#Road #Cross #Section | #Shorts #Construction #CivilEngineering #Highway #Engineering
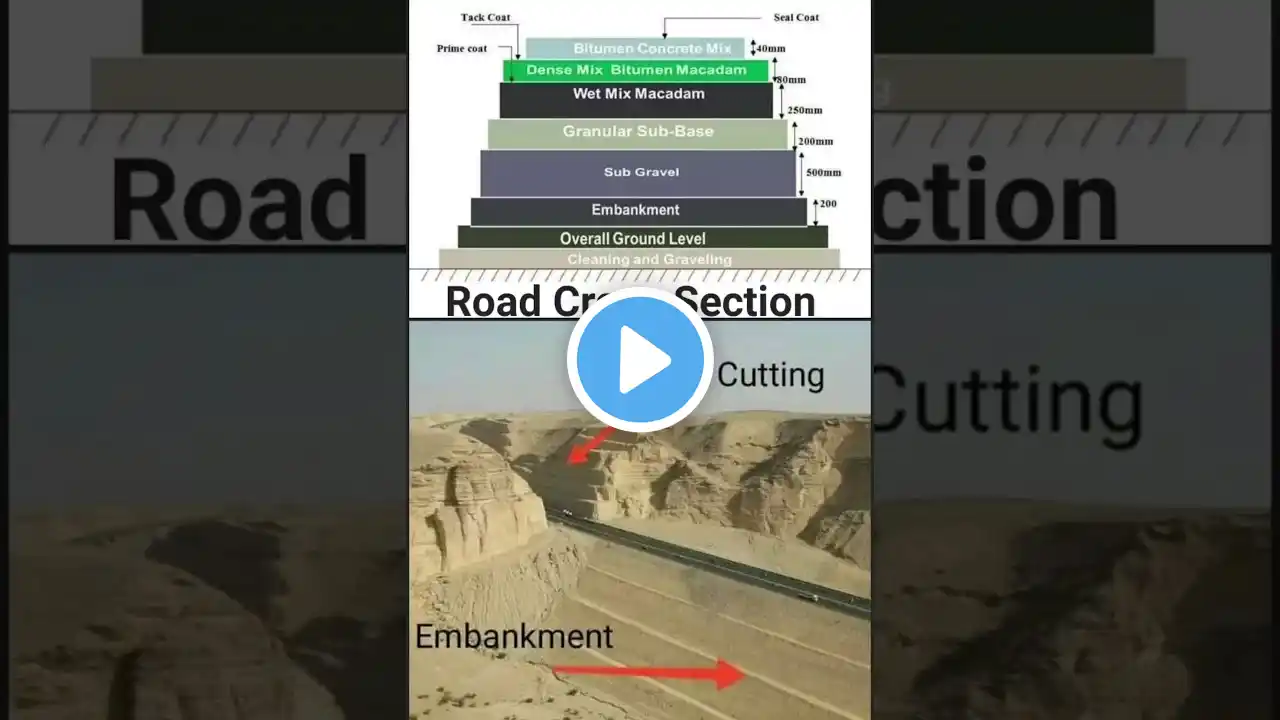
🚧 𝗥𝗢𝗔𝗗 𝗖𝗥𝗢𝗦𝗦 𝗦𝗘𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡 🚧 In this detailed guide, we’ll walk you through the various layers of a road cross-section and explore essential components such as the bitumen concrete mix, dense mix bitumen macadam (DBM), wet mix macadam (WMM), granular sub-base (GSB), sub gravel, embankment, overall ground level, cleaning, and grubbing. By understanding these components, you’ll gain a better grasp of road construction and the purpose behind each layer. Let’s dive in! 🔍 ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 🔶 𝗕𝗶𝘁𝘂𝗺𝗲𝗻 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝗰𝗿𝗲𝘁𝗲 𝗠𝗶𝘅 🔶 The bitumen concrete mix (BC) is the topmost layer of the road and plays a vital role in providing a smooth riding surface. This layer is made up of bitumen and graded aggregates, ensuring a durable and weather-resistant road surface. It is designed to handle traffic load while offering water-resistance to prevent damage to the underlying layers. 🔷 𝗗𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗲 𝗠𝗶𝘅 𝗕𝗶𝘁𝘂𝗺𝗲𝗻 𝗠𝗮𝗰𝗮𝗱𝗮𝗺 (𝗗𝗕𝗠) 🔷 Dense Mix Bitumen Macadam (DBM) acts as a base course layer. It provides structural stability to the road and is laid beneath the bitumen concrete layer. DBM comprises coarse aggregates and bitumen, offering a solid foundation for the BC layer above. ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 🔶 𝗪𝗲𝘁 𝗠𝗶𝘅 𝗠𝗮𝗰𝗮𝗱𝗮𝗺 (𝗪𝗠𝗠) 🔶 The Wet Mix Macadam (WMM) layer is made using crushed aggregates and water, which are compacted to create a strong, stable base. It serves as a base layer beneath the DBM and plays a critical role in distributing traffic load to the lower layers. 🔷 𝗚𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘂𝗹𝗮𝗿 𝗦𝘂𝗯 𝗕𝗮𝘀𝗲 (𝗚𝗦𝗕) 🔷 The Granular Sub-Base (GSB) is the foundation layer of the road cross-section. It is composed of coarse and fine aggregates and functions to provide drainage and structural support to the upper layers. A well-designed GSB layer ensures the longevity and stability of the road. ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 🔶 𝗦𝘂𝗯 𝗚𝗿𝗮𝘃𝗲𝗹 🔶 The sub gravel layer lies below the GSB and acts as a transitional layer between the natural ground and the GSB. It helps in further distributing the load and enhancing road stability. 🔷 𝗘𝗺𝗯𝗮𝗻𝗸𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 🔷 The embankment is the earthwork layer that forms the foundation of the entire road structure. It is constructed by compacting soil to the desired elevation, ensuring that the road’s overall level is above the natural ground to provide proper drainage and stability. ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 🔶 𝗢𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗚𝗿𝗼𝘂𝗻𝗱 𝗟𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗹 🔶 The overall ground level is the base reference point from which all other levels in road construction are determined. Ensuring a uniform and consistent ground level is crucial for proper drainage and road stability. 🔷 𝗖𝗹𝗲𝗮𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗚𝗿𝗮𝗯𝗯𝗶𝗻𝗴 🔷 Before starting the construction, the site undergoes cleaning and grubbing to remove vegetation, debris, and other obstructions. This step ensures a clear and stable foundation for road construction. ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 📢 𝗙𝗲𝗲𝗱𝗯𝗮𝗰𝗸 & 𝗤𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 💬 Have any questions about road cross-section components? Let us know in the comments below! 💬👇 If you found this video helpful, give it a 👍 and share it with others who might benefit from it. Don’t forget to subscribe to our channel for more insightful content on civil engineering! 🚀🔔 ═════════•°•🛤️ °•═════════ 📌 #RoadConstruction #BitumenMix #CivilEngineering #RoadCrossSection #MirzaJahanzaibZameer