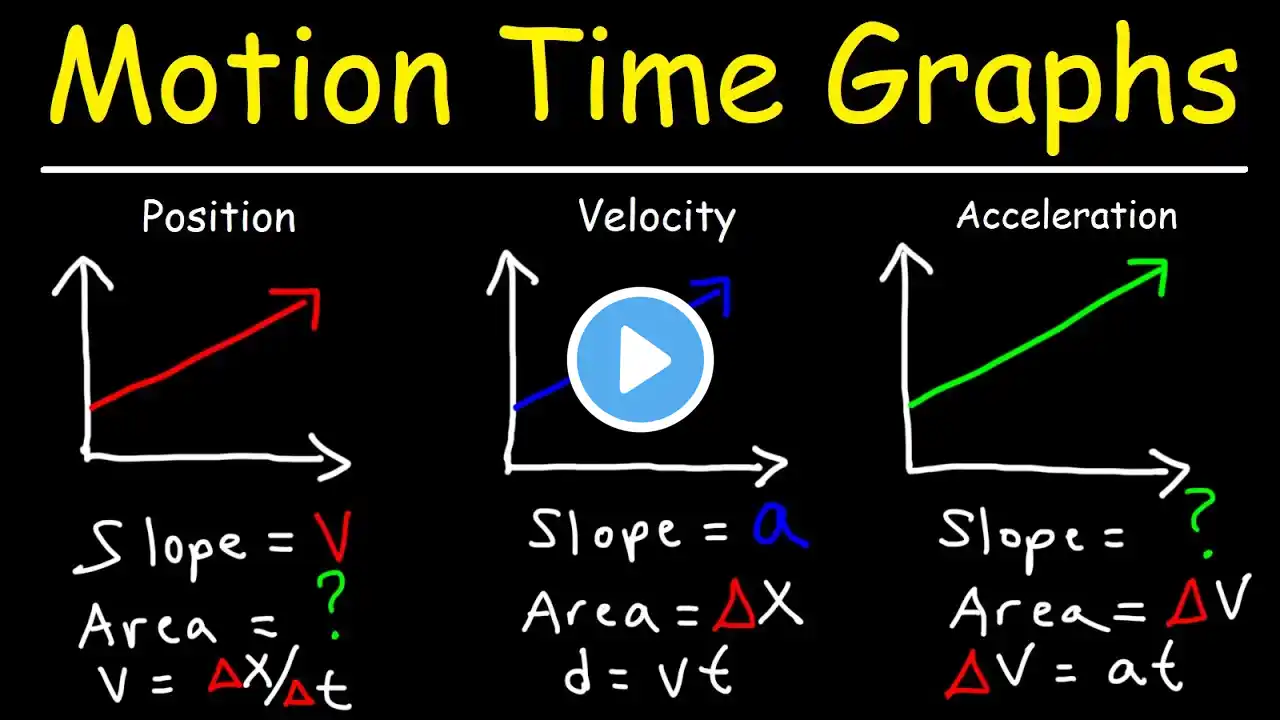
Acceleration | પ્રવેગ | 11th science physics | Motion In A Straight Line
Acceleration પ્રવેગ 11th science physics Motion In A Straight Line Follow US: / earthedutech http://earthedutech.com/ / earthedutech / edutechearth #Like, #Share, #Subscribe.... In physics, and more specifically kinematics, acceleration is the change in velocity over time.Because velocity is a vector, it can change in two ways: a change in magnitude and/or a change in direction. In one dimension, i.e. a line, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, as a vector quantity, acceleration is also the rate at which direction changes. Acceleration has the dimensions L T−2. In SI units, acceleration is measured in metres per second squared (m/s2). In common speech, the term acceleration commonly is used for an increase in speed (the magnitude of velocity); a decrease in speed is called deceleration. In physics, a change in the direction of velocity also is an acceleration: for rotary motion, the change in direction of velocity results in centripetal (toward the center) acceleration; where as the rate of change of speed is a tangential acceleration.