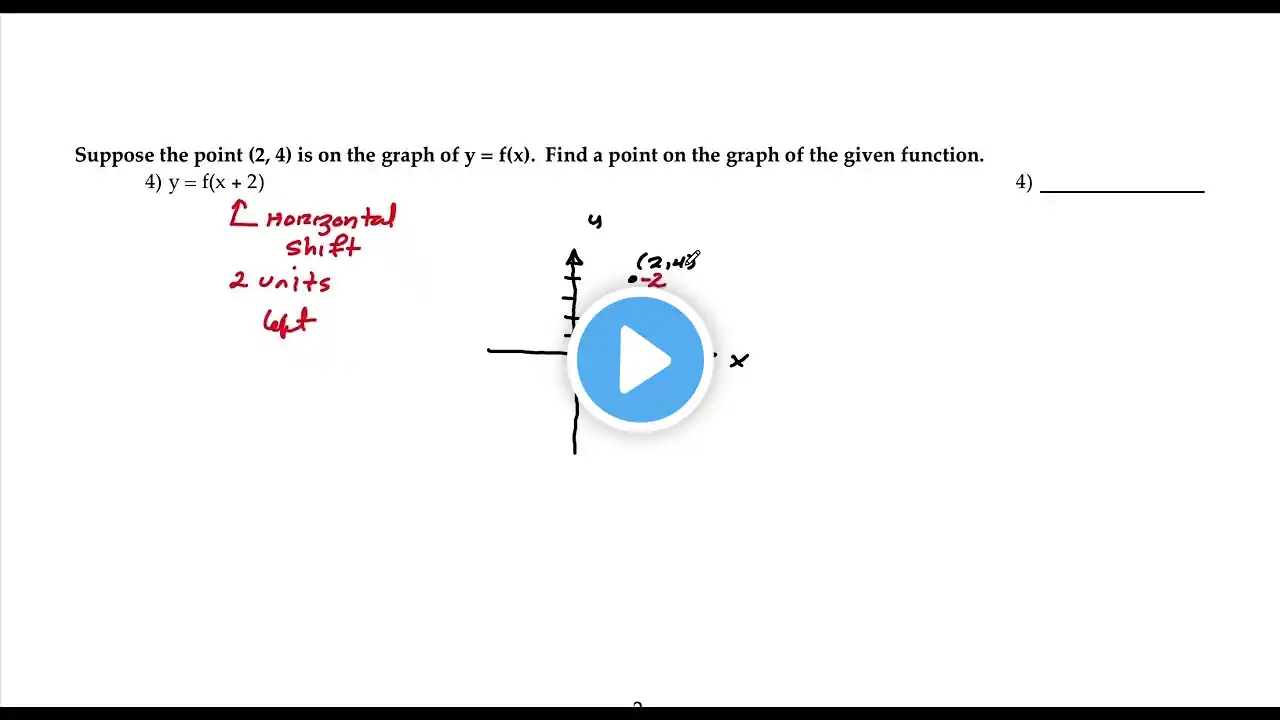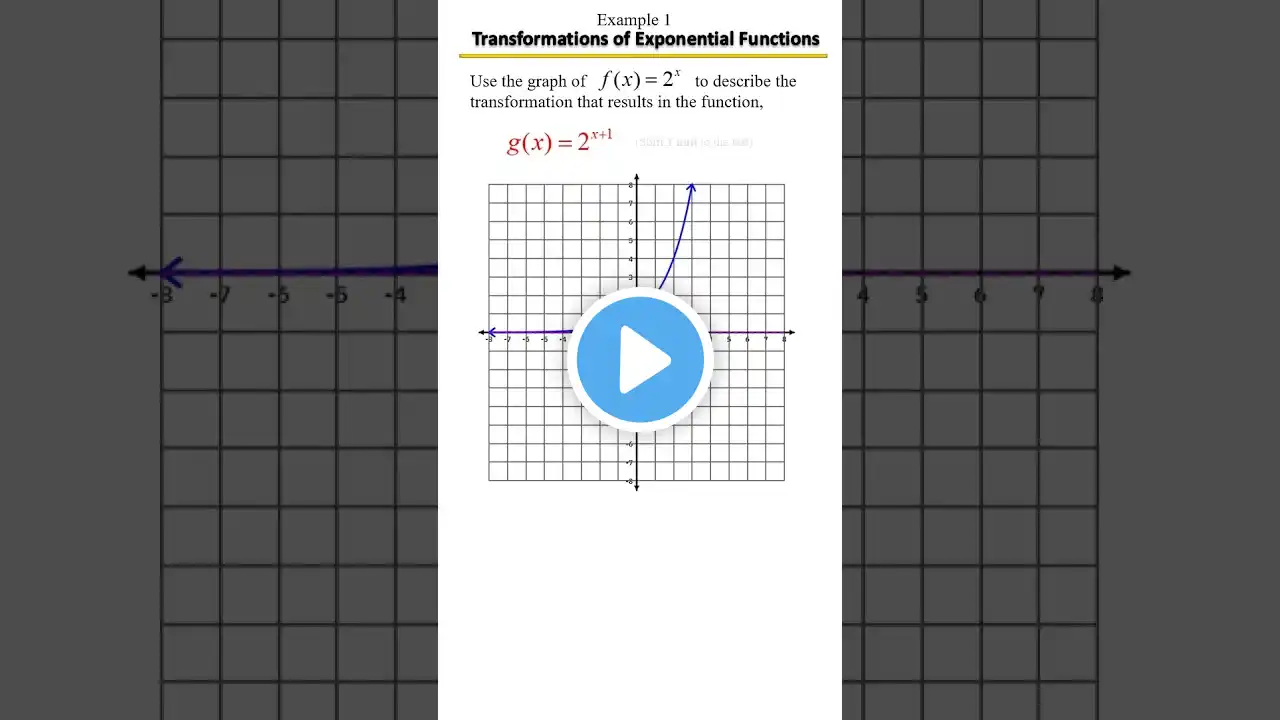
Vertical and Horizontal Shifts | Graph Transformations.
Vertical and horizontal shifts are additional graph transformations that involve moving the entire graph up/down or left/right without altering its shape or orientation. These shifts are also known as translations. Vertical Shift: This transformation moves the graph vertically along the y-axis. A positive vertical shift moves the graph upward, while a negative shift moves it downward. For a vertical shift of 'c', the new function can be represented as y = f(x) + c. The 'c' value determines the amount and direction of the shift. Horizontal Shift: This transformation moves the graph horizontally along the x-axis. A positive horizontal shift moves the graph to the right, while a negative shift moves it to the left. For a horizontal shift of 'd', the new function can be represented as y = f(x - d). The 'd' value determines the amount and direction of the shift. To apply multiple transformations, you can combine them. For example, a graph can undergo both horizontal and vertical shifts, along with compression/stretching, by using the appropriate equations to represent the transformations. Keep in mind that these transformations affect the position of the graph but not its shape or slope. They are useful for understanding how altering certain parameters in a function affects its graphical representation.