Cell cycle #biology #genetics available full video link 🖇️🔗
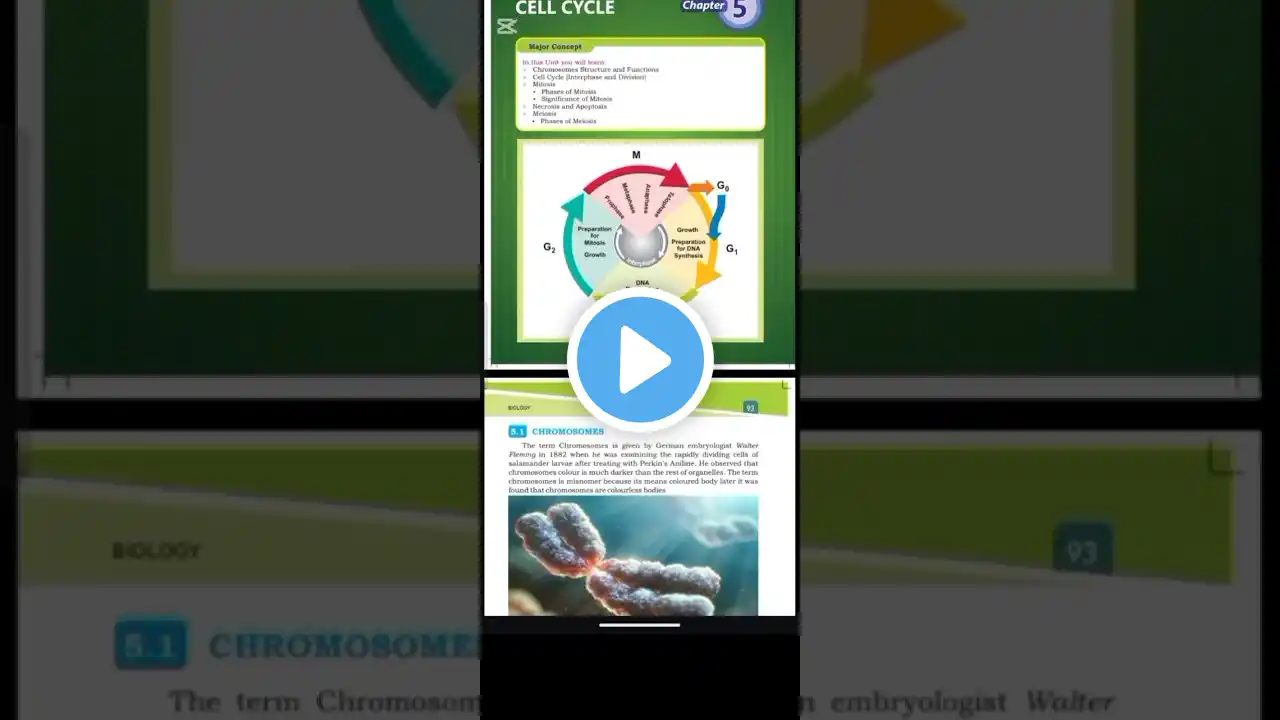
Cell Cycle and Chromosomes The cell cycle is the process by which a cell grows, replicates its DNA, and divides into two daughter cells. Chromosomes play a crucial role in this process. Chromosome Structure Chromosomes are thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins. They come in different shapes and sizes. Types of Chromosomes Based on Centromere Position 1. *Metacentric*: Centromere is near the center, dividing the chromosome into two equal arms. 2. *Submetacentric*: Centromere is slightly off-center, creating arms of different lengths. 3. *Acrocentric*: Centromere is near one end, resulting in a long and a short arm. 4. *Telocentric*: Centromere is at the very end, theoretically resulting in a single arm (though true telocentric chromosomes are rare in humans). Formation of Chromosomes Chromosomes form during cell division through a process called chromatin condensation. This involves: 1. *DNA replication*: Genetic material is duplicated. 2. *Chromatin condensation*: DNA coils and condenses into visible chromosomes. 3. *Sister chromatids*: Identical copies of DNA are held together by the centromere. Importance of Chromosomes Chromosomes carry genetic information and play a vital role in: 1. *Genetic inheritance*: Passing traits from parents to offspring. 2. *Cell division*: Ensuring each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes. #CellCycle #Chromosomes #Metacentric #Submetacentric #Acrocentric #Telocentric #Genetics #CellBiology #DNA #GeneticInheritance