Understanding CDF in Probability Distributions
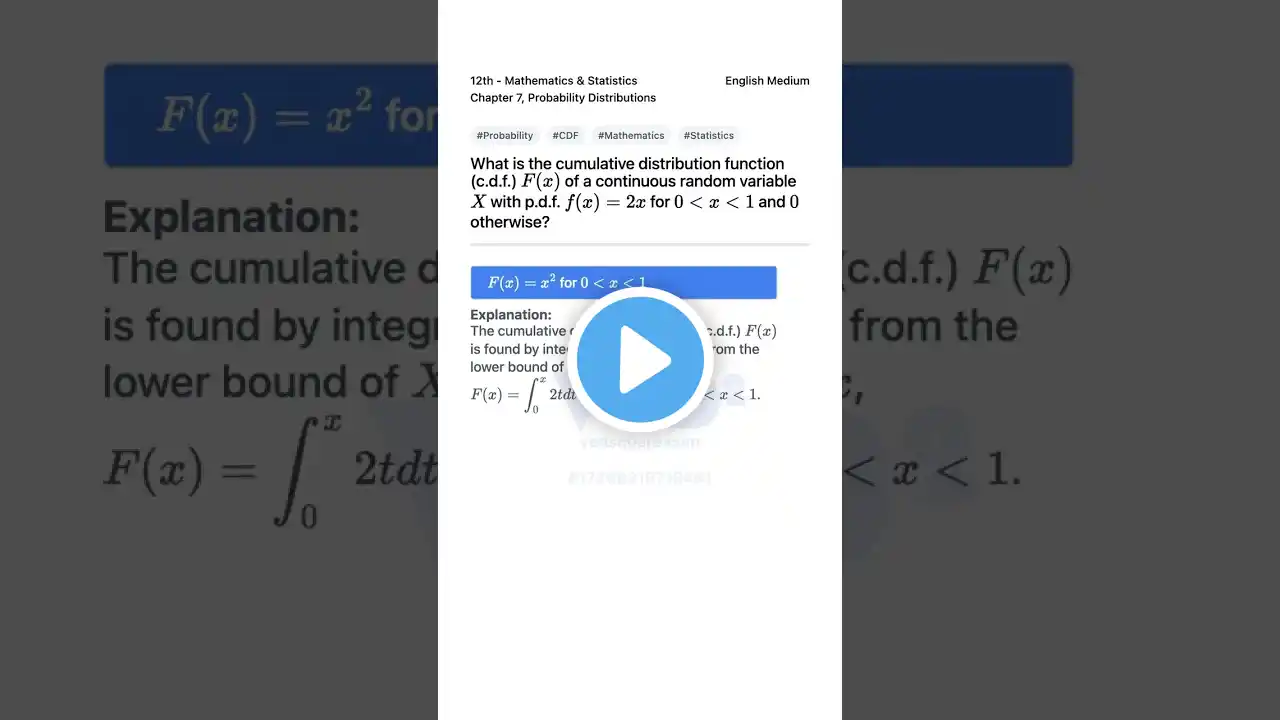
Dive into the world of Probability Distributions with this quick guide on finding the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) for a continuous random variable. Given the probability density function (PDF) f(x) = 2x for 0 lt x lt 1 and 0 otherwise, learn how to calculate the CDF, F(x). The correct answer is F(x) = x^2 for 0 lt x lt 1. This example is perfect for 12th-grade students studying Mathematics & Statistics, specifically from Chapter 7: Probability Distributions on page 219. Enhance your understanding and ace your exams with this concise explanation. Standard: 12th Subject: Mathematics & Statistics Medium: English Chapter: Probability Distributions Chapter Number: 7 Book Page: 219 Difficulty: medium 17368316718461