How a Muscle Contracts | Muscle Physiology 101
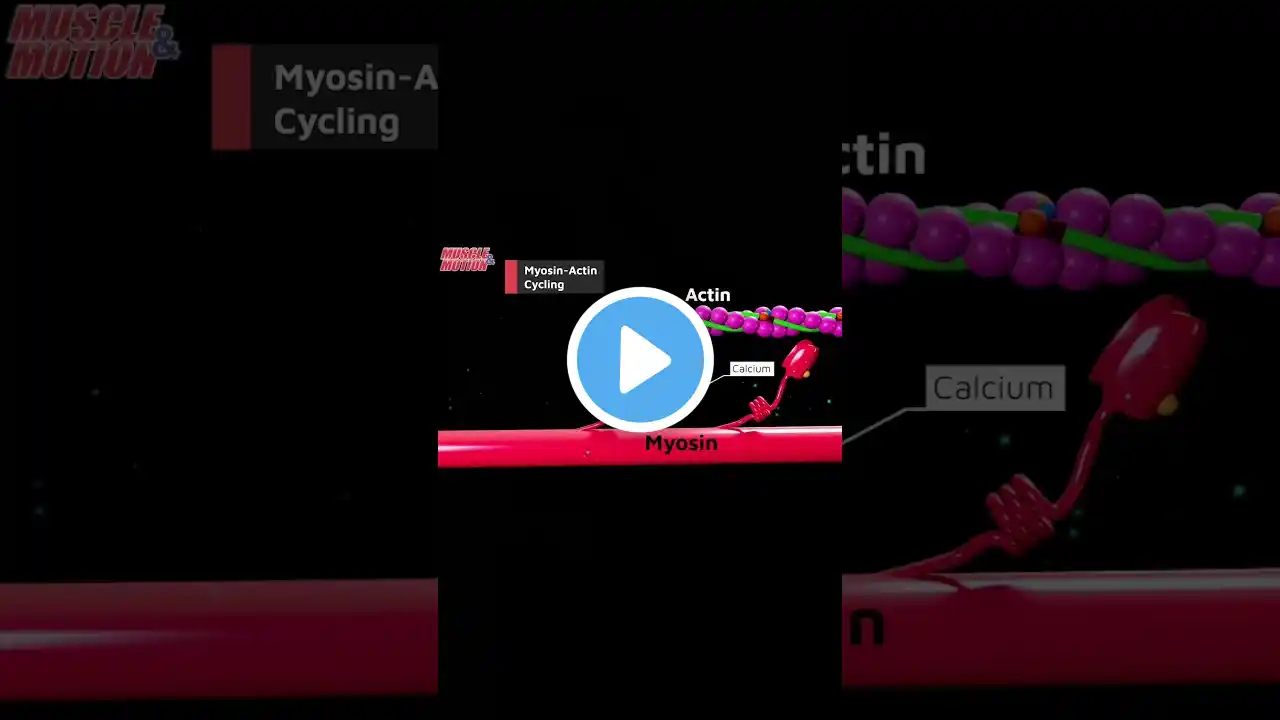
Here’s how a Muscle Contraction works: 1️⃣ Neural signal becomes strong enough to send an action potential 2️⃣ Action potential crosses the Neuromuscular junction and causes a release of calcium ions 3️⃣ Calcium binds to troponin 4️⃣ Troponin moves the tropomyosin to explode the binding sites 5️⃣ Myosin binds to actin 6️⃣ ATP can create a muscle contraction (shortening) by “resetting” the myosin heads to an active position 💪 Graphics from @muscleandmotion



















