erythematous or purplish in color and may be either macular or papular. (Causes) • Exposed to cold and humidity. (Risk factors) • female (Treatment) • avoiding cold, damp environments • wearing gloves and warm socks to keep the feet and hands warm (Types) • idiopathic chilblains (primary chilblains): Caused by exposure to non-freezing and damp conditions. • secondary chilblains: Due to an underlying connective tissue disease (CTD), monoclonal gammopathy, or cryoglobulinemia. • kibes: Ulcerated chilblains. • familial chilblain lupus: Autosomal dominant form of lupus erythematosus caused by heterozygous mutations in TREX1, mostly in Asian populations, that typically presents in early childhood. It manifestes cold-induced, bluish-red infiltrates on peripheral surfaces, which are painful and tend to ulcerate. (Diseases that show similar symptoms) • Raynaud syndrome: Arterioles in the skin become narrow, limiting blood flow to affected areas (vasospasm). Feels numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. • erythromelalgia: Usually triggered by increased body temperature. • frostbite: Damage to skin and tissue caused by exposure to freezing temperatures (typically temperature below -0.55 degrees Celsius). It most likely affects the extremities. • trench foot (immersion foot syndrome): Results from the feet being wet for too long. For example, in cold, wet conditions in trenches without the extra socks or boots to help keep the feet dry. • vasculitis: An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and narrowing of blood vessels. Triggered by an infection, a medicine, or other causes. • systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): An autoimmune disease, linked to environmental, genetic, and hormonal factors. • embolic event: Sudden blocking of an artery by an embolus that has been brought by the blood stream. The embolus is most often a blood clot, but may be a fat globule, air bubble, piece of tissue, or clump of bacteria. • Aicardi-Goutières syndrome: An inherited encephalopathy that affects newborn infants and usually results in severe mental and physical handicap with chilblain-like symptoms.